MongoDB’s Benefits & Disadvantages
MongoDB has complete aggregation capabilities. You may run many analytic queries on MongoDB with out exporting your knowledge to a third-party device. Nonetheless, these aggregation queries are often CPU-intensive and might block or delay the execution of different queries. For instance, On-line Transactional Processing (OLTP) queries are normally quick learn operations which have direct impacts on the consumer expertise. If an OLTP question is delayed as a result of a read-heavy aggregation question is operating in your MongoDB cluster, your customers will expertise a decelerate. That is by no means factor.
These delays will be prevented by offloading heavy learn operations, akin to aggregations for analytics, to a different layer and letting the MongoDB cluster deal with solely write and OLTP operations. On this scenario, the MongoDB cluster doesn’t should sustain with the learn requests. Offloading learn operations to a different database, akin to PostgreSQL, is one choice that accomplishes this finish. After discussing what PostgreSQL is, this text will have a look at methods to offload learn operations to it. We’ll additionally study among the tradeoffs that accompany this selection.
What Is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an open-source relational database that has been round for nearly three a long time.
PostgreSQL has been gaining lots of traction just lately due to its capability to offer each RDBMS-like and NoSQL-like options which allow knowledge to be saved in conventional rows and columns whereas additionally offering the choice to retailer full JSON objects.
PostgreSQL options distinctive question operators which can be utilized to question key and worth pairs inside JSON objects. This functionality permits PostgreSQL for use as a doc database as effectively. Like MongoDB, it offers assist for JSON paperwork. However, not like MongoDB, it makes use of a SQL-like question language to question even the JSON paperwork, permitting seasoned knowledge engineers to write down advert hoc queries when required.
In contrast to MongoDB, PostgreSQL additionally means that you can retailer knowledge in a extra conventional row and column association. This fashion, PostgreSQL can act as a conventional RDBMS with highly effective options, akin to joins.
The distinctive capability of PostgreSQL to behave as each an RDBMS and a JSON doc retailer makes it an excellent companion to MongoDB for offloading learn operations.
Connecting PostgreSQL to MongoDB
MongoDB’s oplog is used to take care of a log of all operations being carried out on knowledge. It may be used to comply with all the adjustments taking place to the information in MongoDB and to duplicate or mimic the information in one other database, akin to PostgreSQL, in an effort to make the identical knowledge out there elsewhere for all learn operations. As a result of MongoDB makes use of its oplog internally to replicate knowledge throughout all duplicate units, it’s the best and most easy approach of replicating MongoDB knowledge outdoors of MongoDB.
If you have already got knowledge in MongoDB and need it replicated in PostgreSQL, export the whole database as JSON paperwork. Then, write a easy service which reads these JSON recordsdata and writes their knowledge to PostgreSQL within the required format. In case you are beginning this replication when MongoDB continues to be empty, no preliminary migration is critical, and you’ll skip this step.
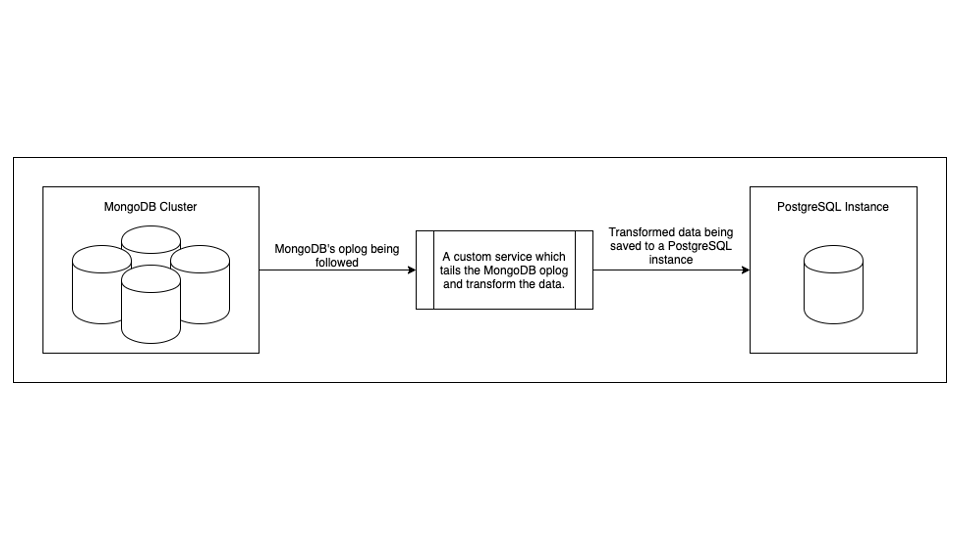
After you’ve migrated the prevailing knowledge to PostgreSQL, you’ll have to write down a service which creates a knowledge circulation pipeline from MongoDB to PostgreSQL. This new service ought to comply with the MongoDB oplog and replicate the identical operations in PostgreSQL that had been operating in MongoDB, much like the method proven in Determine 1 under. Each change taking place to the information saved in MongoDB ought to finally be recorded within the oplog. This will likely be learn by the service and utilized to the information in PostgreSQL.
