
The time period molybdenum disulfide could sound acquainted to some automobile drivers and mechanics. No marvel: the substance, found by U.S. chemist Alfred Sonntag within the Nineteen Forties, continues to be used right this moment as a high-performance lubricant in engines and generators, but additionally for bolts and screws.
That is because of the particular chemical construction of this strong, whose particular person materials layers are simply displaceable relative to 1 one other. Nonetheless, molybdenum disulfide (chemically MoS2) not solely lubricates properly, however additionally it is attainable to exfoliate a single atomic layer of this materials or to develop it synthetically on a wafer scale.
The managed isolation of a MoS2 monolayer was achieved just a few years in the past, however is already thought-about a supplies science breakthrough with huge technological potential. The Empa staff now desires to work with exactly this class of supplies.
The layered construction of particular person atomic layers makes this materials fascinating for physicists searching for base supplies for next-generation nanocomputers. MoS2—and its chemical family referred to as transition metallic dichalcogenides (TMDs)—are one of many fundamental “capturing stars” in a complete vary of two-dimensional (2D) supplies.
TMDs are 2D semiconductors and have a direct band hole, however solely as a single layer, making them significantly enticing for final miniaturized built-in circuits or optical detectors. The sturdy quantum mechanical properties of 2D supplies are additionally being intensively explored to be used in quantum metrology, quantum cryptography, and quantum data know-how.
However not solely the bottom materials issues, however particularly additionally the flexibility to handle defects in there: Analogous to chemical doping of “classical” semiconductors in built-in circuits or international ions in solid-state lasers, atomic defects are “just like the icing on the cake,” particularly in 2D supplies, Schuler mentioned.
Atomically skinny quantum computer systems
The Empa researcher desires to characterize atomic defects in TMDs utilizing a novel sort of instrument and examine their suitability as so-called quantum emitters. Quantum emitters type the interface between two worlds: electron spin—the quantum mechanical analog of the electron torque—which is appropriate for processing quantum data, and photons, i.e., mild particles, which can be utilized to transmit quantum data over lengthy distances with out loss.
2D supplies supply the good benefit that the related power scales are a lot bigger than for 3D supplies, so it’s anticipated that the know-how can be utilized above cryogenic environments—ideally even at room temperature. As well as, the defects must be situated on the floor of the 2D materials, making them a lot simpler to seek out and manipulate.
However first, the defects within the two-dimensional MoS2 layer must be detected and their digital and optical properties must be investigated exactly. Exact, on this case implies that the situation beneath investigation is explored to the accuracy of 1 angstrom. For comparability: 1 angstrom is to a meter what 4 cm is to the gap of Earth to the moon (400,000 km).
And the snapshot used to report the digital excitation of the quantum dot should be correct down to 1 picosecond (ps)—1 ps is as small of a fraction of a second as two days are in comparison with the age of planet Earth (5 billion years).
These ultrashort and atomically exact measurements then present a really detailed image of what dynamic processes are occurring on an atomic scale and what components are affecting these processes.
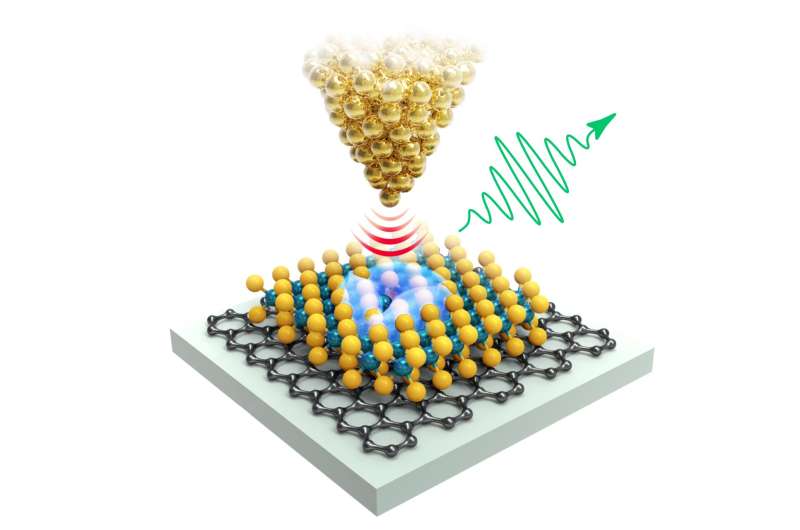
An equipment product of two halves
The equipment wherein the experiments will happen is already situated in a room within the basement of Empa’s laboratory constructing in Dübendorf—the place the ground is essentially the most secure. “Now we have invested over a 12 months and a half of preparation and growth work to finish our experimental setup,” Bruno Schuler explains.
“In October 2022, we related the 2 halves of our system and had been in a position to measure lightwave-induced currents for the primary time. The precept works. An enormous milestone within the mission.”
The 2 halves that Schuler’s staff will now work with are, on the one hand, a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). An ultrathin tip is used to scan the atomic floor of the pattern. The scientists will place the tip at a defect web site, i.e., a emptiness or a “international” atom within the construction.
Then the second half of the system, which Schuler’s colleague Jonas Allerbeck has arrange, comes into play: A 50-watt infrared laser sends ultrashort laser pulses onto a nonlinear lithium niobate crystal. This generates a phase-stable electromagnetic pulse within the terahertz frequency vary. This pulse is just a single oscillation of sunshine lengthy and could be break up with particular optics right into a pair of pump and probe pulse—each of which observe one another with variable delay and might measure the electron dynamics in a stroboscopic method.
An electron ‘jumps’ onto the defect web site
The 2 pulses are then despatched into the STM and directed to the probe tip. The primary pulse detaches an electron from the tip, which “jumps” onto the defect web site of the two-dimensional MoS2 layer and excites electrons there. “This may be both an electrical cost, a spin excitation, a lattice vibration or an electron-hole pair that we create there,” Schuler explains.
“With the second pulse, we then look just a few picoseconds later at how our defect web site responded to the excitation pulse and by that we are able to research decoherence processes and power switch into the substrate.”
On this manner, Schuler is one in all just a few specialists on the earth to mix picosecond-short time decision with a way that may detect particular person atoms. The staff makes use of the intrinsic localization of states within the 2D materials system to carry excitations in a single place lengthy sufficient to be detected.
“The ultrafast lightwave scanning probe microscope permits fascinating new insights into quantum mechanical processes on the atomic scale, and 2D supplies are a novel supplies platform to create these states in a managed manner,” says the Empa researcher.
Quotation:
Characterizing atomic defects in 2D supplies to find out suitability as quantum emitters (2023, July 25)
retrieved 25 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-characterizing-atomic-defects-Second-materials.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

