On the Knowledge and AI Summit 2023, we launched Volumes in Databricks Unity Catalog. This function allows customers to find, govern, course of, and observe lineage for any non-tabular information, together with unstructured, semi-structured, and structured information, together with the tabular information in Unity Catalog. Immediately we’re excited to announce the general public preview of Volumes, which is on the market on AWS, Azure, and GCP.
On this weblog, we talk about frequent use circumstances associated to non-tabular information, present an summary of the important thing capabilities with Volumes in Unity Catalog, showcase a working instance demonstrating a sensible software of Volumes, and supply particulars on the best way to get began with Volumes.
Widespread makes use of circumstances related to the governance and entry to non-tabular information
Databricks Lakehouse Platform can retailer and course of giant quantities of information in quite a lot of codecs. Whereas a lot of this information is ruled by means of tables, there are lots of use circumstances, significantly for machine studying and information science workloads, which require entry to non-tabular information, resembling textual content, picture, audio, video, PDF, or XML recordsdata.
Widespread use circumstances now we have heard from our clients embrace however are usually not restricted to:
- Operating machine studying on giant collections of unstructured information resembling picture, audio, video, or PDF recordsdata.
- Persisting and sharing coaching, check, and validation information units used for mannequin coaching and defining places for operational information resembling logging and checkpointing directories.
- Importing and querying non-tabular information recordsdata in information exploration phases in information science.
- Working with instruments that do not natively help Cloud object storage APIs and as an alternative anticipate recordsdata within the native file system on cluster machines.
