Supplies
Chitosan quaternary ammonium salt (HACC) with an 95% diploma of quaternization, and budesonide (BUD, 98%) had been bought from Macklin (Shanghai, China). Sodium cellulose sulfate (NaCS) was supplied by Institute of Bioengineering, Zhejiang College. Cellulase was ordered from Meilunbio (Dalian, China). Lauroyl chloride, pyridine, and iron oleate had been obtained from Aladdin (Shanghai, China). Compritol® 888 ATO was ordered from Gattefosse (Shanghai, China). Dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) was obtained from Yeasen (Shanghai, China). Pyrene was supplied by Shanghai Dibo Chemical substances Expertise Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Ethanol, acetaldehyde, sodium chloride, potassium chloride, dibasic sodium phosphate, and potassium dihydrogen phosphate had been bought from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent Co., Ltd (Shanghai, China). 3, 5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) reagent was obtained from Phygene Biotechnology Co., Ltd (Fuzhou, China).
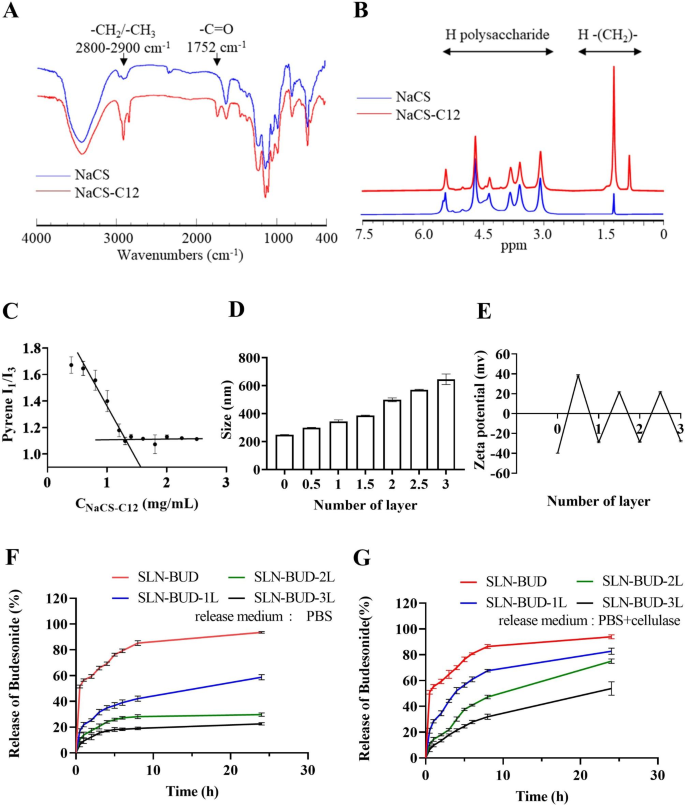
Synthesis of lauryl chloride-esterified NaCS (NaCS-C12)
The esterification of NaCS with long-chain fatty acids was carried out in line with the tactic beforehand reported for carboxymethyl cellulose esterification [24]. The response scheme is proven in Fig. 1A. Briefly, NaCS (500 mg) was suspended in 20 mL of pyridine and stirred at room temperature, and lauryl chloride (0.4 mL) was added dropwise. Subsequently, the response was carried out at 80 °C for 3 h. Ethanol was added to the combination to precipitate the crude product and the precipitate was obtained by vacuum filtration. Lastly, the NaCS-C12 was obtained by precipitated (×3) in 3-fold extra ethanol and dried below vacuum.
Characterization of NaCS-C12
Fourier rework infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) evaluation was carried out with a Nicolet iS50 (Thermo Fisher, USA) spectrometer. Samples had been pressed into KBr discs and measured at room temperature, and 32 scans with a decision of 4 cm− 1 had been measured in a wavenumber vary of 400–4000 cm− 1. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1 H NMR) spectra had been measured with an Avance III 500 MHz NMR spectrometer (Bruker, Switzerland) at 25 °C utilizing DMSO-d6 because the solvent.
The essential micelle focus (CMC) of amphiphilic NaCS-12 was measured by measuring the fluorescence spectra of pyrene [24]. Briefly, a identified quantity of pyrene resolution in benzene was added to a sequence of vials to present a closing focus of 6.0 × 10− 5 M. When benzene was evaporated fully, aqueous options of NaCS-C12 at varied concentrations had been added, sonicated in an ultrasonic water bathtub for 30 min, and stirred at room temperature in a single day in darkish. The fluorescence spectra of pyrene had been measured with an F-4500 fluorescence spectrometer (Hitachi, Japan). The excitation wavelength was 340 nm, and the emission intensities measured at 373 nm (I1, of the primary peak) and 383 nm (I3, of the third peak) had been used to calculate the I1/I3 ratio. The CMC values had been obtained primarily based on the purpose of two tangents to the curve on the inflection.
Preparation of PEC-coated and uncoated SLNs
SLNs had been ready in line with a beforehand reported methodology [25] with some modifications. Briefly, Compritol® 888 ATO (500 mg) was melted in a glass vial at 85 °C. For the drug-loaded formulation (SLN-BUD), BUD (5 mg) was steadily added to the melted lipid with steady stirring to make sure the dissolution of the drug. The aqueous part was ready by dissolving 100 mg of NaCS-C12 in 10 mL of distilled water. After warming up on the identical temperature because the lipid part, the aqueous resolution was rapidly added into the lipid part, after which a Scientz-II D probe sonicator (Scientz, China) was utilized to sonicate the combination for 20 min. Throughout the ultrasound course of, the coarse emulsion was always maintained at a temperature above 85 °C. Lastly, the microemulsion was dispersed in 30 mL of prechilled water (4 °C) below stirring for 30 min to induce SLN formation.
The washless layer-by-layer (LBL) self-assembly of PEC layers on the SLN-BUD floor was carried out as proven in Fig. 1B [26, 27]. Earlier than the LBL coating course of, polymer options of anionic NaCS and cationic HACC had been ready at a focus of 40 mg/mL and 10 mg/mL respectively. For the LBL buildup, SLN-BUD dispersion (1% w/v, 10 mL) was titrated with the cationic HACC aqueous options at completely different quantity ratios of below mild stirring for 30 min. To find out the minimal quantity of HACC resolution required to fully coat SLN-BUD nanocore surfaces, the HACC resolution was step-wise added to the SLN-BUD dispersion and the combination was stirred for not less than 30 min. Then the zeta potential of the ensuing nanoparticle was monitored, and the HACC resolution was added till the outcomes of the zeta potential reached stabilization. Subsequently, the second oppositely charged polyelectrolyte (NaCS) was added in an analogous method. The LBL meeting was carried out by means of the alternate addition of HACC and NaCS to kind as much as 3 bilayers. SLN-BUD with 1, 2, and three PEC bilayers had been ready for additional research.
Physicochemical characterization of SLN-BUD with completely different numbers of PEC layers
The Z-average nanoparticle diameter (dimension), polydispersity index (PDI) and zeta potential floor cost of SLN-BUD with completely different numbers of PEC layers had been assessed at 25 °C utilizing the dynamic mild scattering (DLS) methodology through a Zetasizer nano (ZS 90, Malvern Devices, Malvern, UK).
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM, HT-7700, Hitachi, Japan) was used to research the form and floor morphology of the nanoparticles.
The drug loading capability (DL) and encapsulation effectivity (EE) of SLN-BUD had been calculated by measuring the focus of free BUD within the supernatant after ultrafiltration by 10 kDa filter tubes (Millipore, Germany). The free BUD within the aqueous resolution was quantitatively detected with a UV‒Vis spectrophotometer at 245 nm. DL and EE had been calculated in line with the next equations:
EE% = [(M1-M2)]/M1] * 100.
DL% = [(M1-M2)/M3] * 100.
the place M1 is the overall BUD used within the formulation, M2 is the quantity of BUD within the supernatant, and M3 is the quantity of drug-loaded nanoparticles. The quantity of drug-loaded nanoparticles was decided by instantly weighing the freeze-drying drug-loaded nanoparticles.
The short-term stability of SLN-BUD-2L was investigated below completely different temperatures (4℃ and 25℃), and the particle dimension, PDI, zeta potential and EE of the SLNs had been monitored utilizing dynamic mild scattering (Malvern Zetasizer, UK) and UV‒Vis spectroscopy at specified time intervals (0, 4, 7 days of storage).
BUD launch from SLN-BUD with completely different numbers of PEC layers
The BUD launch profiles of SLN-BUD with completely different numbers of PEC layers (SLN-BUD, SLN-BUD-1L, SLN-BUD-2L, SLN-BUD-3L) had been investigated utilizing a dialysis methodology. Briefly, 3 mL of 1% w/v SLNs (BUD 0.167 mg/mL) with or with out cellulase (1200 U/L) [28] was transferred right into a dialysis bag with a molecular weight cutoff of 14,000 Da, after which a dialysis tube was immersed in 30 mL of PBS as the discharge medium. At chosen time intervals, 0.5 mL launch medium was collected, and 0.5 mL recent PBS resolution was used to replenish the answer. The BUD focus was analyzed by UV‒Vis spectroscopy at 245 nm. The cumulative launch was calculated as the overall proportion of drug launched by means of the dialysis membrane over time. Experiments had been run in triplicate (n = 3). The information proven within the graphs characterize the averages ± normal deviations (SDs).
In vitro drug launch of SLN-BUD-2L
The in vitro drug launch profile of SLN-BUD-2L was investigated in three completely different simulation fluids, together with simulated gastric fluid (SGF, pH 1.2), simulated small intestinal fluid (SIF, pH 6.8) and simulated colonic fluid (SCF, pH 7.4, containing 1200 U/L cellulase). For SCF, because the enzyme couldn’t penetrate the dialysis bag, cellulase was added to the SLN-BUD-2L dispersion as an alternative of the discharge medium to simulate colonic circumstances. Three milliliters of SLN-BUD-2L (1% w/v) containing 0.5 mg of BUD was positioned in a dialysis bag (molecular weight cutoff of 8000–14,000 Da), and the bag was positioned in one of many three simulation fluids. Then, the entire setup was positioned in an incubation shaker (100 rpm) at 37 °C. At chosen time factors, 0.5 mL simulation fluid was collected from the discharge medium, and the identical quantity of recent launch buffer was changed. The launched BUD was spectrophotometrically quantified by UV‒Vis at 245 nm.
The BUD launch profile of SLN-BUD-2L was additionally investigated following the sequential immersion of samples in SGF, SIF and SCF to imitate the in vivo environmental adjustments within the GI tract after oral dosing. Three milliliters of SLN-BUD-2L (1% w/v) containing 0.5 mg of BUD was positioned in a dialysis bag (molecular weight cutoff of 14,000 Da) and incubated in 30 mL of SGF (pH 1.2) for two h at 37 °C. The dialysis tube was then transferred to 30 mL of SIF (pH 6.8) for 3 h and at last positioned in 30 mL of SCF (pH 7.4, containing 1200 U/L cellulase) for as much as 24 h [29]. Then, 0.5 mL launch medium was collected at sure time factors and changed with the identical quantity of recent launch medium. The BUD focus within the launch medium was measured in the identical method as beforehand talked about.
Animal experiments
All animal experiments had been performed with the approval of the Zhejiang College Experimental Animal Welfare and Ethics Committee below Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee pointers. Male C57BL/6J mice (6–8 weeks; physique weight: 20–25 g) and male SD rats (6–8 weeks; physique weight: 180–200 g) had been obtained from the Animal Middle of the Hangzhou Medical Faculty. Animals had been housed in normal mouse cages below normal circumstances, with advert libitum entry to water and meals.
Intestinal lavage fluid drug launch of SLN-BUD-2L and cellulase exercise detection
Ex vivo drug launch was carried out utilizing intestinal lavage fluids from rats. Briefly, SD rats (180–200 g) had been euthanized by cervical dislocation. Subsequent, the massive gut and small gut had been excised, and the intestinal contents had been individually collected, weighed and added at 15% w/v to phosphate buffer (pH 6.8). The PBS buffer containing intestinal content material was stirred in a shaking incubator at 37 °C in a single day after which centrifuged at 10,000 × g for five min to acquire small gut lavage fluid (SILF) or giant gut lavage fluid (LILF). Comparable in vitro drug launch experiments had been carried out for SLN-BUD-2L in SILF or LILF.
The cellulolytic exercise in SILF and LILF was quantified utilizing 9 mL of NaCS resolution (1% w/v) as a substrate, and 1 mL of LILF or SILF was added because the enzyme resolution. The hydrolysis response was carried out at 37 °C and 200 rpm for 1 h, and a 1 mL pattern was taken from the combination. The focus of lowering sugar within the pattern was detected by the Ghose methodology, and a calibration plot was established over a variety of glucose concentrations [30]. The cellulolytic exercise unit was outlined as the quantity of enzyme required to catalyze the hydrolysis of NaCS to supply 1 µmol of lowering sugar per min at 37 °C and pH = 7.0.
Anti-inflammation analysis of SLN-BUD-2L
Thirty male C57BL/6J mice had been randomly assigned to five teams (n = 6): group 1: wholesome + PBS; group 2: mannequin + PBS; group 3: mannequin + free BUD; group 4: mannequin + SLN-BUD; and group 5: mannequin + SLN-BUD-2L. Apart from the group of wholesome mice, which had been supplied with pure water, the opposite mice had been supplied with consuming water containing 3% (w/v) DSS for 7 days to induce colitis, adopted by regular water through the subsequent 5 days of therapy. In a therapeutic setting, the mice in teams 3, 4, and 5 had been orally administered free BUD, SLN-BUD, and SLN-BUD-2L, respectively. SLN formulations (0.15 mL) containing equal doses of BUD (0.168 mg/kg/day) had been orally gavaged each day from day 8 to day 12 [23]. The mice in teams 1 and a pair of had been orally dosed with PBS. Modifications within the physique weight, fecal bleeding, and stool consistency of the mice had been noticed each day. Illness exercise index (DAI) scores, which had been outlined because the summation of the stool consistency index (0–4), fecal bleeding index (0–4), and weight reduction index (0–4), had been evaluated (Fig. 5E) [31]. The fecal bleeding index was decided with a BO check equipment (BASO, China).
Characterization of NaCS-C12 and SLNs coated with completely different numbers of PEC layers. (A) FT-IR spectra of NaCS and NaCS-C12. (B) 1 H NMR spectra of NaCS and NaCS-C12. (C) CMC of NaCS-C12. (D) Z-average dimension of SLNs coated with completely different numbers of PEC layers and (E) the zeta potential of SLNs. (F) Cumulative BUD launch profiles of SLNs coated with completely different numbers of PEC layers in PBS and (G) in PBS with cellulase (1200 U/L).
On the final day of the experiment, the mice had been euthanized, and whole colons and spleens had been collected. The lengths of the colons had been measured and washed with saline, and the spleens had been weighed. Then, 2 cm distal colon sections had been used for histological evaluation. The colon segments had been fastened in 10% formalin resolution for 48 h after which embedded in paraffin. Then, the colon samples had been sectioned at a thickness of 5 μm and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for histological evaluation, adopted by imaging with an optical microscope (Nikon Eclipes E200, Japan) outfitted with a digicam. The exercise of myeloperoxidase (MPO) within the colon tissue was measured with an MPO check equipment (Elabscience, China) following the operation handbook. One unit of MPO exercise was outlined as the quantity of MPO wanted to degrade 1 µmol of peroxidase per minute. To find out the interleukin 6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis issue alpha (TNF-ɑ) concentrations within the colon tissue, colon segments in 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.0) had been homogenized (1:10 w/v) at 4 °C and centrifuged for 10 min at 10,000 × g. The degrees of cytokines within the ensuing supernatants had been decided with a industrial ELISA equipment (Nan Jing Herb Supply, China).
Statistical evaluation
Statistical evaluation was carried out utilizing GraphPad Prism 9. Information are proven because the means with the SDs in parentheses. A t check was used to evaluate the importance of the distinction between two means. The statistical significance of the variations was expressed as p values * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001, **** < 0.0001.