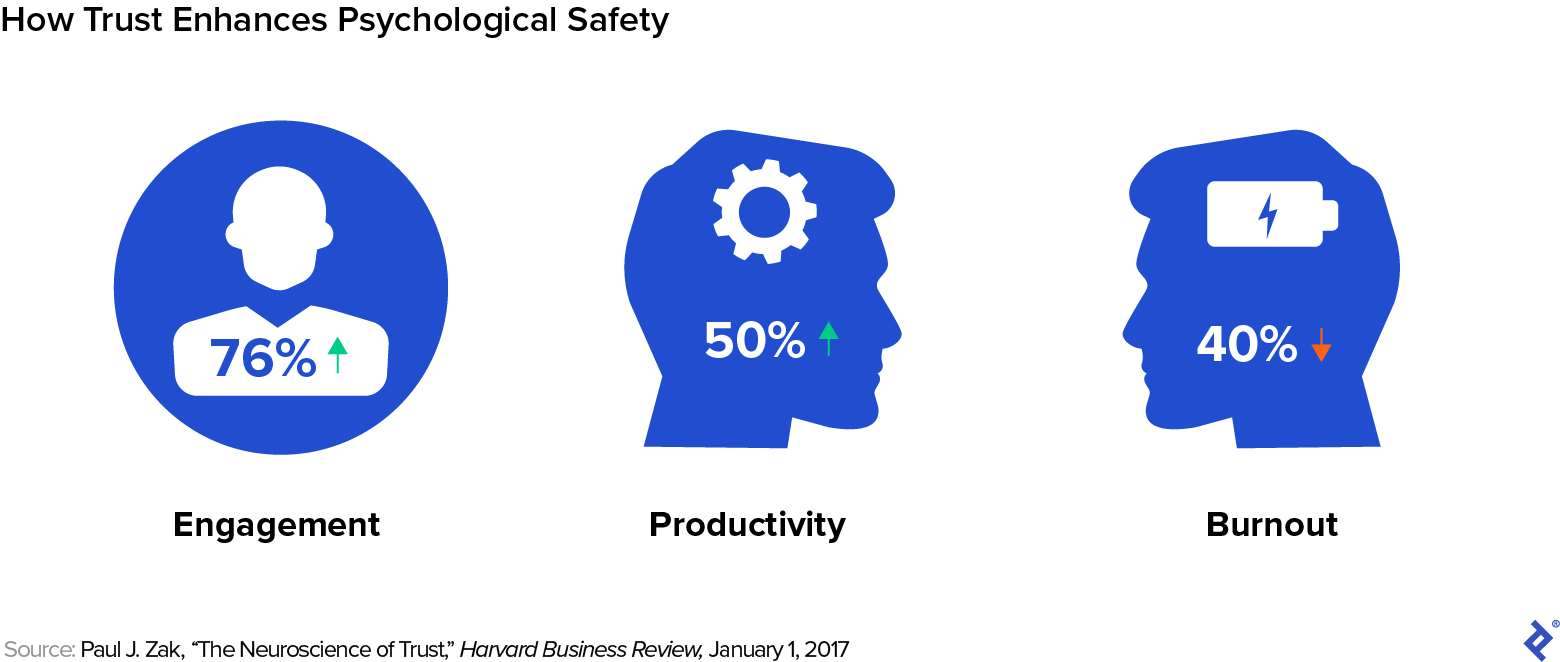
Psychological security at work is a shared notion amongst colleagues that they’ll suggest concepts, voice considerations, pose questions, and acknowledge errors with out concern of detrimental repercussions. Google’s Venture Aristotle discovered that psychological security was a very powerful determinant of workforce success, far outweighing elements like seniority and particular person efficiency. Staff at organizations that promote belief, a element of psychological security, get pleasure from notable benefits in comparison with their counterparts at low-trust firms, in keeping with analysis by neuroeconomics researcher Paul Zak. For example, staff at high-trust organizations report being 76% extra engaged, 50% extra productive, and 40% much less burned out than these at low-trust firms.
As staff more and more search psychological well being help from employers, psychological security has grow to be a urgent subject for a lot of groups and disciplines, together with design. And whereas designers are consultants at empathizing with customers, it doesn’t at all times observe that designers create empathetic environments for themselves.
In my expertise as a design supervisor and marketing consultant, I’ve found that design groups that battle with belief and openness are likely to expertise excessive turnover and lack creativity and confidence. I’ve additionally witnessed how designers in psychologically secure environments are emboldened to experiment, collaborate, and develop modern and infrequently sudden options. On this article, I share how firms can foster psychological security within the office and supply ideas and instruments to assist design groups really feel related and engaged.
