An array is a particular assemble whose objective is to retailer a number of values in a single variable, as a substitute of declaring separate variables for every worth. Furthermore, in Java, an array is a set of comparable sort of components which has contiguous reminiscence location. Not like the Arraylist Class, the primitive array (lowercase “a”) holds a set variety of values. On this programming tutorial, builders will learn to work with arrays in Java. Particularly, we’ll focus on learn how to declare, initialize, and entry array components with the assistance of loads of code examples.
You’ll be able to be taught extra concerning the Arraylist Class in our information: Overview of the Java Arraylist Class.
Learn how to Declare an Array in Java
The syntax to declare an array in Java is much like that of any knowledge sort, besides we add sq. brackets ([]) after the info sort or variable identify, as proven within the code instance under:
dataType[] arrayName; OR dataType arrayName[];
Word that arrays could include any dataType from primitive varieties like int, char, double, byte, and even Java objects. The one caveat is that they have to all be of the identical sort.
Listed here are some examples of learn how to declare arrays in Java:
int intArray[]; int[] intArray2; byte byteArray[]; brief shortsArray[]; boolean booleanArray[]; lengthy longArray[]; float[] floatArray; double[] doubleArray; char[] charArray; MyClass myClassArray[]; Object[] arrO, // array of Object Assortment[] arrC; // array of Assortment
Instantiating an Array in Java
It’s price noting that when an array is asserted, solely a reference of an array is created. As such, no precise array exists but. This reference merely tells the compiler that the array variable will maintain an array of a given sort. To affiliate the array variable with an precise, bodily array of values, builders should allocate one utilizing the new key phrase and assign it to the array as follows;
arrayName = new sort[size];
The measurement parameter specifies what number of discreet values the array will include in order that the Java Digital Machine (JVM) can allocate the required reminiscence. Every slot within the array is known as an factor.
Listed here are the Java statements used to declare and allocate 10 components to an int array:
int intArray[]; // declaring array intArray = new int[10]; // allocating reminiscence to array
Each the variable declaration and reminiscence allocation statements could also be mixed:
int[] intArray = new int[10];
You is perhaps questioning what’s inside the ten slots that we simply allotted? Within the case of arrays, Java follows the identical conventions as for variables that include a single worth. Therefore, the weather within the array allotted by new will robotically be initialized to 0 (for numeric varieties), false (for boolean), or null (for reference varieties).
Learn: Prime On-line Programs to Be taught Java
Learn how to Populate an Array in Java
Since we most likely don’t want our arrays to have default values, we should add our personal values to any array we create. There are a couple of methods to try this; the simplest is to create an array literal, which we are able to do with the next code:
int[] intArray = new int[]{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
This methodology is good for conditions the place the scale of the array (and variables of the array) are already recognized. Word that the scale doesn’t should be specified, because the JVM will allocate no matter measurement is required to carry the given values.
Utilizing the newer Java variations, we are able to additionally dispose of the brand new int[] portion of our code and easily use:
int[] intArray = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
Learn how to Entry Java Array Components
Builders may also initialize every array factor individually, however as a way to do this, we have to know learn how to entry a particular factor. Array components could be accessed utilizing their index quantity. Java arrays are zero primarily based, which means that the primary factor has a zero (0) index. Right here is the syntax for accessing components of an array in Java:
array[index]
With this in thoughts, we might initialize our intArray as follows:
intArray[0] = 12; intArray[1] = 4; intArray[2] = 5; intArray[3] = 9; //and so forth...
Programmers can make use of the identical syntax to learn factor values:
System.out.println("First Aspect: " + intArray[0]);
System.out.println("Second Aspect: " + intArray[1]);
System.out.println("Third Aspect: " + intArray[2]);
/* prints:
First Aspect: 12
Second Aspect: 4
Third Aspect: 5
*/
Traversing Java Array Components Utilizing Loops
The for loop is tailored for iterating over arrays, since its counter variable could be readily utilized to entry the present array factor. The one catch is that builders should watch out to not proceed previous the top of the array. In any other case, we’ll get a java.lang.
public class Fundamental
{
public static void major(String[] args) {
int[] intArray = new int[]{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 };
for (int i = 0; i < intArray.size; i++) {
System.out.println("intArray[" + i + "]: " + intArray[i]);
}
}
}
Executing the above code outputs the next outcomes:

You’ll be able to be taught extra about loops in our tutorial: Introduction to the Java For Loop.
Traversing Java Arrays with the For-each Loop
Java model 5 launched an enhanced for assertion often called a for-each loop. This type of loop permits programmers to iterate over arrays or lists with out having to calculate the index of every factor. The improved for has the next format and syntax:
for (<loop variable> : <iterable>) {
// do your stuff right here
}
Right here is our earlier loop instance, refactored as a for-each loop:
for (int elt : intArray) {
System.out.println("intArray[" + i + "]: " + elt);
}
Multidimensional Arrays
Array components could themselves maintain a reference to different arrays, creating multidimentional arrays. In Java, a multidimensional array is asserted by appending one set of sq. brackets ([]) per dimension, like so:
int[][] intArray2D = new int[10][15]; //a 2D array int[][][] intArray3D = new int[10][20][20]; //a 3D array
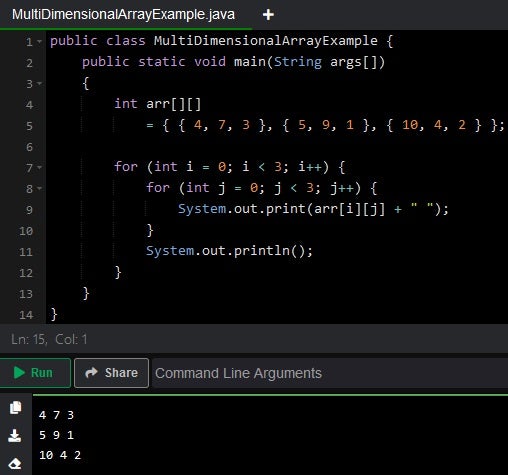
Here’s a program that declares and initializes a two-dimentional array earlier than printing its contents to the console:
public class MultiDimensionalArrayExample {
public static void major(String args[])
{
int arr[][]
= { { 4, 7, 3 }, { 5, 9, 1 }, { 10, 4, 2 } };
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
We are able to see the total program and output under:

Closing Ideas On Java Arrays
On this programming tutorial, we realized learn how to declare and initialize Java arrays, in addition to learn how to entry their components. We additionally mentioned learn how to create multidimensional arrays and realized to traverse arrays use the for and for-each loops. Arrays are the perfect selection for holding a set variety of values of the identical sort. Nevertheless, when you want dynamic sizing, contemplate going with an ArrayList as a substitute.
Seeking to be taught extra about Java arrays? Try these tutorials: