As extra authorities acquisition packages undertake an Agile improvement methodology, there are extra alternatives for Agile to work together with and maybe take care of earned worth administration (EVM) ideas. EVM has been a mainstay inside the U.S. authorities acquisition group for longer than Agile has, however each are firmly entrenched in coverage that mandates their use. Whereas not all EVM packages are Agile and never all Agile packages use EVM, it’s changing into extra frequent that authorities packages use each strategies. Professionals inside the acquisition group are often extra comfy with one methodology than they’re with the opposite, and a few even understand them to be at odds. This notion is probably forgivable upon examination of the basic assumptions for each practices. This weblog put up will focus on the interactions between Agile and EVM.
To establish potential disconnects and to assist acquirers achieve most profit from these methodologies, we focus on on this put up a few of the variations between Agile and EVM and discover concepts for the best way to make them work nicely collectively. We summarize the primary supply of incompatibility, perceived or in any other case, as follows:
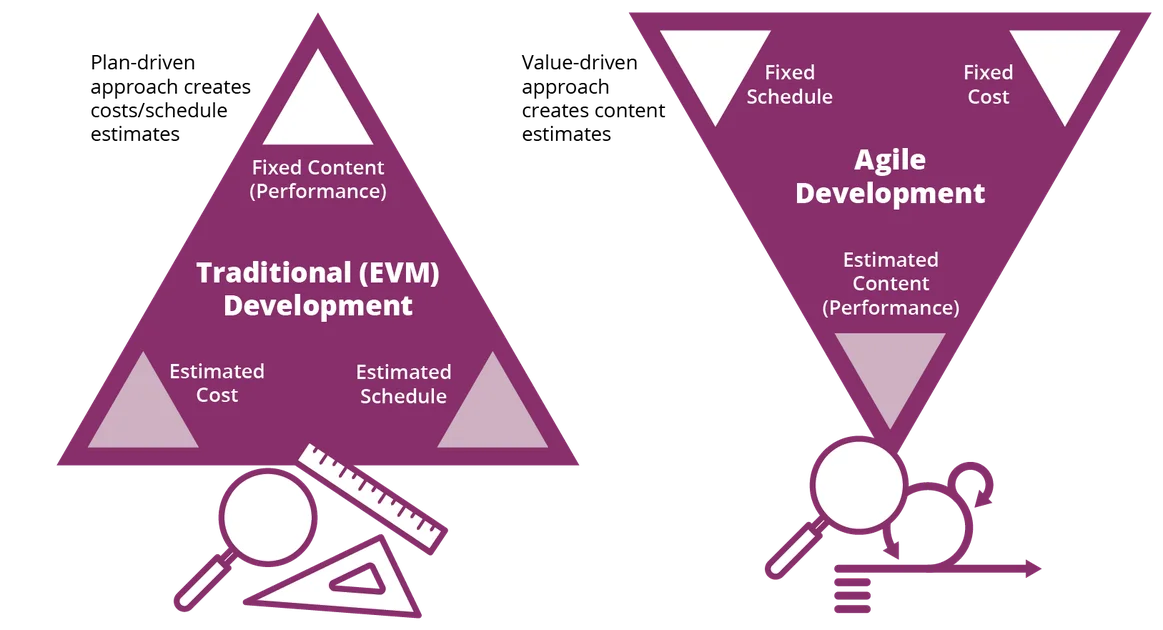
- EVM makes an attempt to baseline the undertaking administration triangle of price, schedule, and efficiency early in a program’s lifecycle. The potential evolution (efficiency) of the system being acquired is mapped over time (schedule) with the labor and supplies (price) wanted to carry out the event. These components are captured within the efficiency measurement baseline (PMB). This system’s earned worth administration system (EVMS) assesses the precise price and schedule to attain the said efficiency evolution in opposition to the predicted price and schedule that’s baselined within the PMB. Basically, with this system, the answer is mounted early and the EVMS assesses worth by how nicely this system progresses to that resolution based mostly on how a lot price and schedule it takes to attain it.
- Agile inverts this PM triangle as a result of it makes use of cadence-based planning as a substitute of the capability-based planning utilized by EVM. The iterative and glued timeboxes that Agile employs to develop the system being acquired welcome evolutionary modifications within the system’s efficiency as a result of studying is anticipated over time. With Agile, price and schedule are comparatively mounted inside the iterative timeboxes, and the answer that emerges is assessed for worth.
Determine 1: Conventional Undertaking-Administration Triangle vs. Inverted Agile Triangle
EVM and Agile each drastically affect how a program conducts operations and informs its selections. Agile, although, is extra involved with the method, and EVM is extra involved with measuring the efficiency of that course of, when it comes to price and schedule. These strategies may and may help one another. But, anecdotal proof captured in SEI engagements with packages reveals that many packages are struggling to observe Agile improvement processes and precisely measure their progress with EVM.
Acknowledging that each EVM and Agile strategies are often tailor-made to fulfill the wants of every program, we is not going to take a one-size-fits-all method on this put up to unravel this dilemma. (It is value acknowledging that Agile ideas additionally apply nicely to ongoing evolution of a deployed system, the place steady supply fashions are used. In these settings, constructs that derive from Kanban and eXtreme Programming shall be extra outstanding than the acquainted constructs of Scrum. As nicely, in these settings, EVM is probably not used, or could also be utilized very otherwise.) As an alternative, we’ll spotlight the place SEI employees members have noticed a few of the extra problematic interactions. The next will present some real-world issues that acquisition professionals ought to concentrate on with Agile and EVM acquisition packages and tasks. Ideally, these issues can be resolved early in a program’s lifecycle, however they are often encountered all through this system’s evolution.
Huge Design Up Entrance (BDUF) Versus Planning as Late as Doable
Conventional acquisition professionals are biased towards planning the way forward for this system with as a lot outlined granularity within the schedule as potential to help the assorted methods engineering technical opinions (SETRs). The SETRs operate as formal and complete opinions the place this system is meant to convey how nicely the design is known and justify the associated fee and schedule to develop. This method encourages a program to forecast a mature, long-term plan and supply the artifacts to help and defend that plan, manifesting in a plan-driven, fixed-requirements method, sometimes called massive design up entrance (BDUF). The EVMS measures progress in opposition to that plan, and acquirers consider this system’s success based mostly on its adherence to the plan. This conventional method, which is sort of muscle reminiscence to many within the acquisition group, can discourage program agility all through the efficiency interval when new data, studying, or technological advances might counsel a greater however completely different path ahead.
Conversely, the Agile technique usually presumes that this system doesn’t know as a lot now as it should later, and never solely permits but in addition expects options to evolve over time with studying. Program pivots are made as long as evolutionary modifications match inside the comparatively mounted cost-and-schedule guiderails. Sometimes, Agile will use timeboxed planning that has comparatively quick home windows of time to be taught, develop, and consider the answer set. There’s minimal element planning past the present release-planning timebox, sometimes called the program increment/planning interval (PI) or the Agile cadence launch. Finally these two mindsets (conventional acquisition BDUF and Agile) will conflict early in this system, usually as the primary SETR approaches.
These two mindsets might be regarded as two ends of a planning continuum—massive up-front (long-term) planning versus cadence-based short-term planning (generally known as rolling wave planning). A program ought to concentrate on the professionals and cons of every. The EVM mindset is usually related to a BDUF method, and it’ll seemingly be extra acquainted to the group’s professionals. However EVM is much less versatile in supporting the answer and necessities flexibility which are basic to Agile. Profitable packages discover a stability between such extremes, and managing progress requires long-term however less-defined high-level plans and short-term element planning captured within the EVMS. It’s greatest that this system supervisor, EVM, and engineering communities focus on this continuum early and make sure that they’re synchronized to forestall confusion later.
As is often the case, the optimum method lies someplace in between, and it’s situational. Generally, the bigger the viewers or the upper up within the organizational hierarchy that the choice straight impacts, the earlier the choice and planning needs to be carried out. Typically this case implies that enterprise-wide planning occurs earlier than portfolio planning, and portfolio planning occurs earlier than crew planning. This method is especially related with architectural planning selections. As an illustration, in methods of methods, the architectural plan and imaginative and prescient should be sufficiently outlined up entrance to allow groups to construct appropriate work. Issues like communication protocols, working methods, and timing, which have an effect on your complete enterprise, are greatest decided up entrance. However architectural selections that have an effect on solely a single crew needs to be deferred till later to use potential tradeoffs earlier than being documented and carried out.

