| Jul 13, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) Astronomers on the College of Sydney have proven {that a} small, faint star is the coldest on report to supply emission at radio wavelength.
|
|
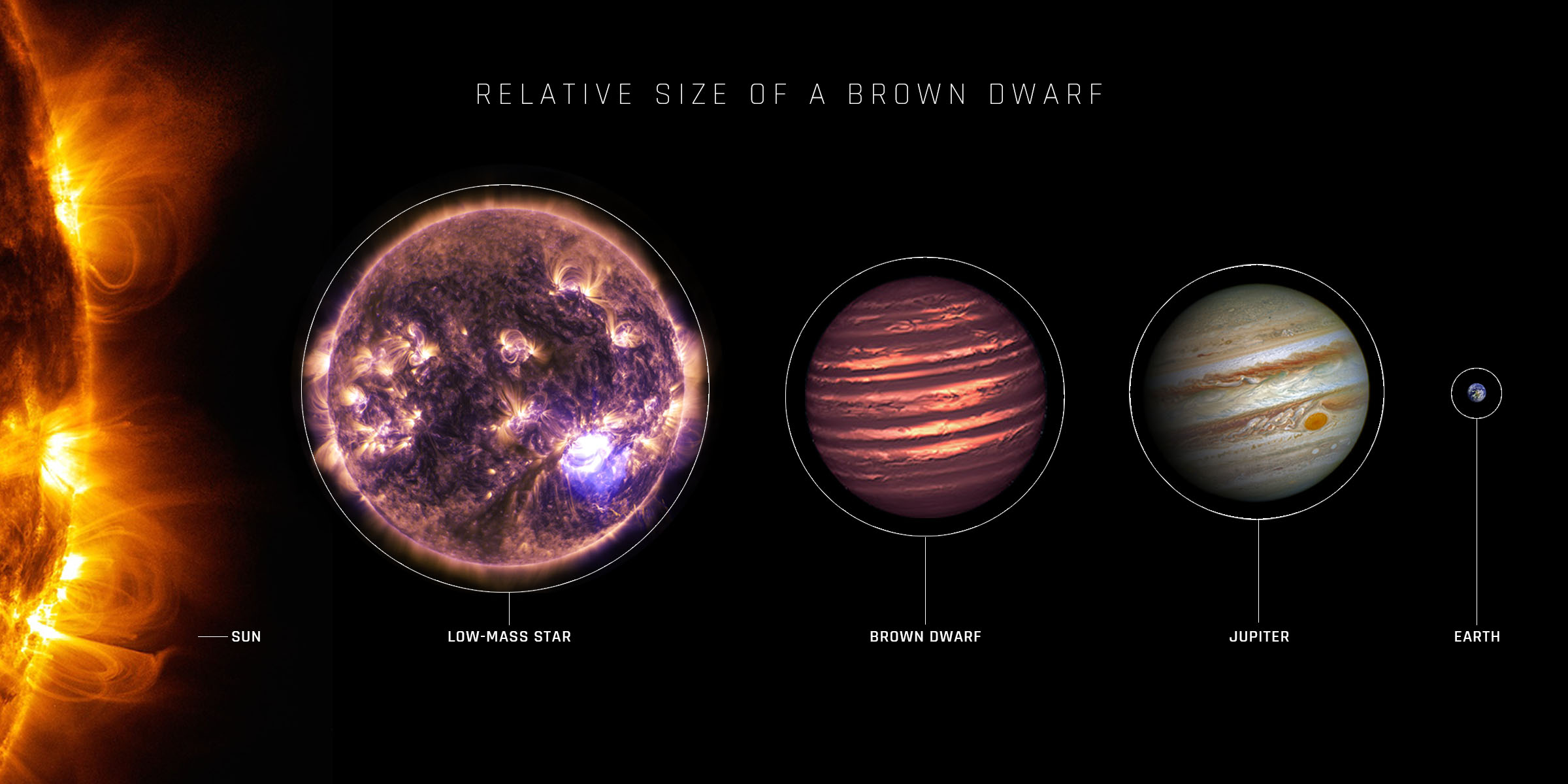
The ‘ultracool brown dwarf’ examined within the research is a ball of gasoline simmering at about 425 levels centigrade – cooler than a typical campfire – with out burning nuclear gasoline.
|
|
In contrast, the floor temperature of the Solar, a nuclear inferno, is about 5600 levels.
|
|
Whereas not the coldest star ever discovered, it’s the coolest to this point analysed utilizing radio astronomy. The findings are revealed in The Astrophysical Journal.
|
 |
| Brown dwarf stars are widespread within the universe however are hardly ever discovered to emit radio waves. (Picture: NASA)
|
|
Lead writer and PhD scholar within the Faculty of Physics, Kovi Rose, mentioned: “It’s very uncommon to seek out ultracool brown dwarf stars like this producing radio emission. That’s as a result of their dynamics don’t normally produce the magnetic fields that generate radio emissions detectable from Earth.
|
|
“Discovering this brown dwarf producing radio waves at such a low temperature is a neat discovery.”
|
|
“Deepening our data of ultracool brown dwarfs like this one will assist us perceive the evolution of stars, together with how they generate magnetic fields.”
|
|
How the interior dynamics of brown dwarfs typically produce radio waves is one thing of an open query. Whereas astronomers have a good suggestion how bigger ‘foremost sequence’ stars just like the Solar generate magnetic fields and radio emissions, it’s nonetheless not totally identified why fewer than 10 p.c of brown dwarf stars produce such emission.
|
|
The speedy rotation of ultracool dwarfs is assumed to play an element in producing their sturdy magnetic fields. When the magnetic discipline rotates at a unique velocity to the dwarf’s ionised environment, it may well create electrical present flows.
|
|
On this occasion, it’s thought the radio waves are being produced by the influx of electrons to the magnetic polar area of the star, which, coupled with the rotation of the brown dwarf star, is producing usually repeating radio bursts.
|
|
Brown dwarf stars, so referred to as as they offer off little vitality or gentle, usually are not large sufficient to ignite the nuclear fusion related to different stars like our Solar.
|
|
Mr Rose mentioned: “These stars are a form of lacking hyperlink between the smallest stars that burn hydrogen in nuclear reactions and the most important gasoline big planets, like Jupiter.
|
|
The star, with the catchy identify T8 Dwarf WISE J062309.94−045624.6, is positioned about 37 gentle years from Earth. It was found in 2011 by astronomers at Caltech in america.
|
|
The star’s radius is between 0.65 and 0.95 that of Jupiter. Its mass will not be nicely understood however is at the very least 4 instances extra large than Jupiter however not more than 44 instances extra large. The Solar is 1000 instances extra large than Jupiter.
|
|
The evaluation of the star was made by Mr Rose utilizing new knowledge from the CSIRO ASKAP telescope in Western Australia and adopted up with observations from the Australia Telescope Compact Array close to Narrabri in NSW and the MeerKAT telescope in South Africa.
|
|
Professor Tara Murphy, co-author and Head of the Faculty of Physics on the College of Sydney, mentioned: “We have simply began full operations with ASKAP and we’re already discovering a whole lot of attention-grabbing and weird astronomical objects, like this.
|
|
“As we open this window on the radio sky, we are going to enhance our understanding of the celebrities round us, and the potential habitability of exoplanet techniques they host.”
|

