A product technique is a roadmap for creating and delivering a product to market. It allows alignment between product administration, mission administration, and product design, and ensures that the product helps enterprise goals. Designers might not be accountable for creating the product technique, however their work and successes are inevitably impacted by it, particularly in the event that they work in growth-driven and lean environments.
As a product designer who has constructed a number of internet and cellular options on cross-functional product groups, I do know the indicators of a failing product technique. On this article, I share these purple flags and focus on with different Toptal specialists how designers can assist their groups overcome these shortcomings.
Purple Flag No. 1: Missing a Clear Product Imaginative and prescient
Crucial consideration when crafting a product technique is the product imaginative and prescient. A sturdy and well-defined product imaginative and prescient helps groups set an final objective, offers a way of objective, creates alignment, and avoids technique issues from the outset. When points do come up, the product imaginative and prescient acts as a north star, guiding groups again to base.
The product imaginative and prescient is the long-term goal for the product and might be outlined by way of a product imaginative and prescient assertion that communicates the product’s targets to stakeholders. For instance, eBay’s imaginative and prescient assertion for commerce accommodates “enabled by individuals, powered by know-how, and open to everybody.” In distinction, unhealthy imaginative and prescient statements generate confusion for groups and stakeholders, and lack clear focus and course for the enterprise.
With out a clear product imaginative and prescient, it’s laborious for anybody (enterprise house owners, builders, designers) to see the large image. Groups could find yourself altering course whereas disagreeing on how greatest to maneuver ahead. So how do you make sure that everyone seems to be heading towards the identical vacation spot?
Product Technique Resolution: Measure Your Product’s Success
A product imaginative and prescient ought to be outlined from the outset. Nonetheless, to maintain a product group heading in the right direction, the product imaginative and prescient should be revisited and assessed all through the product life cycle. These small changes usually result in important enhancements.
Because the product grows and markets change, groups should constantly measure a product’s success to keep away from a stagnant product imaginative and prescient. That is the place product success metrics enter the image.
Product success metrics present goal insights that assist an organization forecast a product’s incomes potential and measure its engagement efficiency. For example, buyer lifetime worth is a formulation that predicts how a lot income somebody will generate throughout their time as a paying buyer, whereas bounce charge measures how many individuals depart a web site or app after visiting a single web page. Usually talking, they’re measured by the product supervisor. Nonetheless, as a product designer, it’s possible you’ll be requested to assist measure UX success metrics to know how customers navigate digital merchandise and resolve design flaws.
There are two forms of UX success metrics: behavioral (what customers do), equivalent to time on process, and attitudinal (what customers say), such because the buyer satisfaction rating.
Product and UX success metrics have the potential to ship invaluable insights and make sure that product targets stay aligned with the product imaginative and prescient. Nonetheless, for metrics to be significant, they should be actionable, accessible, and auditable. When figuring out which metrics to measure, take into account asking these questions:
- What sort of metric most accurately fits my product?
- The place is my product within the life cycle?
- Who’re the stakeholders for these metrics?
Purple Flag No. 2: Permitting Buyer Requests to Override Product Necessities
The key to crafting a product technique that delivers sensible options begins with a transparent understanding of the product necessities, the encapsulation of a product’s features, options, and behaviors. It doesn’t lie in giving undue precedence to buyer requests—queries about gross sales or options that aren’t essentially based mostly on the great objective of the product.
Whereas buyer requests are motivators that drive a buyer to purchase or use a services or products—equivalent to the will for a smartphone improve for entry to extra feature-rich functions—product necessities are wants which might be explicitly articulated by way of market analysis, equivalent to the necessity for added smartphone storage and larger performance. Clients are demanding by nature, and though we ought to be empathetic to their wants, a robust product technique can not essentially accommodate each buyer request.