Determine 2: Hierarchy of Planning Ranges
Assessing Feasibility
Each EVM and Agile improvement place vital emphasis on assessing the feasibility of a program; nevertheless, there are vital variations of their approaches.
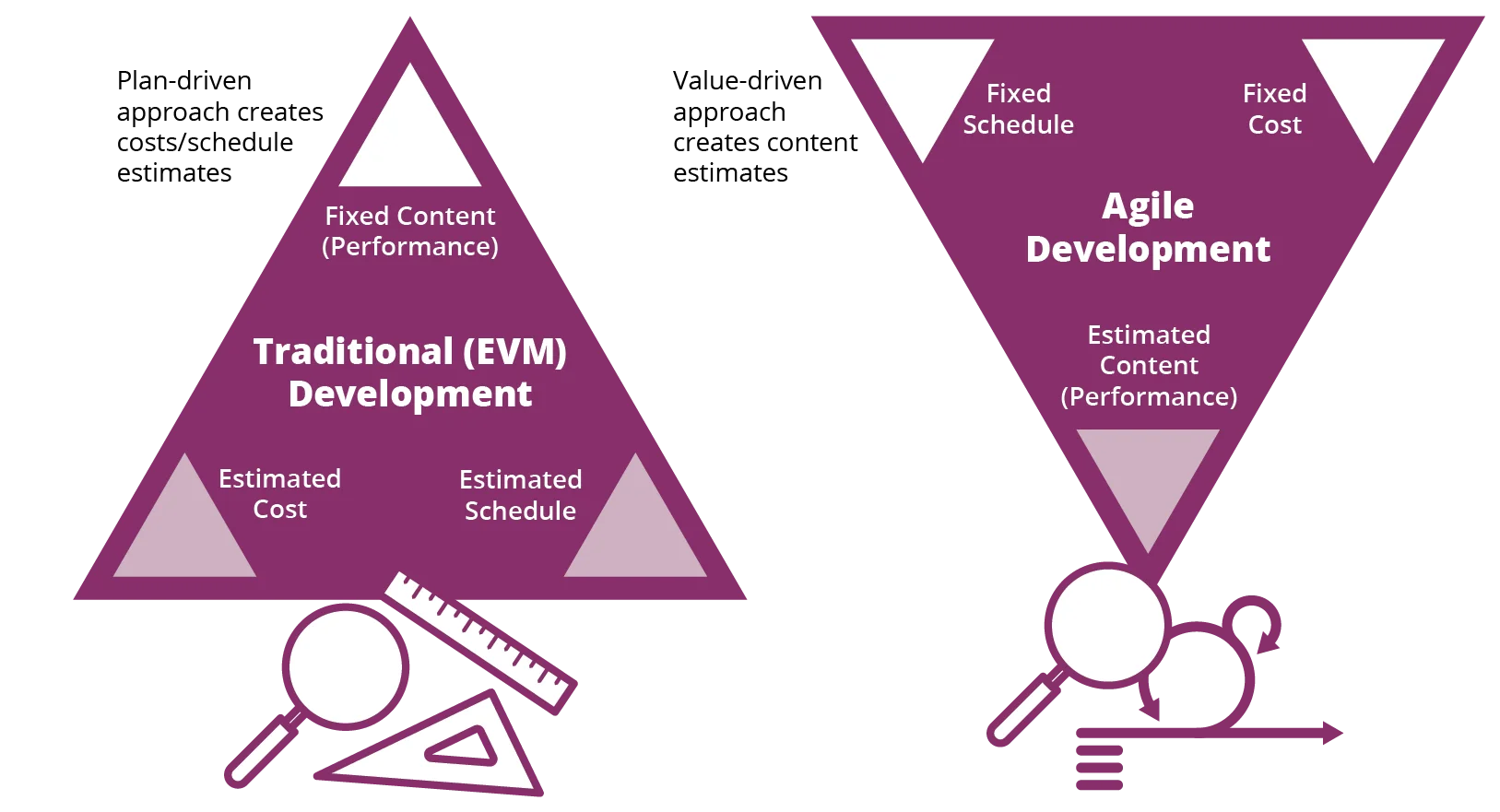
For packages that may use EVM, there’s a requirement that an built-in baseline evaluate (IBR) be carried out during which each work and organizational buildings are examined within the context of schedule, price range, and different assets, in addition to any identified dangers. The primary functions of the IBR are to establish further threat and assess whether or not the baseline defines a program that may be achieved. The EVM crew performs a major function in assessing the feasibility of this system. In essence, the IBR is a forward-looking, multi-factor (e.g., price, schedule, efficiency, threat) method to assessing feasibility based mostly on the plans developed for this system.
In distinction, Agile packages, notably these following the Lean Startup mannequin, deal with the event of a minimal viable product (MVP), which is a improvement of software program to verify or refute the speculation that this system (or some a part of it) is possible. It is an engineering drawback, based mostly on schedule and complexity, to find out when an MVP can and needs to be produced. For the reason that MVP should be constructed first, feasibility is assessed in a backward-looking method to find out whether or not the speculation was sustained.
In giant, complicated packages, an IBR might happen lengthy earlier than an MVP might be developed, notably when the speculation to be examined is of a fancy nature. Furthermore, the IBR considers a broad vary of things whereas the everyday MVP is restricted to answering a smaller set of questions. The MVP, nevertheless, is a concrete demonstration, based mostly on executing code, whereas the IBR is invariably based mostly on projections into the longer term.
The 2 approaches are appropriate with one another. For big packages that may use each Agile strategies and EVM, it’s seemingly that an IBR shall be carried out as normal, although it needs to be thought of that part of the IBR may embrace an illustration of an MVP (if it may be developed in time). Whatever the presence of an MVP, the next questions needs to be answered no later than the IBR:
- How will the EVM and Agile buildings be aligned in order that the EVM coding buildings [such as the work-breakdown structure (WBS) and organizational breakdown structure (OBS)] are mirrored within the software lifecycle administration instrument’s hierarchy?
- How will the Agile roadmap be synchronized with EVM artifacts such because the built-in grasp schedule (IMS)?
- How are the Agile backlog(s), priorities, and commitments built-in with the approved scope?
- How will the baseline schedule be aligned with the Agile cadence-based timeboxes?
- What mechanisms shall be used to replicate Agile studying within the baseline schedule?
- How will rework be dealt with?
