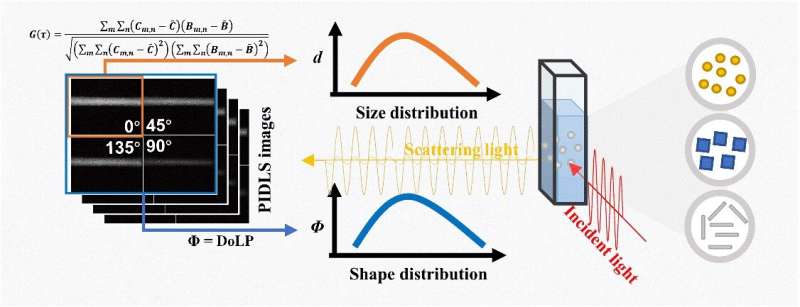
A group of researchers proposed a quick and handy technique referred to as polarized imaging dynamic mild scattering (PIDLS) that quantitively evaluates nanoparticle dimension, morphology and distribution on the identical time. A dimensionless amount, named optical sphericity, is proposed to explain the diploma of deviation of nanoparticles from spheres. This technique will significantly contribute to in-situ synthesis, structure-function evaluation, and high quality evaluation of nanoparticles.
The group of Chinese language researchers from the College of Shanghai for Science and Expertise and Jiaxing MeaParTech Instrument Expertise Co., Ltd revealed their work within the journal Particuology.
The efficiency of nanoparticles is continuously influenced by components like particle dimension and form. Historically, electron microscopy or atomic drive microscopy is employed for nanoparticle dimension and morphology evaluation. Nonetheless, this strategy poses challenges resembling advanced pattern preparation, time-consuming processing, and difficulties in attaining quantitative characterization. A quick, correct, and statistically significant technique to measure the dimensions and morphology of nanoparticles will facilitate the associated business.
In contrast to electron microscopy and atomic drive microscopy strategies, the PIDLS technique doesn’t immediately measure the nanoparticle dimension and morphology. In truth, PIDLS will be seen as a mix of the imaging dynamic mild scattering (IDLS) technique and polarized mild scattering (PLS) technique.
By illuminating a pattern of nanoparticles with a polarized laser beam, a polarized digital camera receives the scattered mild and obtains scattering photos within the 0°, 45°, 90°, and 135° polarization instructions. Because of the steady random Brownian movement of the particles, the spatial positions and orientations of the particles consistently fluctuate, leading to fluctuations within the depth and polarization state of the scattered mild.
In line with the Stokes-Einstein equation, the speed of depth fluctuations within the scattered mild is expounded to the particle dimension, and in line with the sunshine scattering principle, the polarization state of the scattered mild is expounded to the particle morphology. By calculating the spatial correlation of two consecutive scattering photos within the 0° polarization course, the speed of depth fluctuations within the scattered mild will be decided, and thus the particle dimension will be decided.
Steady measurements can present a number of particle dimension measurement outcomes, together with the typical worth and the polydispersity index. By analyzing the depth of scattered mild from 4 polarization photos in 0°, 45°, 90°, and 135° polarization instructions taken on the identical time, the diploma of linear polarization (known as optical sphericity on this paper) will be obtained, which can be utilized to judge the diploma of approximation of particles to a sphere.
A price of 1 signifies an ideal sphere, whereas the smaller worth signifies the extra deviation from a sphere. Steady measurements can present the optical sphericity of the nanoparticles, thus acquiring statistical morphological distribution.
On this examine, measurements have been carried out on spherical, octahedral, flat, rod-shaped, and filamentous nanoparticles. The outcomes of particle dimension, morphology, and distributions obtained from the PIDLS technique have been in keeping with these obtained from electron microscopy, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed technique.
The examine additionally measured 5 industrial-grade titanium dioxide powders and efficiently recognized the samples with considerably bigger particle sizes, decrease optical sphericity, and poor consistency in each dimension and morphology. This highlights the potential utility of the PIDLS technique in high quality management of nano powders.
“This examine gives a brand new software for evaluating the morphology of nanoparticles,” stated Xiaoshu Cai, a professor at College of Shanghai for Science and Expertise. The PIDLS technique will be carried out at room temperature and atmospheric stress in a liquid-phase atmosphere with barely any pattern preparation. With its simplicity and quick measurement velocity, the PIDLS technique holds nice potential for widespread utility in nanomaterial synthesis in laboratories, nano powder manufacture in crops, and lots of different cutting-edge fields.
“Within the subsequent step, our analysis group will additional validate the universality of the optical sphericity. Moreover, we plan to additional examine the connection between particle morphology and far-field scattering patterns primarily based on polarization scattering principle, aiming to realize the classification of particle morphology,” stated Cai.
On this manner, the researchers would possibly develop the appliance eventualities of PIDLS and enhance the potential for sensible functions. “Our analysis group constantly give attention to multi-parameter measurement and on-line measurement of particles, and constantly develop new measurement strategies and units,” stated Cai.
Extra data:
Bingyao Wang et al, Polarized imaging dynamic mild scattering for simultaneous measurement of nanoparticle dimension and morphology, Particuology (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.partic.2023.06.004
Quotation:
Polarized imaging of dynamic mild scattering to measure nanoparticle dimension, morphology, and distributions (2023, July 5)
retrieved 5 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-polarized-imaging-dynamic-nanoparticle-size.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