Tips on how to Construct Psychological Security Into the Design Course of
Timothy R. Clark, founder and CEO of LeaderFactor—a consultancy that facilitates cultural change at organizations—categorizes psychological security into 4 distinct steps: inclusion security, learner security, contributor security, and challenger security. To make these phases related to design, I’ll map them to the 4 phases of the British Design Council’s Double Diamond design course of: Uncover, Outline, Develop, and Ship.
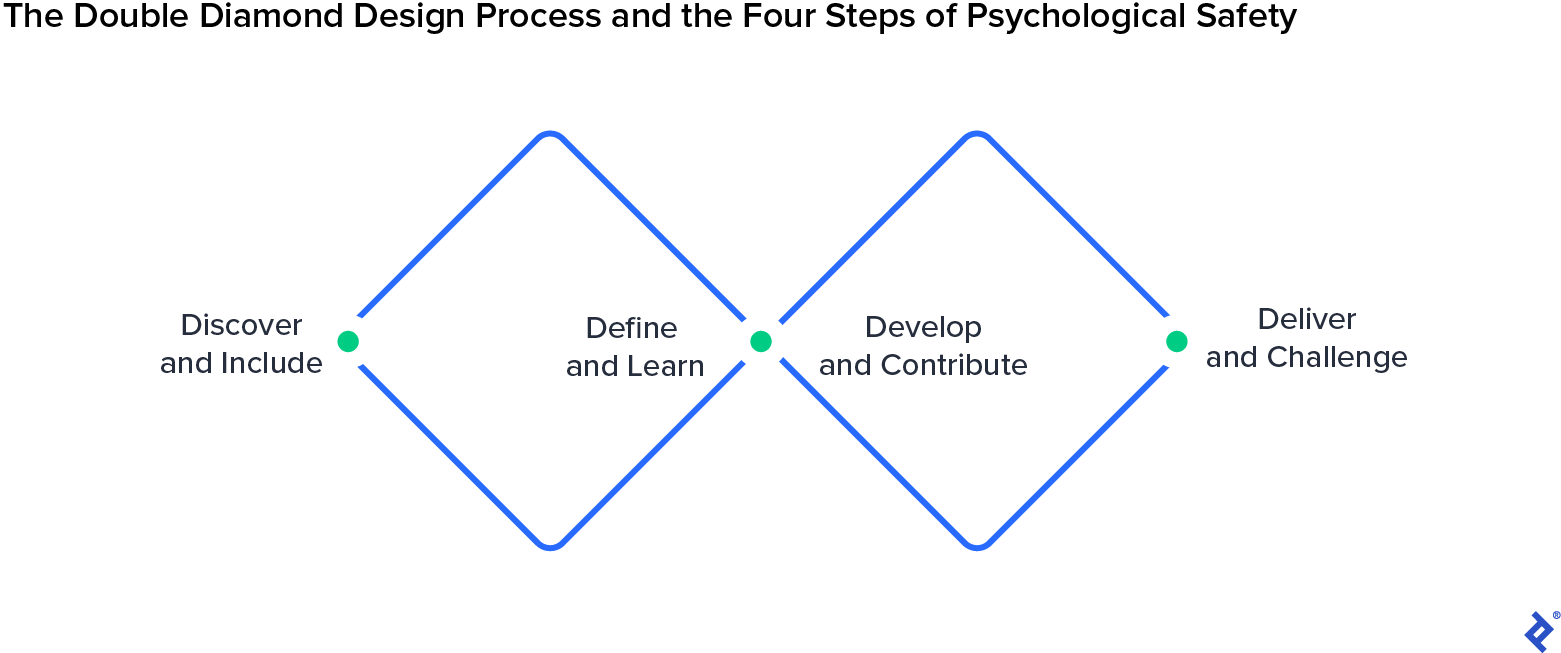
Uncover and Embrace
The Double Diamond’s Uncover section is when designers acquire enter from stakeholders, conduct person analysis, and description challenge objectives. Throughout this stage, it’s important to advertise inclusion security, the psychological security stage that ensures workforce members really feel valued, included, and conscious of related info and processes.
This stage offers a chance to study the wants of stakeholders not normally concerned within the design course of, corresponding to salespeople and buyer help representatives. This section additionally entails sharing info corresponding to product roadmaps and analysis findings to encourage collaboration and unite stakeholders round a shared goal. Along with selling workforce unity, collaborating with cross-functional groups reveals designers the broader implications of their work on the group’s objectives.
Outline and Be taught
Within the Outline section, groups take away pointless info and concepts from the design course of to higher outline the design drawback. Outline is a time when designers articulate hypotheses, trade opinions, and problem assumptions, so it’s important to guard learner security and promote an academic environment the place workforce members can ask clarifying questions. For example, the 5 Whys is a Outline train that entails asking “why” 5 instances to find out an issue’s root trigger and discover options. An alternative choice properly suited to Outline is affinity diagramming, a method for organizing an in depth assortment of details, statistics, and concepts into thematic clusters. The 5 Whys and affinity diagrams encourage collaboration, yield nuanced insights that spark inquiry, and prod designers to rethink preconceived notions in regards to the design drawback.

Develop and Contribute
The Develop section is when the design workforce selects ideas (generated in the course of the Outline section) that appear prone to succeed and builds working prototypes to establish issues and reduce the danger of launching a defective product. It’s a extremely energetic stage: Plans are scrutinized, prototypes are examined, and the competing pursuits of cross-functional groups collide. Develop can also be a susceptible time, so prioritize contributor security to assist staff really feel secure whilst they suggest concepts that might falter. For example, when conducting actions like crit classes and design pingpong, make sure that every idea will get a good and thorough evaluate by establishing clear floor guidelines, together with:
- Empowering the presenter to point out work in any stage of design improvement.
- Permitting the presenter to share with out interruption.
- Asking for feedback to be saved inquisitive reasonably than judgmental (e.g., “I’m curious why you selected Design A over Design B” as an alternative of “You must’ve chosen Design B”).
- Encouraging workforce members to keep away from taking suggestions personally.
Ship and Problem
Ship could be the most delicate section of the method. Because the product receives suggestions, typically from stakeholders exterior of design, it’s essential to retain workforce members’ integrity and sense of inclusion. To take action, guarantee challenger security, and permit design workforce members to proceed critiquing the product and proposing new ideas. For instance, if an government asks for a product function to be revised, designers ought to really feel snug drafting a model that will deviate from the chief’s suggestions; whether or not or not the designer’s model is authorized, workforce members will really feel valued realizing that their concepts obtain consideration.
Develop Psychological Security: A Staff Effort
For psychological security practices to be efficient, design leads should set the instance. Analysis suggests {that a} humble management fashion results in an improve in workforce creativity. Humble leaders naturally align with psychologically secure practices corresponding to acknowledging errors, supporting dangers, encouraging suggestions, and cultivating a secure house during which to voice considerations. Listed below are some methods workforce leaders can exhibit humble management and set up psychological security:
Examine in together with your workforce’s feelings. Begin conferences with “How is everybody feeling?”
Be genuine. Inform your workforce about your considerations, doubts, and questions reasonably than pretending to have all of the solutions.
Seek for the optimistic. Discover methods to acknowledge the strengths of a workforce member’s work, particularly when offering essential suggestions.
Reply instantly. Handle points that come up as quickly as you may in order that your workforce is aware of you might be listening.
Have enjoyable. Though it’s work, it doesn’t at all times must be severe. Arrange and attend social occasions to get to know your workforce higher.
Whereas design workforce leads are chargeable for initiating an open and inclusive setting, psychological security can solely take root if workforce members additionally apply it to studying behaviors. In skilled settings, studying behaviors embody actions corresponding to asking for suggestions, exchanging info, searching for assist, discussing errors, and testing new concepts. A technique to make sure such actions promote psychological security is to have workforce members create expectations and processes for collaborating in studying behaviors. For example, utilizing a turn-taking approach such because the spherical robin methodology throughout workforce critiques can permit extra reserved workforce members to voice useful insights that they may not really feel snug sharing in any other case.
Encourage Psychological Security
If your organization or design workforce is beginning its psychological security journey, take into account operating an nameless evaluation to gauge how your workforce members are doing. Alla Weinberg, a designer and company tradition marketing consultant, created a psychological security survey that features questions corresponding to:
- How snug do you’re feeling sharing concepts in entrance of your colleagues?
- How typically do you speak about feelings at work?
- How typically do you productively speak about and study from errors at work?
Psychological security isn’t a brand new idea within the office. However expertise shortages and a tradition shift emphasizing worker well-being has magnified the necessity for organizations to domesticate environments during which staff are snug testing concepts, expressing considerations, and acknowledging errors. By adopting psychological security practices, groups can higher entice and retain gifted designers. In flip, designers who really feel heard and revered will probably be extra empowered to establish person challenges, experiment with concepts, and design compelling options, finally benefiting firms and their prospects.