
Posted by Serban Constantinescu, Product Supervisor
Wouldn’t or not it’s nice if every replace improved start-up instances, execution pace, and reminiscence utilization of your apps? Google Play system updates for the Android Runtime (ART) do exactly that. These updates ship efficiency enhancements, the most recent safety fixes, and unify the core OpenJDK APIs throughout a whole lot of tens of millions of units, together with all Android 12+ units and shortly Android Go.
ART is the engine behind the Android working system (OS). It supplies the runtime and core APIs that every one apps and most OS providers depend on. Each Java and Kotlin are compiled right down to bytecode executed by ART. Enhancements within the runtime, compiler and core API profit all builders making app execution quicker and bytecode compilation extra environment friendly.
Whereas elements of Android are customizable by machine producers, ART is similar for all units and Google Play system updates allow a path to modular updates.
Modularizing the OS
Android was initially designed for monolithic updates, which meant that OS parts didn’t have to have clear API boundaries. It’s because all dependent software program can be constructed collectively. Nonetheless, this made it tough to replace ART independently of the remainder of the OS. Our first problem was to untangle ART’s dependencies and create clear, well-defined, and examined API boundaries. This allowed us to modularize ART and make it independently updatable.

As a core a part of the OS, ART needed to blaze new trails and engineer new OS boundaries. These new boundaries had been so intensive that manually including and updating them can be too time-consuming. Due to this fact, we carried out automated era of these via introspection within the construct system.
One other instance is stack unwinding, which studies the capabilities final executed when a difficulty is detected. Earlier than modularizing the OS, all stack unwinding code was constructed collectively and will change throughout Android variations. This made the transition much more difficult, since there is just one model of ART that’s delivered to many variations of Android, we needed to create a brand new API boundary in addition to design it to be forward-compatible with newer variations of the ART APEX module on units which are not getting full OS updates.
Just lately, for Android 14, we refactored the interface between the Package deal Supervisor, the service that determines how you can set up and replace apps, and ART. This strikes the OS boundary from the ART dex2oat command line to a well-defined interface that allows future optimizations, similar to finer-grained management over the compilation mode.
ART updatability additionally launched new challenges. For instance, the gathering of Java libraries, known as the Boot Classpath, needed to be securely recompiled to make sure good efficiency. This required introducing a brand new safe state for compilation throughout boot in addition to a fallback JIT compilation mode.
On older units, the safe compilation occurs on the primary reboot after an ART replace. On newer units that help the Android Virtualization Framework, the compilation occurs whereas the machine is idle, in an enclave referred to as Remoted Compilation – saving as much as 20 seconds of boot-time.
Testing the ART APEX module
The ART APEX module is a fancy piece of software program with an order of magnitude extra APIs than any different APEX module. It additionally backs 1 / 4 of the developer APIs obtainable within the Android SDK. As well as, ART has a compiler that goals to benefit from the underlying {hardware} by producing chipset-specific directions, similar to Arm SVE. This, along with the a number of OS variations on which the ART APEX module has to run, makes testing difficult.
We first modularized the testing framework from per-platform launch (e.g. Android CTS) to per module. We did this by introducing an ART-specific Mainline Take a look at Suite (MTS), which assessments each compiler and runtime, in addition to core OpenJDK APIs, whereas accumulating code protection statistics.
Our goal is 100% API protection and excessive line protection, particularly for brand spanking new APIs. Along with HWASan and fuzzing, the entire assessments described above contribute to an enormous take a look at load that must be sharded throughout a number of units to make sure that it completes in an inexpensive period of time.

We take a look at the upcoming ART launch day by day by compiling over 18 million APKs and working app compatibility assessments, and startup, efficiency, and reminiscence benchmarks on quite a lot of Android units that replicate the variety of our ecosystem as carefully as attainable. As soon as assessments move with all attainable compilation modes, all Rubbish Collector algorithms, and supported OS variations, we start progressively rolling out the following ART launch.
Advantages of ART Google Play system updates
By updating ART independently of OS updates, customers get the most recent efficiency optimizations and safety fixes as shortly as attainable, whereas builders get OpenJDK enhancements and compiler optimisations that profit each Java and Kotlin.
As proven within the graph under, the runtime and compiler optimizations within the ART 13 replace delivered real-world app start-up enhancements of as much as 30% on some units.
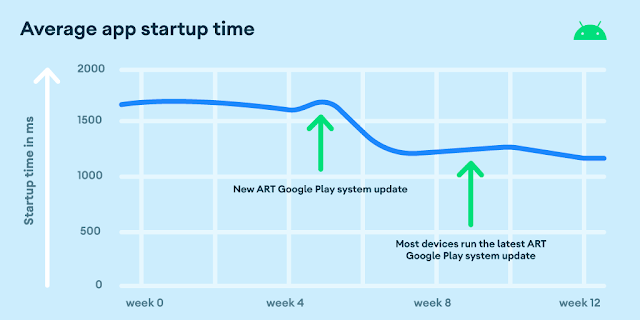
ART updates enable us to steadily deploy fixes with little extra effort from our ecosystem companions. They embody propagating upstream OpenJDK fixes to Android units as shortly as attainable, in addition to runtime and compiler safety fixes, similar to CVE-2022-20502, which was detected by our automated fuzzing assessments.
For builders, ART updates imply that you could now goal the most recent programming options. ART 13 delivered OpenJDK 11 core language options, which was the fastest-ever adoption of a brand new OpenJDK launch on Android units.
What’s subsequent
Within the coming months, we’ll be releasing ART 14 to all appropriate units. ART 14 contains OpenJDK 17 help together with new compiler and runtime optimizations that enhance efficiency whereas lowering code measurement. Keep tuned for extra particulars on ART 14!
Java and OpenJDK are emblems or registered emblems of Oracle and/or its associates.

