Atherosclerosis is characterised by the hardening of blood vessels, particularly sure arteries, because of the native buildup of fibers and lipids (primarily ldl cholesterol) within the interior wall of an artery, inflicting it to slim. It’s a complicated illness that may set off life-threatening occasions, resembling myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke.
Regardless of the severity of this illness, standard diagnostic protocols lack specificity and fail to foretell the kind of atherosclerotic lesion or the danger of plaque rupture.
Because the CIC biomaGUNE Ikerbasque analysis professor Jesús Ruiz-Cabello defined, “diagnosing plaque vulnerability stays a problem because of the lack of efficient diagnostic instruments. To deal with this downside, applied sciences, such because the noninvasive medical imaging of atherosclerotic plaque utilizing custom-made nanotechnology options, are rising. Nonetheless, because of the porosity of the plaque, acquiring photographs utilizing nanoparticles stays a troublesome job.”
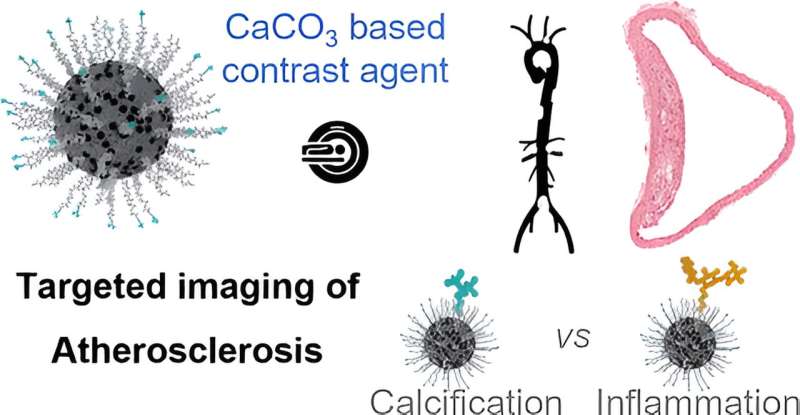
A CIC biomaGUNE group led by Ruiz-Cabello, along with Ikerbasque analysis professor Susana Carregal –each members of the biomedical analysis networking heart CIBERES–, has developed distinction brokers to attain the selective molecular imaging of atherosclerotic plaques utilizing ultrasmall amorphous calcium carbonate nanoparticles. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a secure, biocompatible materials with an extended historical past of use in textiles, cosmetics and foodstuffs.
On this work, printed within the journal ACS Nano, the group in contrast numerous nanoparticles particularly designed for various options of atherosclerosis (resembling calcification or irritation), which give helpful details about the part or stage of plaque growth.
“We managed to modulate the organic interactions and distinction of those nanoparticles for numerous imaging methods, together with magnetic resonance imaging, by rigorously designing their physico-chemical properties,” mentioned Carregal. “Our work exhibits that Gd(III)-doped amorphous calcium carbonate nanoparticles are an efficient software resulting from their excessive magnetic resonance distinction and physico-chemical properties.”
The novelty and influence of the work lies within the mixture of supplies science, molecular imaging and biomedicine to design secure, biocompatible distinction brokers with superior properties for magnetic resonance imaging.
“Our outcomes reveal the potential of this easy but groundbreaking nanoprobe, which may encourage new designs of distinction brokers for atherosclerosis and different varieties of illnesses, and supply the potential of formulating new theranostic brokers (that can be utilized for therapeutic in addition to diagnostic functions),” they concluded.
Extra data:
Lydia Martínez-Parra et al, A Comparative Examine of Ultrasmall Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles for Focusing on and Imaging Atherosclerotic Plaque, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03523
Offered by
CIC biomaGUNE
Quotation:
Enhancing atherosclerosis analysis utilizing ultrasmall calcium carbonate nanoparticles (2023, September 14)
retrieved 16 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-atherosclerosis-diagnosis-ultrasmall-calcium-carbonate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

