Nanoindentation testing is a high-precision instrumented indentation check method that has the benefits of non-destructive testing and ease. Nevertheless, researchers discovered that when testing the identical pattern with completely different Berkovich indenters, inconsistency nonetheless arises even when the indenters are recurrently calibrated. This inconsistency poses challenges in precisely testing materials hardness and evaluating knowledge from completely different laboratories.
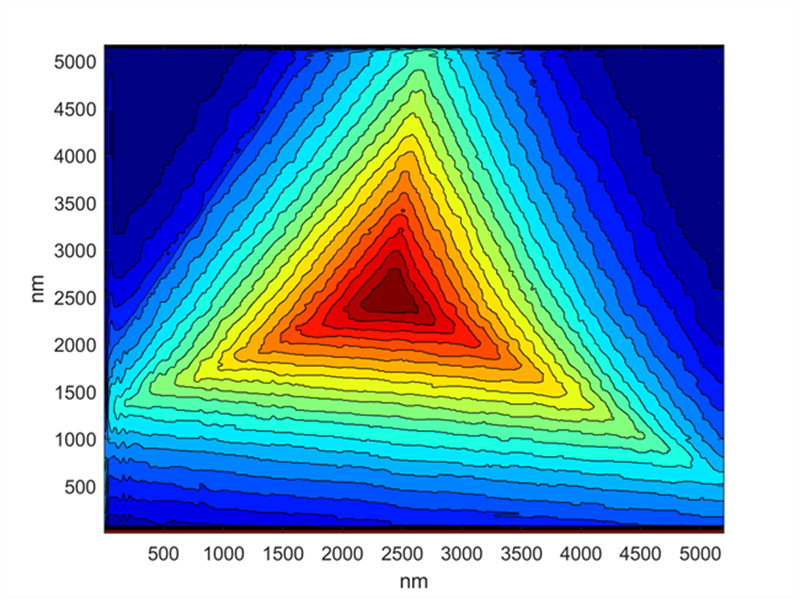
Atomic pressure microscopy (AFM) top contour map of a Berkovich indenter. (Picture by ZHANG Xianlong)
In a examine revealed in Journal of Supplies Analysis and Expertise, researchers from the Supplies Analysis Middle of the Institute of Trendy Physics (IMP) of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (CAS) reported that utilizing completely different Berkovich indenters for nanoindentation testing, excluding fused silica, yields inconsistent outcomes, and analyzed the explanations behind this inconsistency.
The researchers recognized two primary elements contributing to the inconsistent experimental outcomes, i.e., defects within the indenter tip and the indentation dimension impact.
To quantify their influence on experimental outcomes, they developed a finite ingredient mannequin of the indenter utilizing the indenter space operate and proposed a way to right the indentation dimension impact on the load-displacement curve.
The outcomes indicated that whereas defects within the indenter tip have a small direct influence on the experimental outcomes, they do have an effect on the outcomes not directly by influencing the indentation dimension impact.
The indentation dimension impact correction technique and indenter modeling strategy launched on this examine are anticipated to be utilized in inverse finite ingredient evaluation to find out the constitutive relationship of the examined materials.