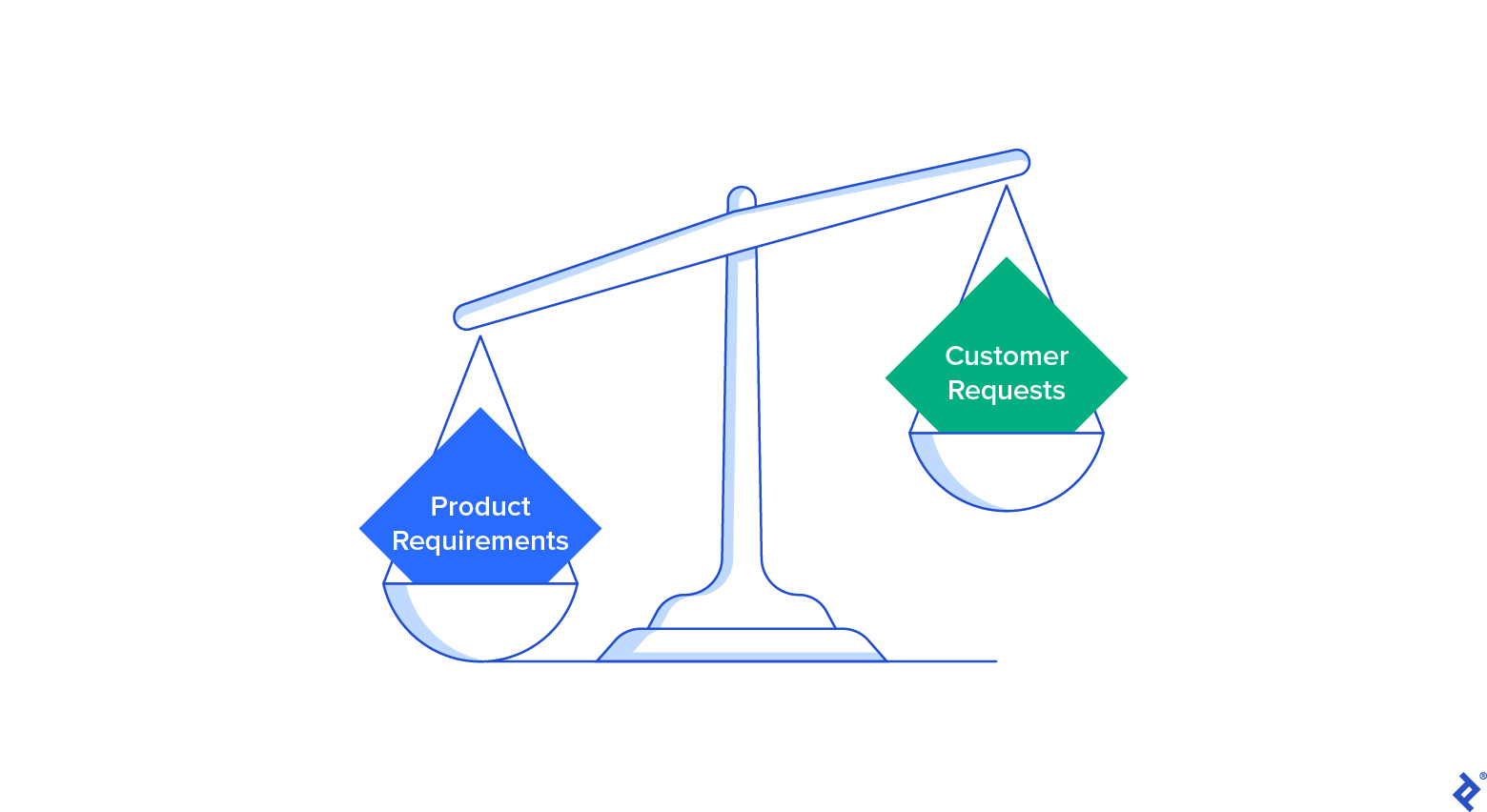
Toptal product and mission administration specialist Milos Belcevic says that the problem posed by attempting to stability necessities and requests might be an expression of an imbalance between the pursuit of product excellence and buyer intimacy. Product excellence is a framework that prioritizes rapidly creating and delivering merchandise that exceed buyer expectations. Buyer intimacy is the follow of participating with particular person prospects to accommodate their wants and enhance their product loyalty.
Neither of those methods is essentially superior to the opposite, however discovering a logical stability between the 2 is essential to managing buyer requests over time.
Product Technique Resolution: Carry out UX Evaluation to Assess Buyer Requests
Generally buyer requests find yourself outweighing product necessities due to a scarcity of correct UX evaluation. With out it, the product group could develop options and functionalities to satisfy one-off buyer or management requests that aren’t truly important to the general product technique. Simply because it’s an engineer’s accountability to push again towards an inferior design, it’s a designer’s accountability to withstand poorly conceived and burdensome requests.