- Storing and offering safe entry throughout workspaces to libraries, certificates, and different configuration recordsdata of arbitrary codecs, resembling .whl or .txt, earlier than they’re used to configure cluster libraries, notebook-scoped libraries, or job dependencies.
- Staging and pre-processing uncooked information recordsdata within the early phases of an ingestion pipeline earlier than they’re loaded into tables, e.g., utilizing Auto Loader or COPY INTO.
- Sharing giant collections of recordsdata with different customers inside or throughout workspaces, and plenty of extra.
With Volumes, you possibly can construct scalable file-based purposes that learn and course of giant collections of non-tabular information no matter its format at Cloud-storage efficiency.
What are Volumes, and how are you going to use them?
Volumes are a brand new sort of object that catalog collections of directories and recordsdata in Unity Catalog. A Quantity represents a logical quantity of storage in a Cloud object storage location and offers capabilities for accessing, storing, and managing information in any format, together with structured, semi-structured, and unstructured information. This lets you govern, handle and observe lineage for non-tabular information together with the tabular information and fashions in Unity Catalog, offering a unified discovery and governance expertise.
Operating picture classification on a picture dataset saved in a Quantity
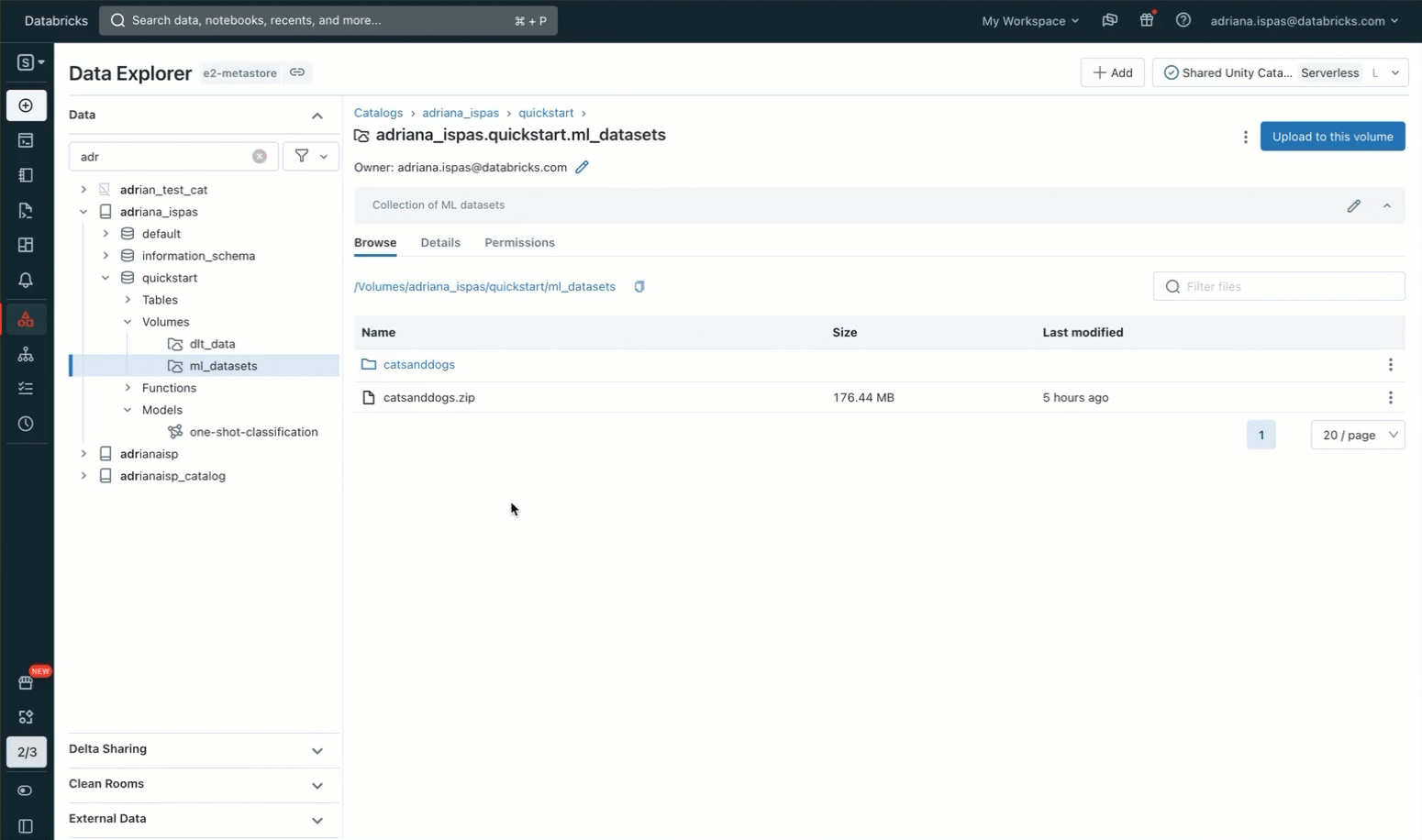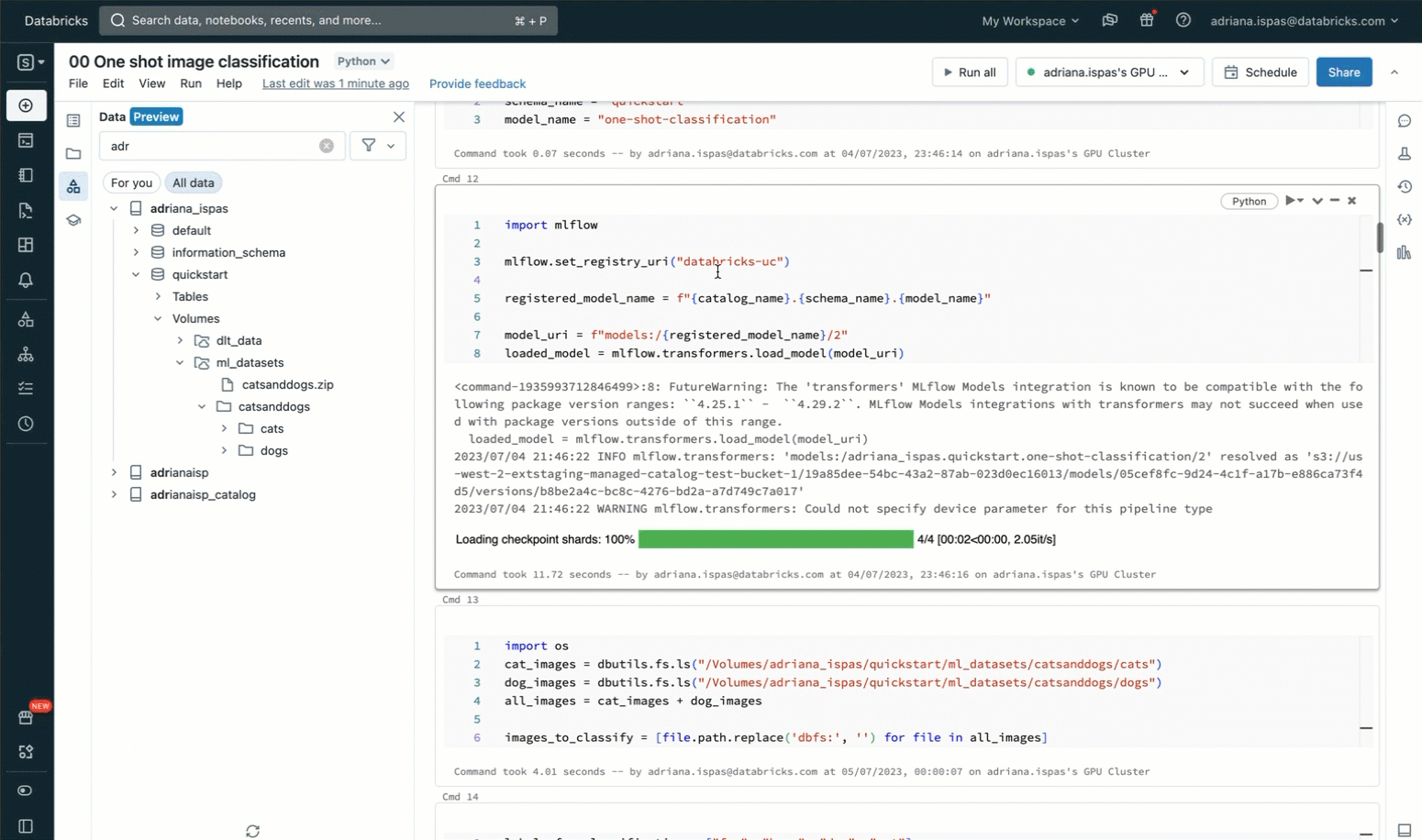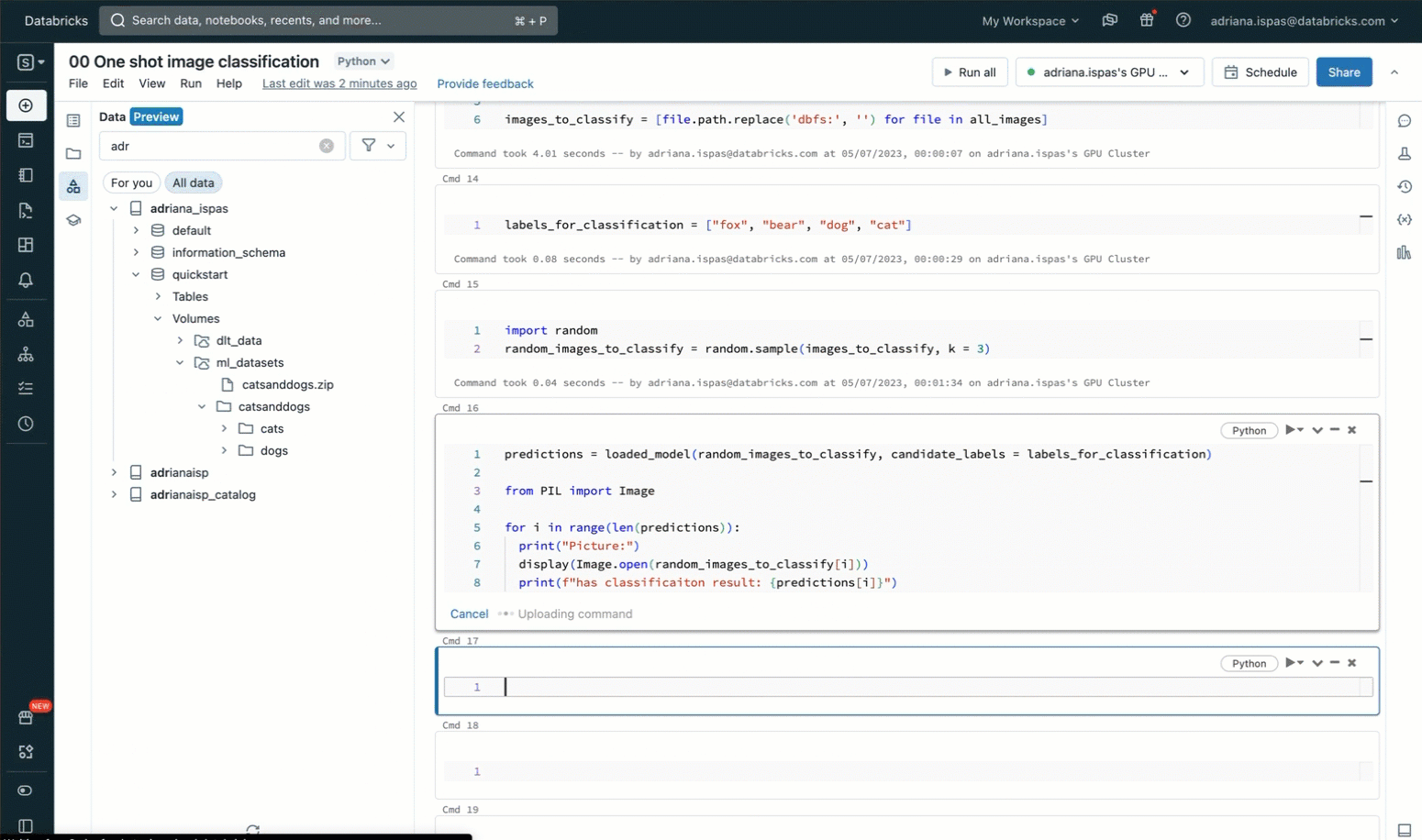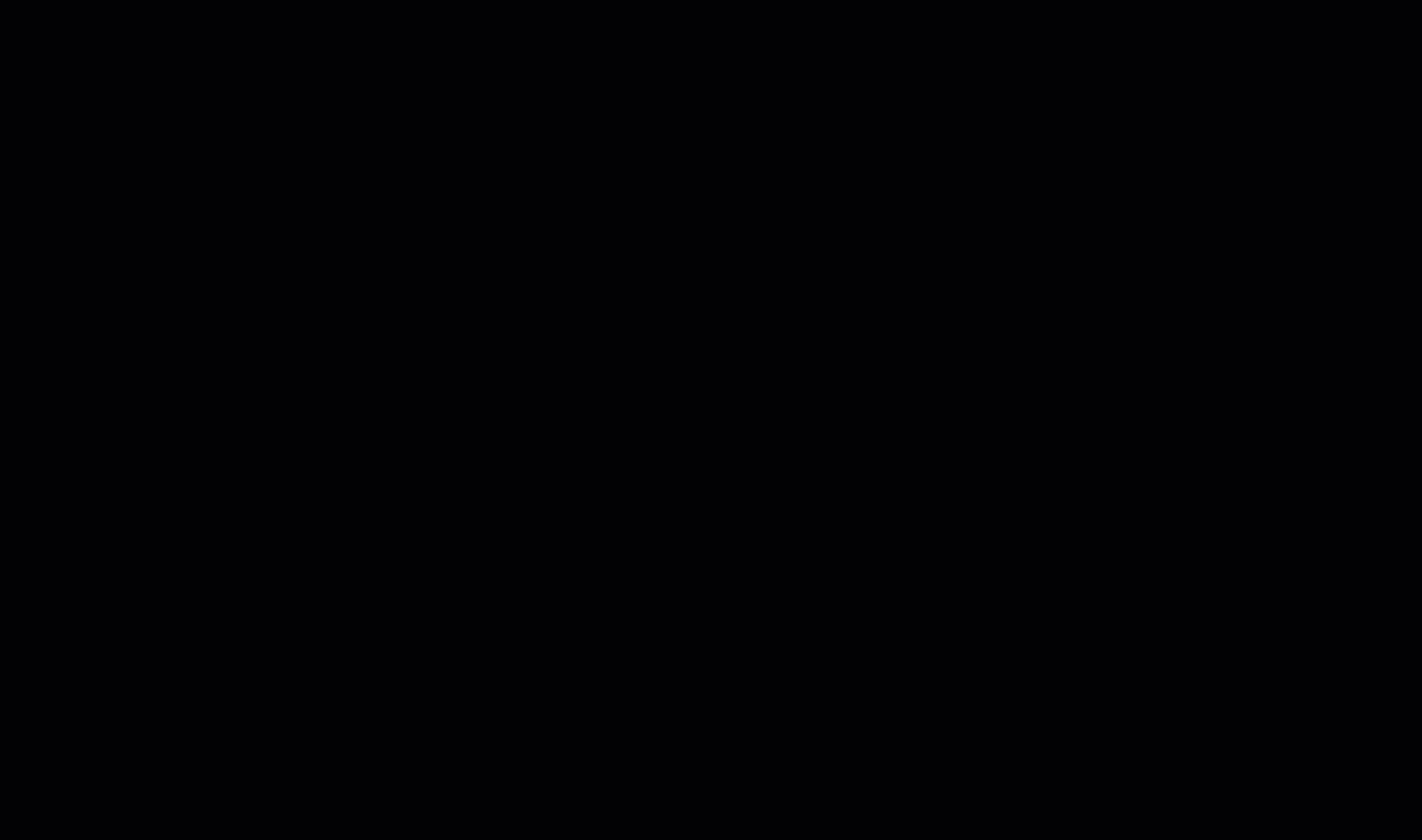
To achieve a greater understanding of Volumes and their sensible purposes, let’s discover an instance. Suppose we need to make the most of machine studying (ML) for picture classification utilizing a dataset consisting of cat and canine photographs. Our first step is to obtain these photographs onto our native machine. Our goal is to include these photographs into Databricks for information science functions.
