
Posted by Francesco Romano, Developer Relations Engineer on Android
It’s been greater than a 12 months because the launch of the Jetpack WindowManager 1.0 secure model, and lots of issues have occurred within the foldables and enormous display house. Many new gadgets have entered the market, and lots of new use circumstances have been unlocked!
Jetpack WindowManager is without doubt one of the most essential libraries for optimizing your Android app for various kind components. And this launch is a serious milestone that features various new options and enhancements.
Let’s recap all of the use circumstances lined by the Jetpack WindowManager library.
Get window metrics (and dimension lessons!)
Traditionally, builders relied on the system show dimension to determine the structure of their apps, however with the provision of various kind components (reminiscent of foldables) and show modes (reminiscent of multi-window and multi-display) details about the dimensions of the app window fairly than the system show has change into important.
The Jetpack WindowManager WindowMetricsCalculator interface offers the supply of fact to measure how a lot display house is at present out there to your app.
Constructed on prime of that, the window dimension lessons are a set of opinionated viewport breakpoints that enable you design, develop, and check responsive and adaptive utility layouts. The breakpoints have been chosen particularly to stability structure simplicity with the flexibleness to optimize your app for distinctive circumstances.
With Jetpack Compose, use window dimension lessons by importing them from the androidx.compose.material3 library, which makes use of WindowMetricsCalculator internally.
For View-based app, you need to use the next code snippet to compute the window dimension lessons:
non-public enjoyable computeWindowSizeClasses() { |
To be taught extra, see our Assist completely different display sizes developer information.
Make your app fold conscious
Jetpack WindowManager additionally offers all of the APIs you must optimize the structure for foldable gadgets.
Particularly, use WindowInfoTracker to question FoldingFeature data, reminiscent of:
- state: The folded state of the system, FLAT or HALF_OPENED
- orientation: The orientation of the fold or system hinge, HORIZONTAL or VERTICAL
- occlusion kind: Whether or not the fold or hinge conceals a part of the show, NONE or FULL
- is separating: Whether or not the fold or hinge creates two logical show areas, true or false
- bounds: The bounding rectangle of the characteristic inside the utility window (inherited from DisplayFeature)
You may entry this knowledge by means of a Stream:
override enjoyable onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { |
When you accumulate the FoldingFeature data, you need to use the information to create an optimized structure for the present system state, for instance, by implementing tabletop mode! You may see a tabletop mode instance in MediaPlayerActivity.kt.
An excellent place to start out studying about foldables is our codelab: Assist foldable and dual-screen gadgets with Jetpack WindowManager.
Present two Actions aspect by aspect
Final, however not least, you need to use the newest secure Jetpack WindowManager API: exercise embedding.
Out there since Android 12L, exercise embedding allows builders with legacy multi-activiity architectures to show a number of actions from the identical utility—and even from a number of functions—side-by-side on giant screens.
It’s an effective way to implement list-detail layouts with minimal or no code adjustments.
|
Observe: Trendy Android Improvement (MAD) recommends utilizing a single-activity structure based mostly on Jetpack APIs, together with Jetpack Compose. In case your app makes use of fragments, try SlidingPaneLayout. Exercise embedding is designed for multiple-activity, legacy apps that may’t be simply up to date to MAD. |
It is usually the largest change within the library, because the exercise embedding APIs are actually secure in 1.1!
Not solely that, however the API is now richer in options, because it lets you:
- Modify the conduct of the cut up display (cut up ratio, guidelines, ending conduct)
- Outline placeholders
- Verify (and alter) the cut up state at runtime
- Implement horizontal splits
- Begin a modal in full window
Concerned about exploring exercise embedding? We’ve received you lined with a devoted codelab: Construct a list-detail structure with exercise embedding.
Many apps are already utilizing exercise embedding in manufacturing, for instance, WhatsApp:

And ebay!
