Researchers at The College of Texas MD Anderson Most cancers Middle have found that sure nano-based most cancers therapies could also be much less efficient in youthful sufferers, highlighting the necessity for additional investigation into the impression of getting older on the physique’s capability to answer therapy.
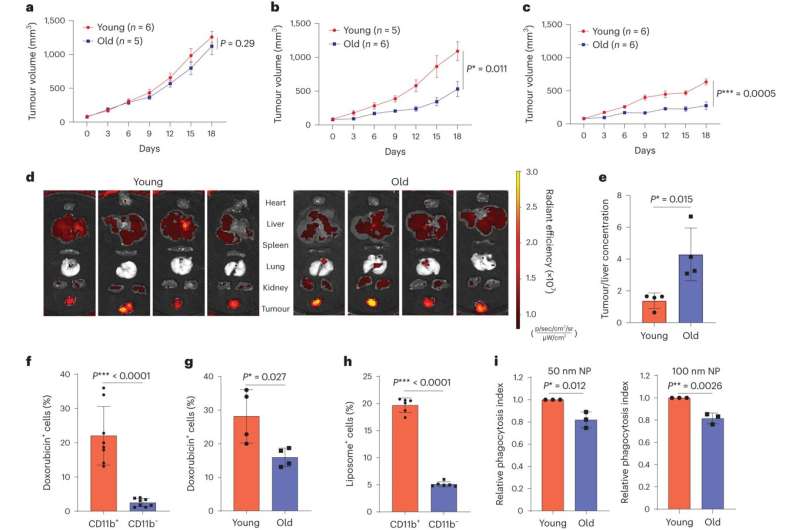
The researchers discovered age-related variations are because of how successfully the liver filters the bloodstream. Youthful livers are extra environment friendly at this course of, which helps restrict toxins within the blood but in addition filters out useful remedies, probably rendering them ineffective.
The research, revealed Sept. 18 in Nature Nanotechnology, was led by Wen Jiang, M.D., Ph.D., affiliate professor of Radiation Oncology, and Betty Kim, M.D., Ph.D., professor of Neurosurgery.
“Put merely, our liver is designed to guard us, however for younger folks it may additionally be defending them in a manner that limits the effectiveness of nanotherapies,” Jiang stated.
“There’s a lot curiosity proper now in nano-scale supply techniques and designs, however no one has actually thought-about how age performs a job within the effectiveness of those techniques. In preclinical fashions, youthful livers really work so effectively that they filter out a big quantity of the nanomedicine. Meaning, in some circumstances, these medicine could also be much less efficient in youthful sufferers than in older ones.”
In contrast to conventional most cancers therapies, through which drugs is straight launched to the physique, nanomedicines use nano-scale carriers to ship remedies. A few of the benefits of nanomedicine formulations can embrace decreased toxicity, elevated goal specificity and elevated dosage, relying on the aim of the therapy.
Up to now, greater than 50 nano-based therapies have been authorized by the Meals and Drug Administration, together with 19 at present listed by the Nationwide Most cancers Institute to be used in most cancers. The research therapy was nanoparticle-albumin-bound paclitaxel, which has been used since 2005 for sure refractory or relapsed cancers.
Scientists don’t absolutely perceive all of the mechanisms for a way, precisely, the liver filters the bloodstream, however earlier research have indicated a correlation between the speed of clearance and the expression of the scavenger receptor MARCO. This protein is expressed extra in youthful Kupfer cells, the immune cells that reside within the liver.
After confirming the disparity in outcomes between younger and outdated fashions, the workforce investigated therapeutic blockade of MARCO as a attainable technique to keep away from drug clearance. Blocking MARCO decreased the uptake of the nanomedicine and improved the drug’s antitumor results from the most cancers therapeutics, however solely within the youthful fashions.
“This is only one instance, however these outcomes present that there might not all the time be a one-size-fits-all drug supply technique that’s efficient throughout numerous affected person populations, and that personalised design is warranted in future nanomedicines,” Jiang stated. “Hopefully, this research additionally opens the door for extra thorough investigation of the clearance course of and learn how to overcome it.”
Jiang emphasised that whereas this research focuses on most cancers, it examines a possible hurdle for any nanodrug supply system. There are totally different proteins, antibodies and viruses with distinctive clearance mechanisms, nevertheless it all comes all the way down to the liver, he defined.
Extra info:
Wen Jiang et al, Age-associated disparity in phagocytic clearance impacts the efficacy of most cancers nanotherapeutics, Nature Nanotechnology (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41565-023-01502-3. www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01502-3
Quotation:
Analysis identifies new potential hurdle for nano-based therapies (2023, September 18)
retrieved 18 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-potential-hurdle-nano-based-therapies.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

