Synthetic muscular tissues are a progressing know-how that would at some point allow robots to operate like dwelling organisms. Such muscular tissues open up new potentialities for a way robots can form the world round us; from assistive wearable gadgets that may redefine our bodily skills at outdated age, to rescue robots that may navigate rubble in the hunt for the lacking. However simply because synthetic muscular tissues can have a powerful societal impression throughout use, doesn’t imply they’ve to depart a powerful environmental impression after use.
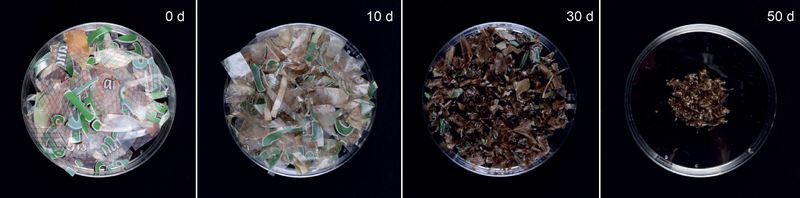
The subject of sustainability in gentle robotics has been introduced into focus by a global staff of researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Clever Techniques (MPI-IS) in Stuttgart (Germany), the Johannes Kepler College (JKU) in Linz (Austria), and the College of Colorado (CU Boulder), Boulder (USA). The scientists collaborated to design a totally biodegradable, excessive efficiency synthetic muscle – primarily based on gelatin, oil, and bioplastics. They present the potential of this biodegradable know-how through the use of it to animate a robotic gripper, which could possibly be particularly helpful in single-use deployments resembling for waste assortment (watch the Youtube video). On the finish of life, these synthetic muscular tissues will be disposed of in municipal compost bins; beneath monitored situations, they totally biodegrade inside six months.
We see an pressing want for sustainable supplies within the accelerating discipline of sentimental robotics. Biodegradable elements may provide a sustainable answer particularly for single-use purposes, like for medical operations, search-and-rescue missions, and manipulation of hazardous substances. As an alternative of accumulating in landfills on the finish of product life, the robots of the long run may turn into compost for future plant development,” says Ellen Rumley, a visiting scientist from CU Boulder working within the Robotic Supplies Division at MPI-IS. Rumley is co-first creator of the paper “Biodegradable electrohydraulic actuators for sustainable gentle robots”, printed in Science Advances.
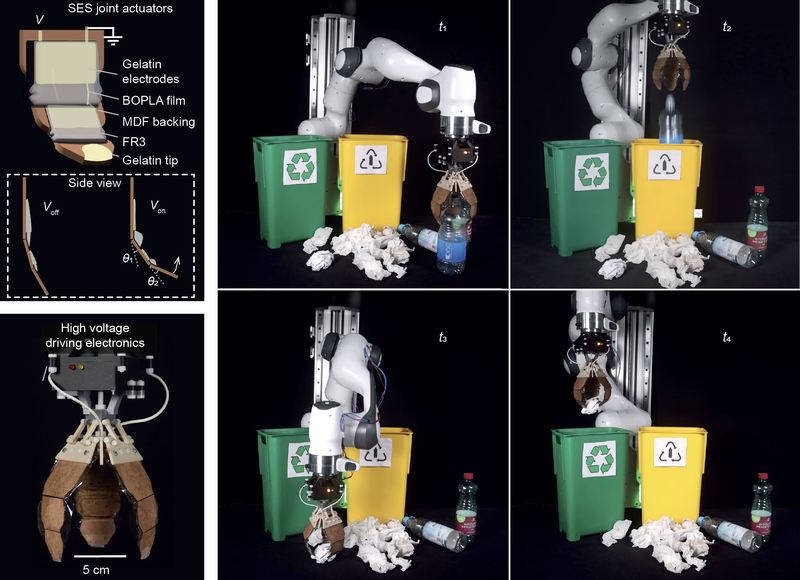
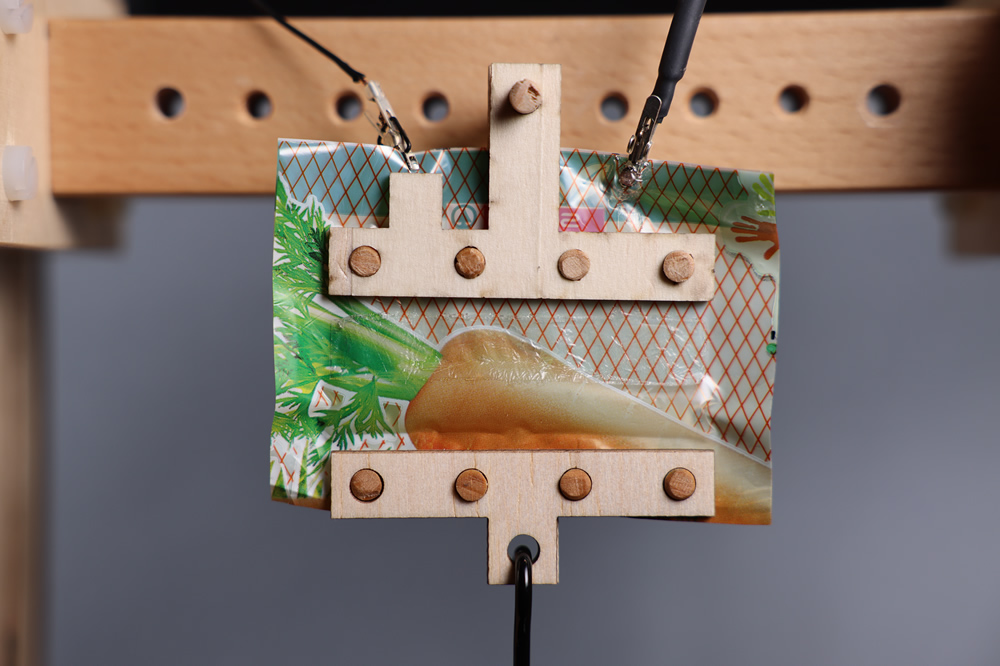
Particularly, the staff of researchers constructed an electrically pushed synthetic muscle known as HASEL. In essence, HASELs are oil-filled plastic pouches which might be partially lined by a pair {of electrical} conductors known as electrodes. Making use of a excessive voltage throughout the electrode pair causes opposing fees to construct on them, producing a pressure between them that pushes oil to an electrode-free area of the pouch. This oil migration causes the pouch to contract, very like an actual muscle. The important thing requirement for HASELs to deform is that the supplies making up the plastic pouch and oil are electrical insulators, which might maintain the excessive electrical stresses generated by the charged electrodes.