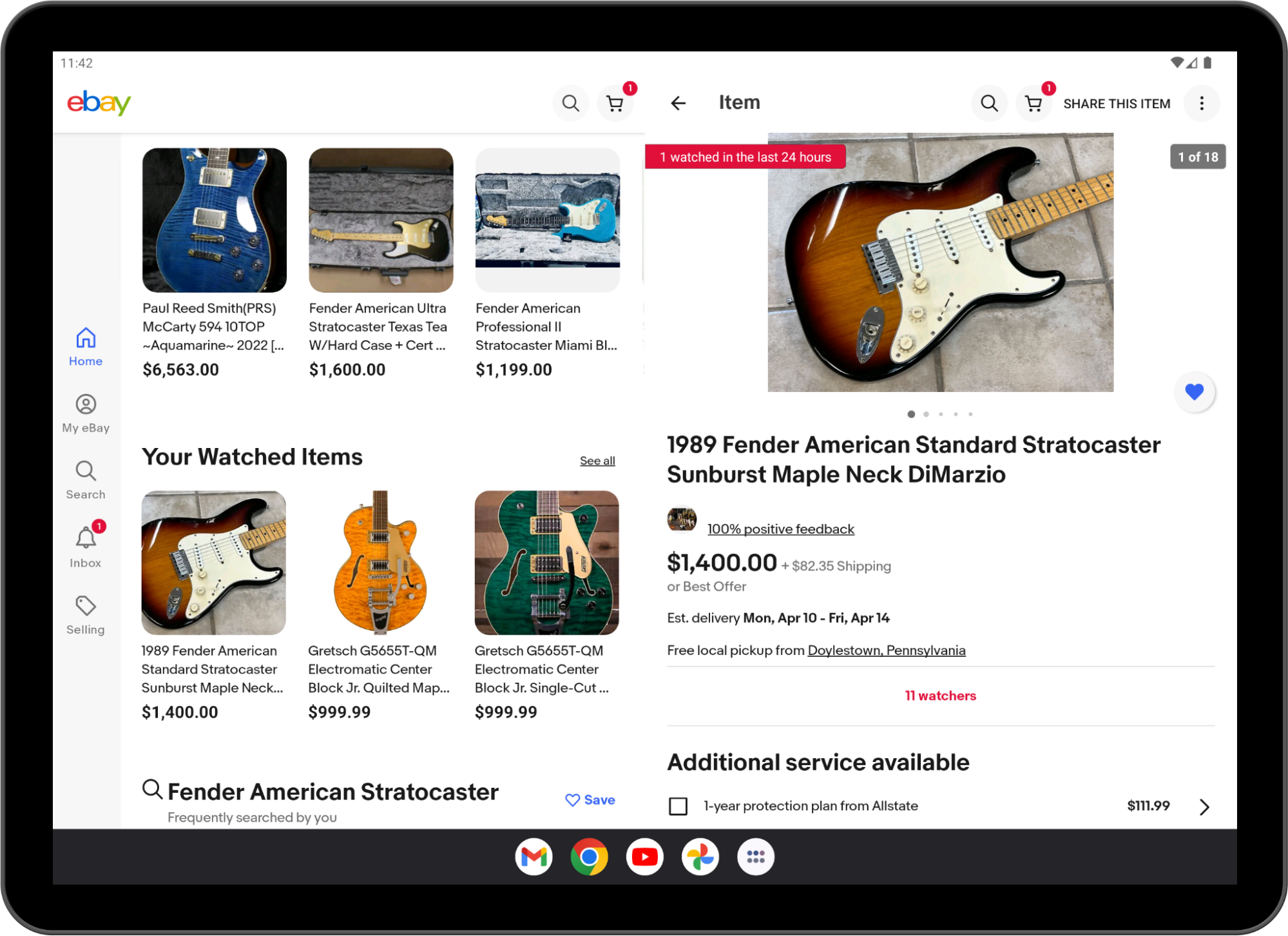
Implementing list-details layouts with a number of actions is just not the one use case of exercise embedding!
Ranging from Android 13 (API stage 33), apps can embed actions from different apps.
Cross‑utility exercise embedding allows visible integration of actions from a number of Android functions. The system shows an exercise of the host app and an embedded exercise from one other app on display aspect by aspect or prime and backside, simply as in single-app exercise embedding.
Host apps implement cross-app exercise embedding the identical manner they implement single-app exercise embedding, however the embedded app should opt-in for safety causes.
You may be taught extra about cross-application embedding within the Exercise embedding developer information.
Conclusion
Jetpack WindowManager is without doubt one of the most essential libraries it’s best to be taught if you wish to optimize your app’s consumer expertise for various kind components.
WindowManager can be including new, attention-grabbing options with each launch, so hold a watch out for what’s coming in model 1.2.
See the Jetpack WindowManager documentation and pattern app to get began with WindowManager at this time!

.png)