Belcevic suggests utilizing alternative mapping to assess and prioritize new requests based mostly on enterprise targets and buyer analysis. It’s additionally wise to think about the rationale behind a buyer request. It’s a lot simpler for a buyer to determine an issue than for the product group to discover a resolution. Figuring out the underlying downside could result in a far superior treatment than what was requested. Analyzing potential customers with UX methods like personas and empathy mapping may also assist product designers higher determine their core product customers and perceive their wants and behaviors.
After I labored as a product designer for Chaka, a web based funding platform, we cultivated our person group to make sure that our product technique was aligned with our prospects’ wants. We labored on a brand new product based mostly initially on analyzing gaps in our present product set. To show out our concepts, we first assessed our prospects’ willingness to buy, their capability to just accept danger, and the sorts of portfolios they’d wish to construct.
To collect this data, we established weekly classes with the shopper group. This allowed us to work together with our prospects all through the product definition and prototyping phases. Of the 7,000 customers we labored with earlier than growth, greater than 5,000 signed up for the product because of our continued interactions with them. By the point we launched, 10,000 present prospects had signed up by way of the corporate’s Telegram channel. I take into account this a robust indication of a profitable product technique that balances enterprise targets and buyer requests.
Purple Flag No. 3: Mistaking Options for Worth
One other signal of a failing product technique is mistaking giant numbers of options for product worth. For digital merchandise, options is perhaps an software’s functionalities, capabilities, or visible traits, equivalent to product filtering, want lists, and checkout on an e-commerce web site.
Constructing a digital resolution with pointless or low-value options can lead to delivering merchandise to market which might be too difficult to make use of, a phenomenon referred to as characteristic creep. Extreme numbers of options, or the flawed options, are related to greater design and implementation prices, decrease returns from these options, and elevated buyer dissatisfaction within the characteristic set.
In accordance with Toptal multidisciplinary designer Austine Eluro, too many options are a troubling signal of diffuse product technique. He says, “Should you add too many options to a single software, you create a hub that may do every thing however can not fulfill anyone. No product might be all issues to all individuals.”
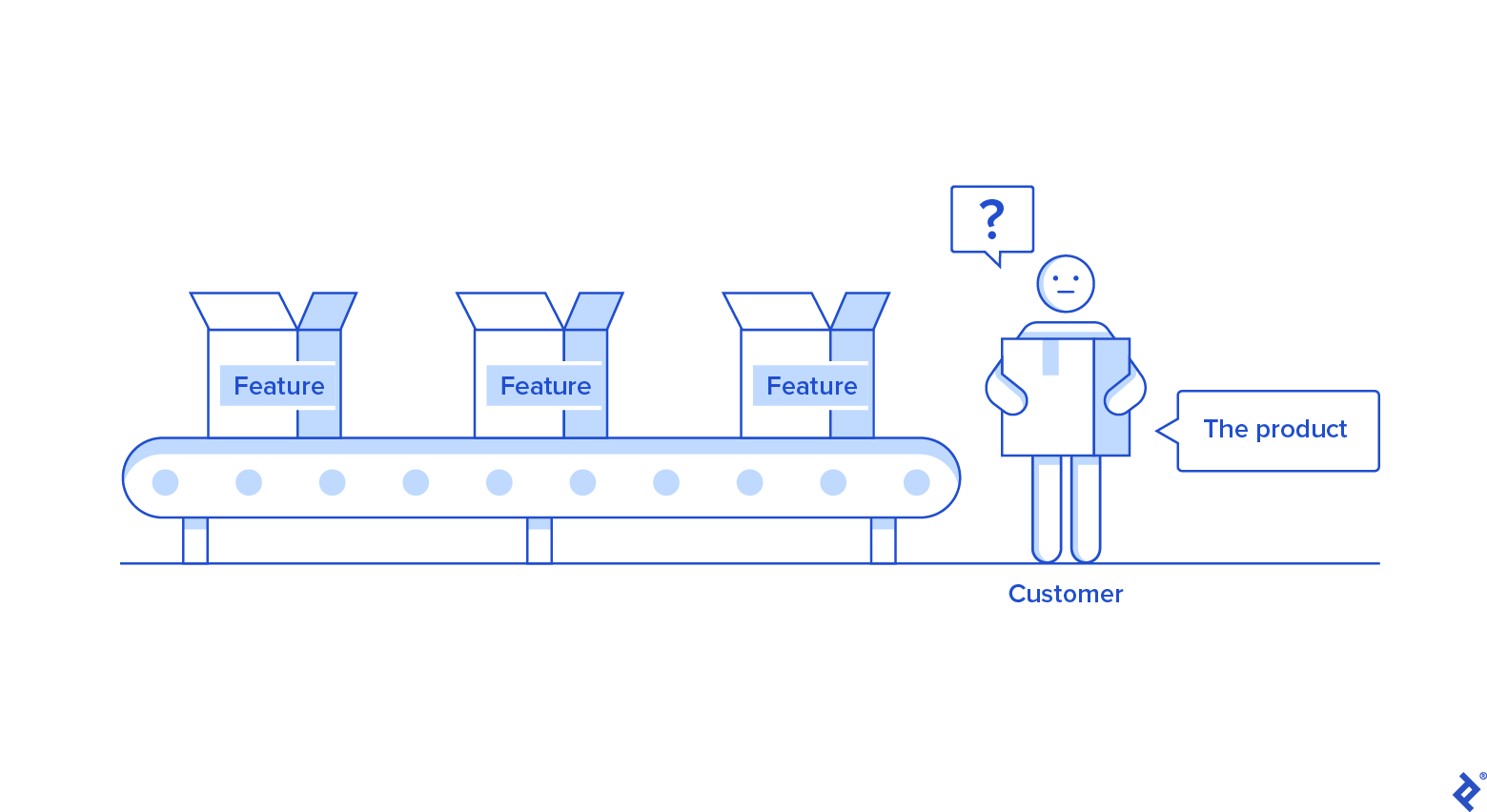