One of many challenges for this undertaking was to develop a conductive, gentle, and totally biodegradable electrode. Researchers at Johannes Kepler College created a recipe primarily based on a mix of biopolymer gelatin and salts that may be straight forged onto HASEL actuators. “It was vital for us to make electrodes appropriate for these high-performance purposes, however with available elements and an accessible fabrication technique. Since our offered formulation will be simply built-in in varied varieties of electrically pushed techniques, it serves as a constructing block for future biodegradable purposes,” states David Preninger, co-first creator for this undertaking and a scientist on the Mushy Matter Physics Division at JKU.
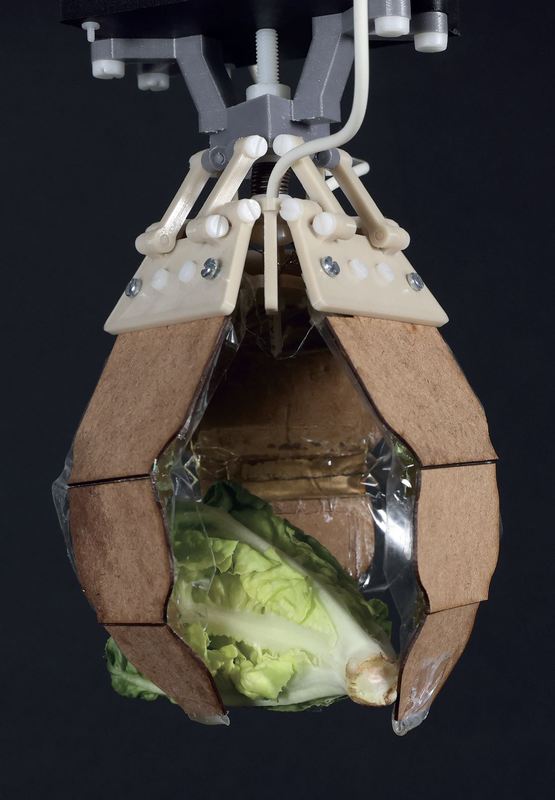

The subsequent step was discovering appropriate biodegradable plastics. Engineers for this kind of supplies are primarily involved with properties like degradation price or mechanical energy, not with electrical insulation; a requirement for HASELs that function at a number of thousand Volts. Nonetheless, some bioplastics confirmed good materials compatibility with gelatin electrodes and adequate electrical insulation. HASELs created from one particular materials mixture had been even in a position to stand up to 100,000 actuation cycles at a number of thousand Volts with out indicators {of electrical} failure or loss in efficiency. These biodegradable synthetic muscular tissues are electromechanically aggressive with their non-biodegradable counterparts; an thrilling end result for selling sustainability in synthetic muscle know-how.
“By displaying the excellent efficiency of this new supplies system, we’re giving an incentive for the robotics group to contemplate biodegradable supplies as a viable materials choice for constructing robots”, Ellen Rumley continues. “The truth that we achieved such nice outcomes with bio-plastics hopefully additionally motivates different materials scientists to create new supplies with optimized electrical efficiency in thoughts.”
With inexperienced know-how changing into ever extra current, the staff’s analysis undertaking is a vital step in the direction of a paradigm shift in gentle robotics. Utilizing biodegradable supplies for constructing synthetic muscular tissues is only one step in the direction of paving a future for sustainable robotic know-how.

Max Planck Institute for Clever Techniques
‘s objective is to analyze and perceive the organizing ideas of clever techniques and the underlying perception-action-learning loop.