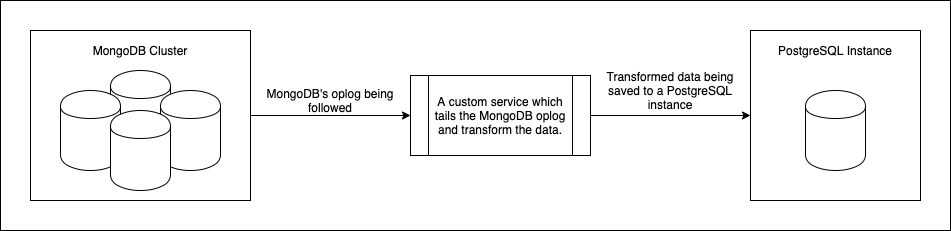
Determine 1: An information pipeline which constantly copies knowledge from MongoDB to PostgreSQL
Schema Choices in PostgreSQL
You now must resolve the way you’ll be storing knowledge in PostgreSQL, for the reason that knowledge from MongoDB will likely be within the type of JSON paperwork, as proven in Determine 2 under.
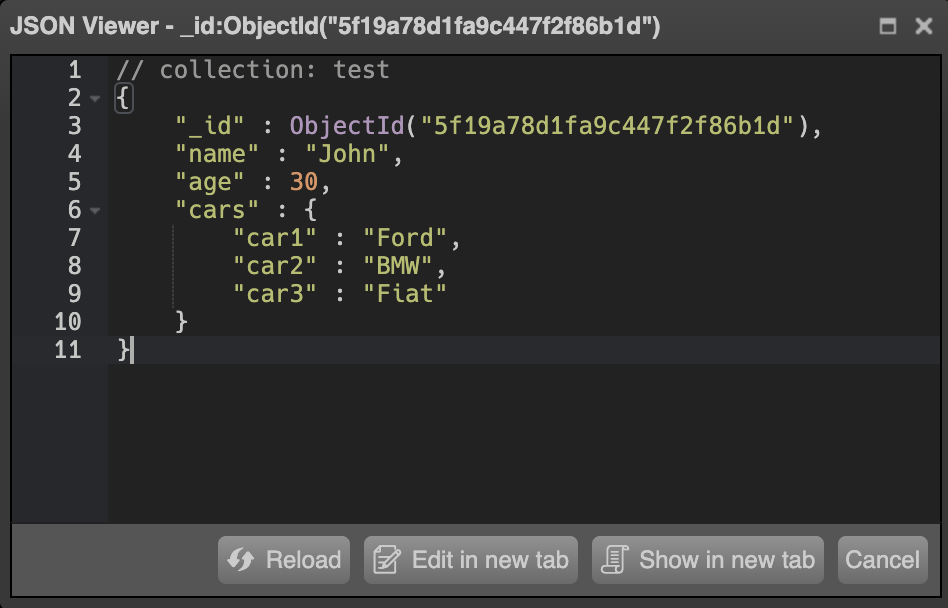
Determine 2: An instance of knowledge saved in MongoDB
On the PostgreSQL finish, you might have two choices. You may both retailer the whole JSON object as a column, or you possibly can remodel the information into rows and columns and retailer it within the conventional approach, as proven in Determine 3 under. This determination ought to be primarily based on the necessities of your software; there isn’t any proper or fallacious method to do issues right here. PostgreSQL has question operations for each JSON columns and conventional rows and columns.