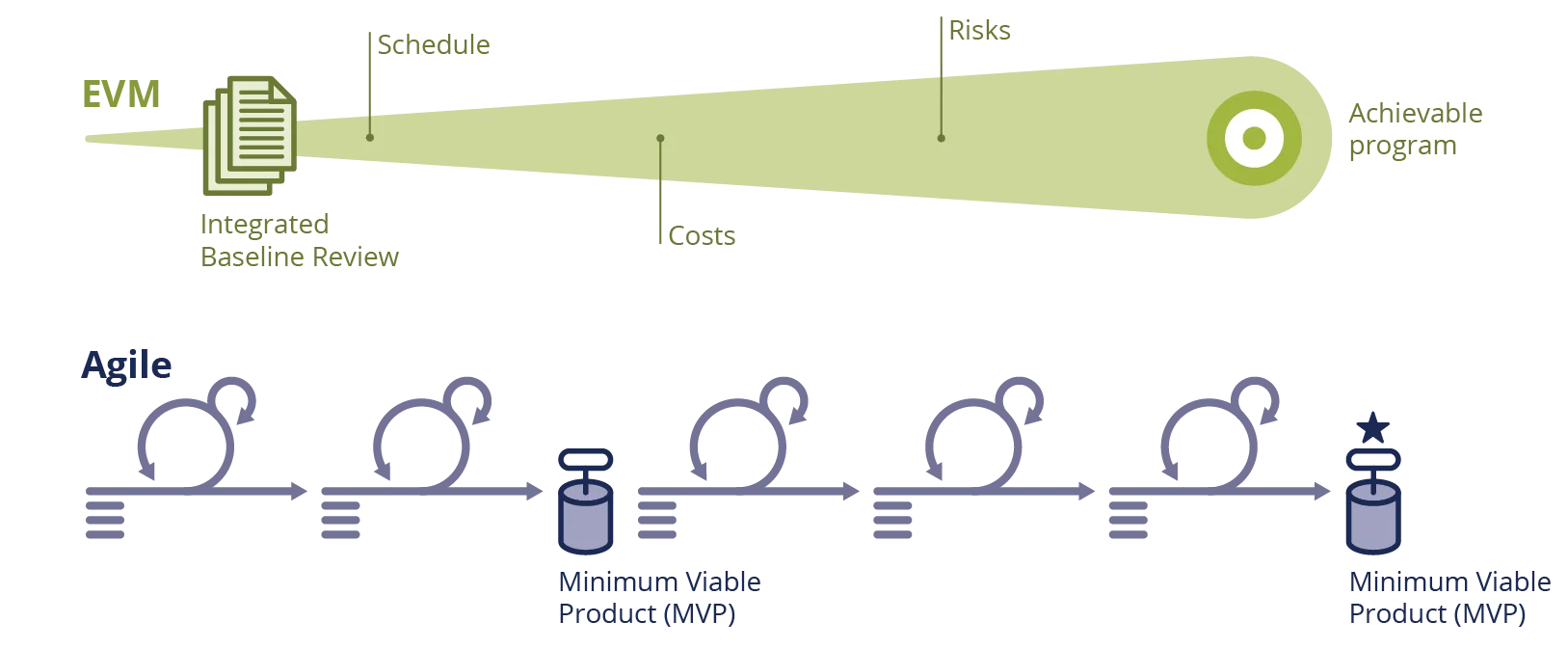
Determine 3: EVM Plan Vs. Agile Product Viability
How Far Down into the Hierarchy of Agile Work Does the EVMS Monitor?
Traditionally, packages have adopted the BDUF technique; not just for the system to be constructed, but in addition for all of the related administration processes. The system isn’t the one factor designed up entrance; so are all organizational and administration buildings. These organizational designs usually observe the organizational assemble and infrequently are usually not seen in Agile developments, although latest work in crew topologies suggests mechanisms for organizing the groups in keeping with the specified construction of the system. For each the system and the organizational construction, although, there’s a pressure between basically mounted buildings in a standard improvement and fluid buildings in an Agile improvement.
An Agile program’s improvement work is damaged down into hierarchical classes based mostly on their ontology. Sometimes, the very best ranges of labor, usually referred to as epics, would be the overarching capabilities or necessities that may take years to finish. This system will then break down that larger stage work into smaller, extra outlined items that match inside the completely different timeboxed cadence releases and iterations. A generally prescribed hierarchy can be to have epics on the high, then options, and eventually tales on the lowest stage.
Options are often outlined as element deliberate work that matches inside a program’s Agile cadence launch or PI and supplies demonstrable worth. Tales are usually items of labor that may be completed by an Agile crew that match inside an iteration timebox, often 1 to 4 weeks. Nonetheless, this nominal hierarchy of epicsàfeaturesàstories is usually not practiced. Many packages have greater than three ranges of hierarchy and use completely different terminology and definitions for causes distinctive to them. Typically the terminology will evolve over a program’s improvement lifetime to accommodate altering enterprise and engineering practices.
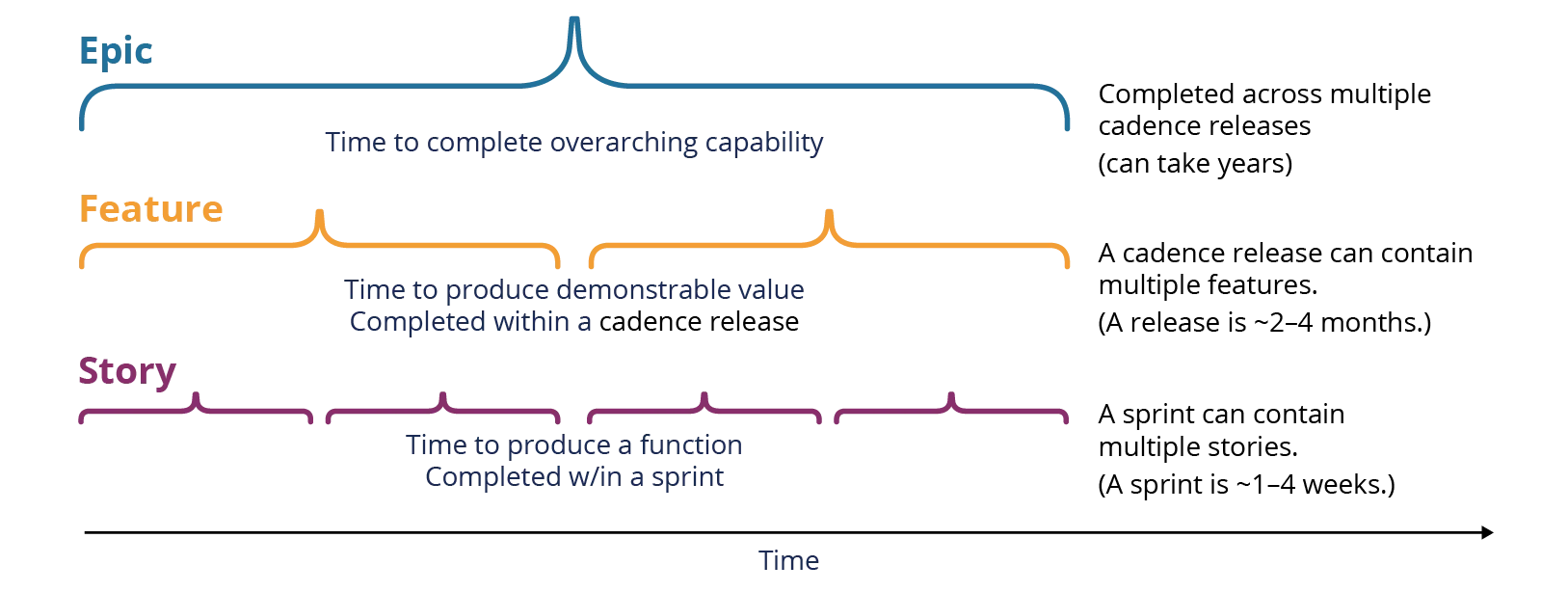
Determine 4: Nominal Agile Hierarchy and Period to Full
No matter terminology or what number of ranges, all Agile packages could have a breakdown of labor that the EVMS will inevitably should measure. Naturally, some might imagine that the EVMS ought to monitor the bottom stage of labor since it’s often probably the most outlined and element deliberate. Nonetheless, this method will seemingly be administratively burdensome and pointless as a result of the bottom stage of labor is just too detailed for the bigger improvement context. The characteristic stage of labor (utilizing the above paragraph’s nominal hierarchy and terminology) will nearly definitely present ample measurable worth to the general program necessities with out having so as to add so many detail-planned work packages into the PMB.
The most effective stage of monitoring is to go no decrease than is important, however low sufficient to achieve the attitude wanted for administration to make the fitting selections. A program should decide what works for them early and make sure that it may be utilized uniformly. In any other case, disconnects between the enterprise and improvement crew will happen.
Resolving the Pressure Between Relative and Absolute Estimation
Estimation is utilized by each EVM and Agile improvement however with completely different objectives in thoughts and, consequently, completely different approaches. In apply neither method assumes excellent estimates. Estimation in EVM is meant to supply administration with an evaluation of how lengthy it should take and the way a lot it should price to construct a required artifact. Consequently, these estimates are often given in models of time and prices related to parts to be constructed. Earned worth is then assessed by comparability of precise time and prices together with reported progress to the estimates.
In distinction, in Agile improvement, estimation is used nearly solely for assessing the feasibility of near-term (and team-specific) targets. Nonetheless, these estimates are usually divorced from any models. The crew performing the estimation identifies the smallest work merchandise then assesses all different work gadgets relative to the smallest work merchandise; no models are implied by the estimate. Furthermore, these estimates are usually created on the time work is about to start and never at some interval upfront, as is important for conventional EVM.
For each EVM and Agile, the estimates are based mostly on historic efficiency. Within the case of EVM the historical past comes from previous packages, whereas in Agile the historical past is from latest timeboxes. In concept, the Agile estimates needs to be extra correct as a result of they’re based mostly on up-to-date data, however these estimates might be flawed, notably when there’s administration strain to hit schedule targets. A closing consideration is that the everyday EVM estimate of effort is usually created in a top-down trend constrained by the ultimate negotiated contract, whereas Agile proponents suggest that the groups develop their estimates with a bottom-up method.
Any Agile improvement that can also be being tracked with EVM should take care of the difficulty of the best way to convert unitless measures to unit-based measures. There are a number of methods this is likely to be completed:
- Settlement that every level equates to some variety of hours of improvement work–This settlement is usually completed by estimating in “ultimate days” as described nicely by Mike Cohn in his guide Agile Estimating and Planning. Though this method is practiced steadily, there are downsides to this method as a result of it encourages the crew to assume in absolute slightly than relative estimates. The human mind is nice at relative estimation. For instance, contemplate the completely different cup sizes on show on the espresso store; with out understanding absolutely the portions, we are able to nonetheless shortly resolve which measurement we wish. One other draw back is that ultimate days imply that the crew should estimate not solely process measurement but in addition process period, whereas relative estimation is concentrated solely on measurement. Chapter 8 of Cohn’s guide is a superb useful resource for extra element on this subject.
- Utilizing a variable mapping of factors to hours—This mapping may very well be achieved by summing up all of the factors related to a bit of labor after which dividing absolutely the estimate produced for EVM functions by the factors to get the mapping for this piece of the work. This might require that the Agile crew decide to the preliminary estimate of all of the work, which can discourage studying as the event progresses. Additional, it could be meaningless to check story-point velocities inside a crew from one piece of labor to the following since it could be unlikely that the ratio of hours to factors can be the identical on any two items of labor.
- Merely ignoring the variations between story factors and hours (or ultimate days)—The previous options level out difficulties with reconciling story factors and hours. The query would then come up as to the worth of utilizing two completely different estimation strategies that, notably for calculation of progress (% full) can be unlikely to provide the identical solutions. Coverage paperwork usually outline the best way to use story factors to compute % full of a characteristic however give no steerage with respect to calculation of prices that will be higher centered on precise hours vs. deliberate hours for accomplished work. The problem is that, for good causes of consistency, EVM requires that price and schedule efficiency indicators be based mostly on the identical knowledge and models. Due to this fact, it could make sense to permit Agile groups and EVM system customers to make use of their very own estimates and never attempt to reconcile them outdoors of the context for which they had been meant.
Phrases Matter—Agree Early
Vocabularies are vital and foster a typical understanding. A shared vocabulary is especially vital in Agile–EVM discussions because the communities (builders and program administration) are usually new to or not very accustomed to one another’s phrases. If individuals don’t take time to develop a typical understanding of phrases, they’ll consider that they’ve agreements when, actually, they don’t due to completely different interpretations of the phrases used.
Agile and EVM each convey an in depth record of not-so-common terminology to an already vocabulary-dense world of DoD acquisitions. It’s seemingly that two events in the identical program have nuanced interpretations of the identical phrase, even after they’ve been on this system for some time. Worse, SEI Agile and EVM practitioners have noticed that the Agile hierarchy phrases and the definitions of every stage could be a supply of confusion and disconnect. These issues can occur as a result of many packages will evolve their Agile hierarchy by including or eradicating ranges, which is able to drive updates to their definitions. The Agile hierarchy varieties the structure by which the EVMS will consider this system’s improvement progress (see How Far Down into the Hierarchy of Agile Work Does the EVMS Monitor?, above). Due to this fact, Agile terminology modifications are analogous to engineering modifications, and the operational definition of key phrases might should be managed in a equally rigorous trend.
A phrase of warning: When frequent Agile phrases, equivalent to characteristic or epic, are used otherwise, there’s a threat of confusion with outdoors entities as nicely since these phrases are sometimes utilized by different packages.
What’s the Proper Quantity of Administrative Assessment When Doing Baseline Change Requests (BCRs)?
When an Agile program plans its work for the following cadence launch or PI, work shall be decomposed from the bigger gadgets within the hierarchy, and element planning will happen with probably the most up-to-date data. Often that is completed collectively throughout the enterprise with subject-matter consultants and stakeholders included for buy-in. The agreed-upon deliberate work then must be captured within the EVMS, which would require baseline change requests (BCRs).