Some organizations grow to be referred to as “characteristic factories,” corporations that reward characteristic amount and don’t cease to evaluate potential options’ worth as long as they match into the event schedules. For digital merchandise, “bloatware” is the same phenomenon: undesirable and doubtlessly dangerous apps come pre-installed on units. Most of those apps are by no means used, customers didn’t ask for them, and so they usually can’t be uninstalled. A brand new spate of bloatware removing instruments has been created to sort out this downside.
Melissa Perri describes this failure mode in her guide Escaping the Construct Lure, really useful by Belcevic. In her guide, Perri says that when corporations fail to know their prospects, they will’t present actual worth. They exchange real understanding with a simplified metric based mostly on options shipped, and that creates a false definition of worth. Organizations fall into the “construct lure” once they begin formally measuring success when it comes to output quantity as a substitute of by consequence.
Product Technique Resolution: Implement an Efficient Prioritization Framework
Prioritization helps make sure that product groups are engaged on probably the most related options and avoiding wasteful practices. Think about asking these questions about all potential options:
- Is that this characteristic invaluable to the tip person?
- Is it important to the product/enterprise goal?
- Do the advantages outweigh the associated fee and complexity of design and implementation?
If the reply to those questions is not any, you must exclude the characteristic out of your product technique or defer it for future consideration.
I like to recommend additionally utilizing a proper prioritization framework to judge new options rationally and constantly within the product technique roadmap. Product prioritization has famously been a matter of confusion for product groups, and typically a extra scientific method is required.
As a product designer, I’ve expertise utilizing the MoSCoW, RICE, and Kano prioritization frameworks. For example, at Chaka we used MoSCoW to assist slim our characteristic set when going through important time constraints. I created MoSCoW quadrants and plotted our prospects’ wants (based mostly on analysis) in should have (M), ought to have (S), might have (C), or gained’t have (W). This helped us cut back our options in only a few hours.
Purple Flag No. 4: Encountering Communication Breakdowns
In product technique growth, there are various stakeholder inputs and opinions to juggle, and communication issues could come up. A few of these issues happen as a result of mission position definitions can differ dramatically from firm to firm and even from mission to mission. For instance, some product managers are technical and deal with engineering; some are designers and assign themselves prototyping tasks; and a few focus extra on advertising, product life cycle, or customers. If you be a part of a mission as a designer, it’s essential to find out the bounds of your position to keep away from conflicts with different group members and make sure that each part of the mission is carried out appropriately.
This type of position readability situation can often be addressed upfront by clarifying the chain of reporting and making certain that every one mission roles are clearly outlined by way of methods equivalent to group discovery. Nonetheless, different communication points and conflicts can come up throughout a mission, equivalent to misunderstandings, lack of suggestions, and working in silos. One of the crucial widespread battle areas is between the product supervisor and the UX designer. Each are involved with person expertise and the relation of necessities to person wants, however they could method issues in a different way.
Product Technique Resolution: Reinforce Product Imaginative and prescient and Foster Battle-resolution Methods
Crew alignment is key for efficient communication inside a cross-functional product group to make sure that the product technique takes priority. For starters, I like to recommend collaborating throughout groups to determine the product imaginative and prescient somewhat than permitting a single particular person or small group to impose their concepts on the entire group. A great way to make sure transparency inside cross-functional groups is to show your product imaginative and prescient assertion on the workplace wall (for in-house groups) and as a part of firm wikis and inner data bases, equivalent to Confluence.
In fact, conflicts will doubtless happen throughout any mission. Conflicts aren’t the issue; issues come up when conflicts aren’t adequately resolved. Inside most Agile frameworks, there are customary patterns for battle decision and position definition. This would possibly begin with making certain that group members with completely different roles (e.g., product managers, product house owners, Scrum masters, product designers) collaborate within the early ideation and product definition levels. Towards the tip of a mission, groups can resolve conflicts by attending and taking part in a retrospective assembly to debate what went effectively and what might be improved.
Purple Flag No. 5: Enabling Pointless Useful resource Loading
Useful resource loading is an important ingredient of useful resource planning for any product group. Because it impacts each group member, it’s vital to acknowledge when there’s an issue with it. Useful resource overloading—when there are too many duties for the obtainable assets—is a transparent signal of a failing product technique. Generally a mission feels burdened with issues from the beginning, even earlier than buyer requests and growth iterations have had an opportunity to affect necessities. Different assets aside from design, like engineering, testing, and advertising, could individually or collectively be stretched to a breaking level with consequent harm carried out to the design course of.
Eluro says that issues with load can come up when product groups fail to acknowledge a mission’s success. “Some groups ignore success indicators. When the product has been launched, they ignore the success that that product has truly achieved. It’s not sufficient to deal with faults.” He says acknowledging success can present course for future necessities, whereas focusing solely on faults or gaps in protection can result in a diffuse growth focus and extreme workloads.
Product Technique Resolution: Create an MVP Prototype
I at all times like to start out the design course of with a minimal viable product (MVP) prototype to cut back prices and time to market. Product designers usually construct prototypes to determine issues, develop options, and share designs with stakeholders with out pointless useful resource expenditure.
The sort of prototype you determine to create will rely upon the place you end up inside the product growth life cycle. In early growth, it’s possible you’ll construct a low-fidelity, static prototype or wireframe utilizing low-cost, available supplies. Lo-fi wireframes embody easy visible representations of on-screen UI parts and content material hierarchy. Later, designers construct high-fidelity, interactive mock-ups to visualise the attributes and interactive options of the product in additional element. These prototypes are usually used to check the product’s capabilities earlier than growth.
Fast MVP prototyping is a specific method utilized in lean environments that permits efficient early suggestions from stakeholders and finish customers. MVP prototypes assist groups obtain an early win and might be developed into deployed merchandise incrementally even within the occasion of reductions in assets and schedule cuts.
A Strong Product Imaginative and prescient Helps You Construct a Fail-proof Product Technique
There are lots of methods for a product technique to fail, however all profitable product methods have one factor in widespread: a transparent product imaginative and prescient. The product imaginative and prescient ought to be developed as a collaborative effort between the product group and the product designer, incorporating buyer and end-user enter as early as attainable.
When constructing a product, issues are inevitably going to happen. Nonetheless, with a well-defined product imaginative and prescient, a transparent understanding of the product necessities and options, and data of conflict-resolution methods, it is going to be simpler to develop and implement lasting options.