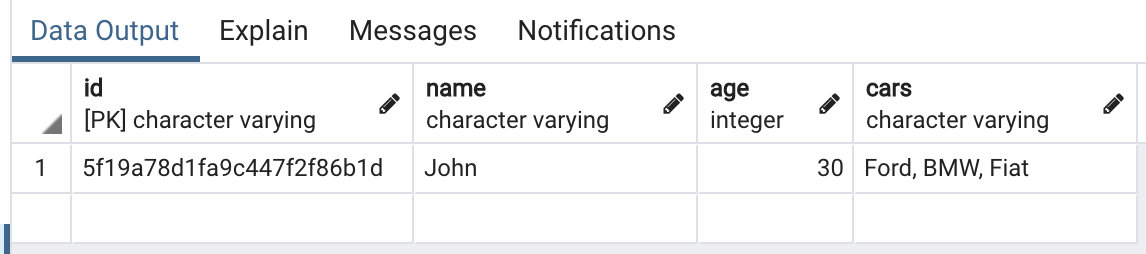
Determine 3: An instance of knowledge saved in PostgreSQL in tabular format
As soon as your migration service has the oplog knowledge, it may be remodeled based on your enterprise wants. You may break up one JSON doc from MongoDB into a number of rows and columns and even a number of tables in PostgreSQL. Or, you possibly can simply copy the entire JSON doc into one column in a single desk in PostgreSQL, as proven in Determine 4 under. What you do right here is dependent upon how you propose to question the information afterward.
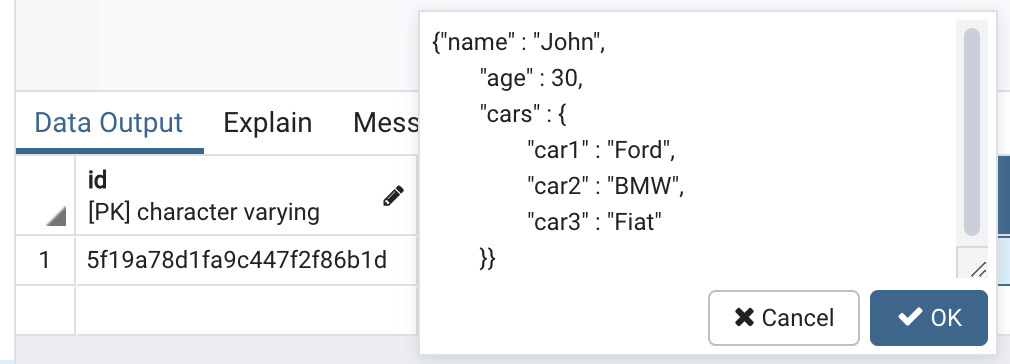
Determine 4: An instance of knowledge saved in PostgreSQL as a JSON column
Getting Information Prepared for Querying in PostgreSQL
Now that your knowledge is being replicated and constantly up to date in PostgreSQL, you’ll must be sure that it’s able to take over learn operations. To take action, work out what indexes you might want to create by your queries and ensuring that each one combos of fields are included within the indexes. This fashion, at any time when there’s a learn question in your PostgreSQL database, these indexes will likely be used and the queries will likely be performant. As soon as all of that is arrange, you’re able to route your whole learn queries from MongoDB to PostgreSQL.
The Benefits of Utilizing PostgreSQL for Actual-Time Reporting and Analytics
There are various benefits of utilizing PostgreSQL to dump learn operations from MongoDB. To start with, you possibly can leverage the facility of the SQL question language. Although there are some third-party companies which give a MongoDB SQL resolution, they typically lack options that are important both for MongoDB customers or SQL queries.
One other benefit, when you resolve to remodel your MongoDB knowledge into rows and columns, is the choice of splitting your knowledge into a number of tables in PostgreSQL to retailer it in a extra relational format. Doing so will permit you to use PostgreSQL’s native SQL queries as an alternative of MongoDB’s. When you break up your knowledge into a number of tables, you’ll clearly have the choice to hitch tables in your queries to do extra with a single question. And, you probably have joins and relational knowledge, you possibly can run advanced SQL queries to carry out a wide range of aggregations. You can even create a number of indexes in your tables in PostgreSQL for higher performing learn operations. Understand that there isn’t any elegant method to be a part of collections in MongoDB. Nonetheless, this doesn’t imply that MongoDB aggregations are weak or are lacking options.
