A crew of Clemson College chemists has constructed a novel two-dimensional electrically conductive metal-organic framework (MOF), a breakthrough that might assist advance trendy electronics and vitality applied sciences.
The crew’s findings have been revealed within the journal Angewandte Chemie within the paper titled “Electrically Conductive π-Intercalated Graphitic Metallic-Natural Framework Containing Alternate π-Donor/Acceptor Stacks.”
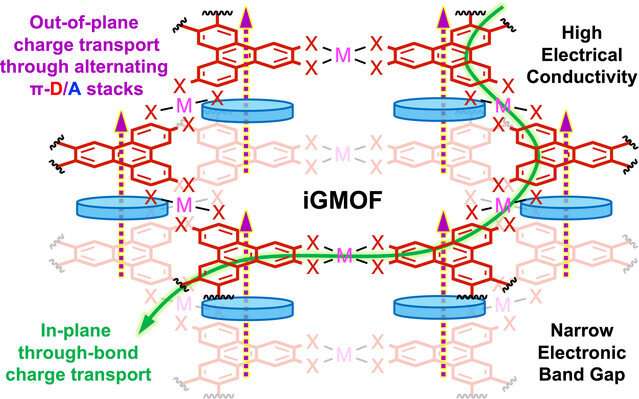
MOFs are nano-sized architectures that resemble miniature buildings fabricated from metallic ions linked by natural ligands. The buildings are largely hole and porous with a rare quantity of inner floor house. Consequently, MOFs can retailer visitor molecules, catalyze chemical reactions and ship medication in a managed method.
Sure MOFs may even conduct electrical energy, making them potential next-generation semiconductors.
“We’d like new supplies for semiconductors for electronics and vitality applied sciences, and this class of supplies has proven nice potential,” stated Sourav Saha, an affiliate professor within the Division of Chemistry, who led the examine. “These supplies (MOFs) are a lot simpler to synthesize, course of and tune their digital and optical properties than conventional inorganic semiconductors.”
The most important impediment to realize excessive framework conductivity is their porosity.
“That’s actually difficult to make porous supplies electrically conducting as a result of the fees do not circulation via the pores or the empty house,” Saha stated. “That’s the holy grail. That’s the foremost problem of the sphere.”
Chemists undertake completely different methods to make these supplies electrically conducting. The fees can circulation via chemical bonds or via the slender gaps between the natural ligands.
“Sometimes, most of those MOFs which can be electrically conducting have both through-bond or through-space conduction pathways. What we completed right here was to mix these two pathways right into a single 2D materials,” he stated.
The brand new MOF has conductivity that’s 10 to fifteen instances greater than the guardian MOF that lacks such environment friendly out-of-plane conduction pathways.
“Dr. Saha’s work helps to ship on the promise that metal-organic framework supplies supply for bettering a variety of applied sciences, together with batteries, photo voltaic cells, and chemical and pharmaceutical manufacturing. His intelligent introduction of electrical conductivity in these open framework supplies is a tour-de-force of molecular design. It’s thrilling to see these advances emerge from Clemson’s analysis enterprise,” stated Stephen Creager, affiliate dean and professor of chemistry within the School of Science.
Saha’s analysis crew at Clemson included postdoc Ashok Yadav and graduate college students Shiyu Zhang and Paola Benavides. Wei Zhou of the Nationwide Institute of Requirements and Expertise’s Middle for Neuron Analysis supplied computational help and validation to Saha’s experimental work.
Extra info:
Ashok Yadav et al, Electrically Conductive π‐Intercalated Graphitic Metallic‐Natural Framework Containing Alternate π‐Donor/Acceptor Stacks, Angewandte Chemie Worldwide Version (2023). DOI: 10.1002/anie.202303819
Offered by
Clemson College
Quotation:
Analysis crew’s novel metal-organic framework might assist advance semiconductors (2023, June 27)
retrieved 11 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-06-team-metal-organic-framework-advance-semiconductors.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