With a standard plan-driven method [see Big Design Up Front (BDUF) Versus Planning as Late as Possible, above], BCRs are sometimes considered to be fixes to errors within the plan—they’re deviations from the in any other case long-term plan that isn’t supposed to vary beneath the standard acquisition paradigm. Due to this, the everyday BCR course of requires oversight by stakeholders related to the BCR, generally by a BCR board, who evaluate to find out if the change might be made to the PMB. Typically, the consultants which are required to evaluate and approve the BCR had been current within the PI planning that generated the BCR. Due to this fact, this BCR oversight by a board could also be duplicative and pointless, particularly if the EVM subject material consultants, just like the management account managers (CAMs) and planners, are additionally part of the discharge planning to make sure that EVM guidelines aren’t breached and surprising schedule perturbations don’t happen.
Packages might wish to have two completely different BCR approval processes:
- A streamlined course of for the planning modifications which are recognized within the cadence-release/PI planning occasions when all stakeholders are current, and
- A conventional, extra thorough evaluate course of (if wanted) for modifications that happen outdoors of the release-planning occasions.
Whatever the approval course of that’s used, it’s additionally vital to leverage software lifecycle administration instruments and real-time data flows to contain stakeholders in a well timed and environment friendly means, and to make sure that the suitable persons are concerned to approve a BCR.
Assessing Progress
EVM’s worth is derived from its use of precise project-performance knowledge to measure progress. This knowledge is then used to find out the worth of the work accomplished. The simplest and commonest method is bodily % full. Whereas it’s easy and simple to know as a result of it’s based mostly on tangible proof of labor completion, it could not contemplate fixed modifications to the scope of the undertaking, may very well be topic to interpretation, and will not present a constant view of progress throughout completely different groups.
Throughout the Agile philosophy, worth is achieved solely with working software program. Within the strictest implementation, there can be solely two choices: 0 % or one hundred pc full. Likewise, EVM steerage means that if work packages shall be accomplished inside one reporting cycle, a 0/100 measure of completeness can be acceptable.
Massive methods of methods usually require involvement with organizations outdoors the management of the software program builders, equivalent to formal check organizations, certification authorities, platform integration, and many others. This method doesn’t precisely symbolize accomplished work and makes accounting for rework troublesome.
On this case, the usage of 0/X/…/Z/100 methodology makes extra sense. Every stage or state is represented with a worth of completion agreed to upfront. Packages should decide what the middleman values needs to be. These values function indicators of stage or state completions versus a precise share full.
For instance, if the system required exterior testing and formal certification, a 0/30/75/100 valuation could also be deemed acceptable. The work package deal can be decided to be 30 % full when it was prepared for the exterior testing. It will then be assessed at 75 % after testing and any required rework was accomplished. Lastly, after certification (and any rework) was full, it could be closed out at one hundred pc full.
Setting Up an EVM and Agile Program for Success: The Twain Shall Meet
All these issues are simply that—issues. Every program has nuances that may decide what the most effective path ahead is for his or her state of affairs. It’s thrilling to know that there is no such thing as a one actual means to do that, however as a substitute there are seemingly limitless methods to arrange an EVM and Agile program for fulfillment. The setup might even be extra of an artwork than a science.
Our expertise reveals that practitioners of EVM and Agile will seemingly encounter all of the tradeoffs detailed on this put up (and possibly extra that weren’t listed). Despite the fact that there’s not one proper solution to treatment these, there’s proof that early engagement between EVM and Agile stakeholders can scale back potential for each disciplines to grow to be burdensome and as a substitute work collectively to supply helpful perception in managing the outcomes of effort. As with most significant issues in life, groups should adapt via the interval of efficiency, so it’s vital to undertake a studying mindset and arrange the Agile and EVM framework to permit for evolution.
We hope that this weblog put up highlights a few of the vital commerce areas early for the readers in order that practitioners shall be in a position to consider them earlier than they current critical issues. All of the completely different issues enumerated on this put up underscore the should be aware when using Agile and EVM; it’s not simply enterprise as normal. It’s vital to recollect the intent of Agile and EVM and leverage probably the most helpful parts of every whereas not utilizing the parts that take away from program execution and monitoring. When completed appropriately, practitioners will benefit from the deserves of each practices.