Upon getting an entire pipeline arrange in PostgreSQL, you possibly can simply swap the database from MongoDB to PostgreSQL for your whole aggregation operations. At this level, your analytic queries received’t have an effect on the efficiency of your main MongoDB database since you’ll have a totally separate arrange for analytic and transactional workloads.
The Disadvantages of Utilizing PostgreSQL for Actual-Time Reporting and Analytics
Whereas there are numerous benefits to offloading your learn operations to PostgreSQL, a variety of tradeoffs come together with the choice to take this step.
Complexity
To start with, there’s the plain new shifting half within the structure you’ll have to construct and keep—the information pipeline which follows MongoDB’s oplog and recreates it on the PostgreSQL finish. If this one pipeline fails, knowledge replication to PostgreSQL stops, making a scenario the place the information in MongoDB and the information in PostgreSQL usually are not the identical. Relying on the variety of write operations taking place in your MongoDB cluster, you may need to take into consideration scaling this pipeline to keep away from it changing into a bottleneck. It has the potential to turn out to be the only level of failure in your software.
Consistency
There will also be points with knowledge consistency, as a result of it takes anyplace from a couple of milliseconds to a number of seconds for the information adjustments in MongoDB to be replicated in PostgreSQL. This lag time may simply go as much as minutes in case your MongoDB write operations expertise lots of site visitors.
As a result of PostgreSQL, which is usually an RDBMS, is your learn layer, it won’t be the perfect match for all functions. For instance, in functions that course of knowledge originating from a wide range of sources, you may need to make use of a tabular knowledge construction in some tables and JSON columns in others. A number of the advantageous options of an RDBMS, akin to joins, won’t work as anticipated in these conditions. As well as, offloading reads to PostgreSQL won’t be the best choice when the information you’re coping with is extremely unstructured. On this case, you’ll once more find yourself replicating the absence of construction even in PostgreSQL.
Scalability
Lastly, it’s necessary to notice that PostgreSQL was not designed to be a distributed database. This implies there’s no method to natively distribute your knowledge throughout a number of nodes. In case your knowledge is reaching the boundaries of your node’s storage, you’ll should scale up vertically by including extra storage to the identical node as an alternative of including extra commodity nodes and making a cluster. This necessity may forestall PostgreSQL from being your greatest resolution.
Earlier than you make the choice to dump your learn operations to PostgreSQL—or another SQL database, for that matter—be sure that SQL and RDBMS are good choices to your knowledge.
Issues for Offloading Learn-Intensive Purposes from MongoDB
In case your software works largely with relational knowledge and SQL queries, offloading your whole learn queries to PostgreSQL means that you can take full benefit of the facility of SQL queries, aggregations, joins, and all the different options described on this article. However, in case your software offers with lots of unstructured knowledge coming from a wide range of sources, this selection won’t be match.
It’s necessary to resolve whether or not or not you need to add an additional read-optimized layer early on within the growth of the venture. In any other case, you’ll possible find yourself spending a major quantity of money and time creating indexes and migrating knowledge from MongoDB to PostgreSQL at a later stage. One of the best ways to deal with the migration to PostgreSQL is by shifting small items of your knowledge to PostgreSQL and testing the applying’s efficiency. If it really works as anticipated, you possibly can proceed the migration in small items till, finally, the whole venture has been migrated.
Should you’re accumulating structured or semi-structured knowledge which works effectively with PostgreSQL, offloading learn operations to PostgreSQL is a good way to keep away from impacting the efficiency of your main MongoDB database.
Rockset & Elasticsearch: Options for Offloading From MongoDB
Should you’ve made the choice to dump reporting and analytics from MongoDB for the explanations mentioned above however have extra advanced scalability necessities or much less structured knowledge, chances are you’ll need to think about different real-time databases, akin to Elasticsearch and Rockset. Each Elasticsearch and Rockset are scale-out options that enable schemaless knowledge ingestion and leverage indexing to velocity up analytics. Like PostgreSQL, Rockset additionally helps full-featured SQL, together with joins.
Study extra about offloading from MongoDB utilizing Elasticsearch and Rockset choices in these associated blogs: