Customers of Metabase, a well-liked enterprise intelligence and information visualization software program bundle, are being suggested to replace to the most recent model following the invention of an “extraordinarily extreme” flaw that might lead to pre-authenticated distant code execution on affected installations.
Tracked as CVE-2023-38646, the problem impacts open-source editions previous to 0.46.6.1 and Metabase Enterprise variations earlier than 1.46.6.1.
“An unauthenticated attacker can run arbitrary instructions with the identical privileges because the Metabase server on the server you’re operating Metabase on,” Metabase mentioned in an advisory launched final week.
The problem has additionally been addressed within the following older variations –
- 0.45.4.1 and 1.45.4.1
- 0.44.7.1 and 1.44.7.1, and
- 0.43.7.2 and 1.43.7.2
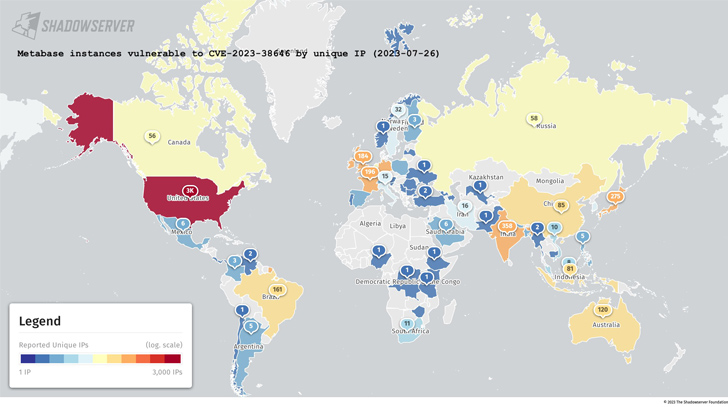
Whereas there isn’t a proof that the problem has been exploited within the wild, information gathered by the Shadowserver Basis reveals that 5,488 out of the entire 6,936 Metabase cases are weak as of July 26, 2023. A majority of the cases are situated within the U.S., India, Germany, France, the U.Ok., Brazil, and Australia.
Protect Towards Insider Threats: Grasp SaaS Safety Posture Administration
Apprehensive about insider threats? We have got you coated! Be a part of this webinar to discover sensible methods and the secrets and techniques of proactive safety with SaaS Safety Posture Administration.
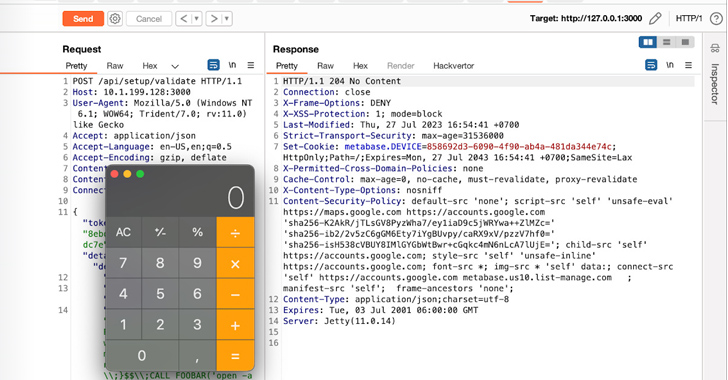
Assetnote, which claimed it found and reported the bug to Metabase, mentioned the vulnerability is because of a JDBC connection difficulty within the API endpoint “/api/setup/validate,” enabling a malicious actor to acquire a reverse shell on the system by the use of a specifically crafted request that takes benefit of an SQL injection flaw within the H2 database driver.
Customers who can’t apply the patches instantly are really useful to dam requests to the /api/setup endpoint, isolate the Metabase occasion out of your manufacturing community, and monitor for suspicious requests to the endpoint in query.