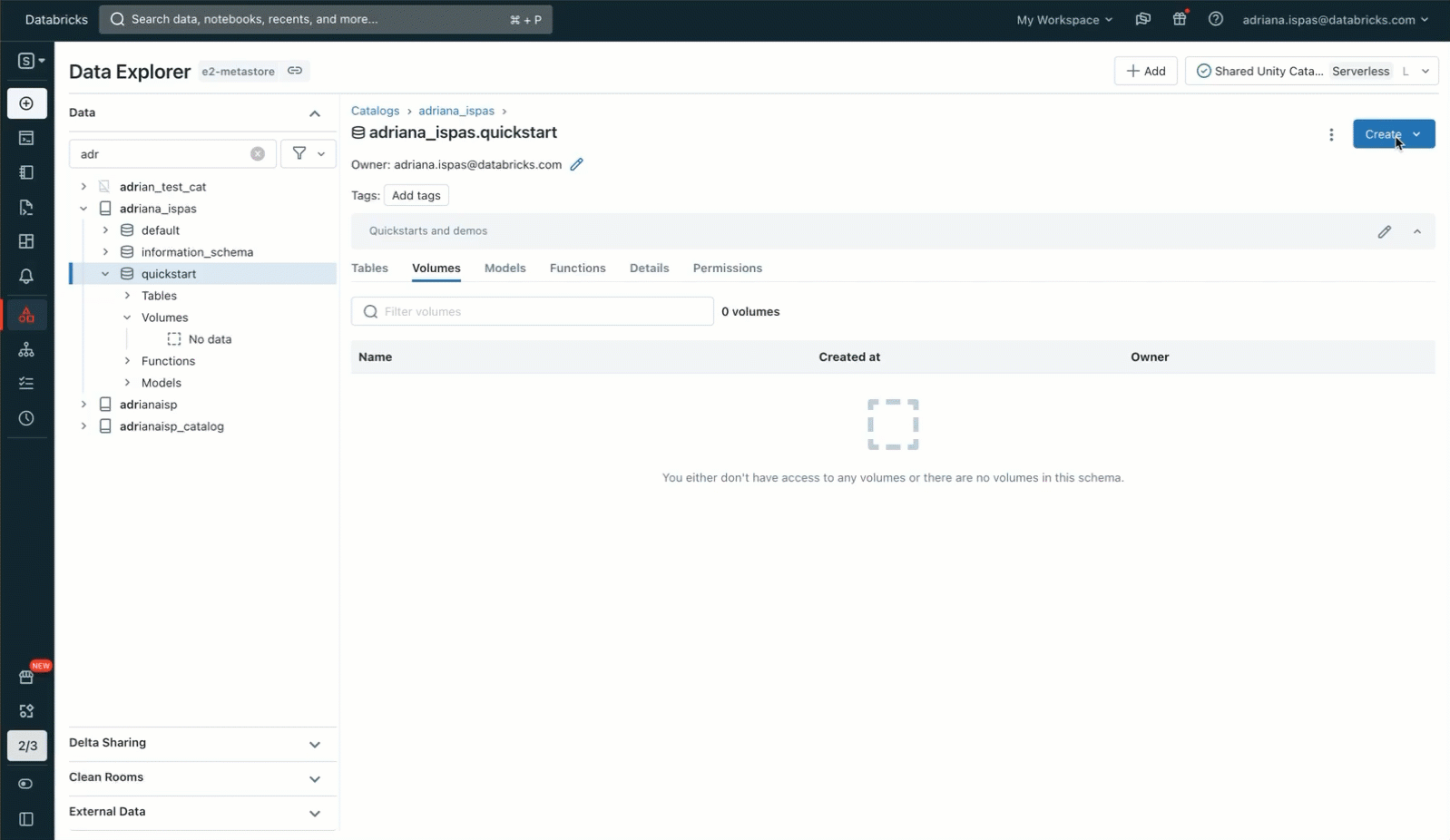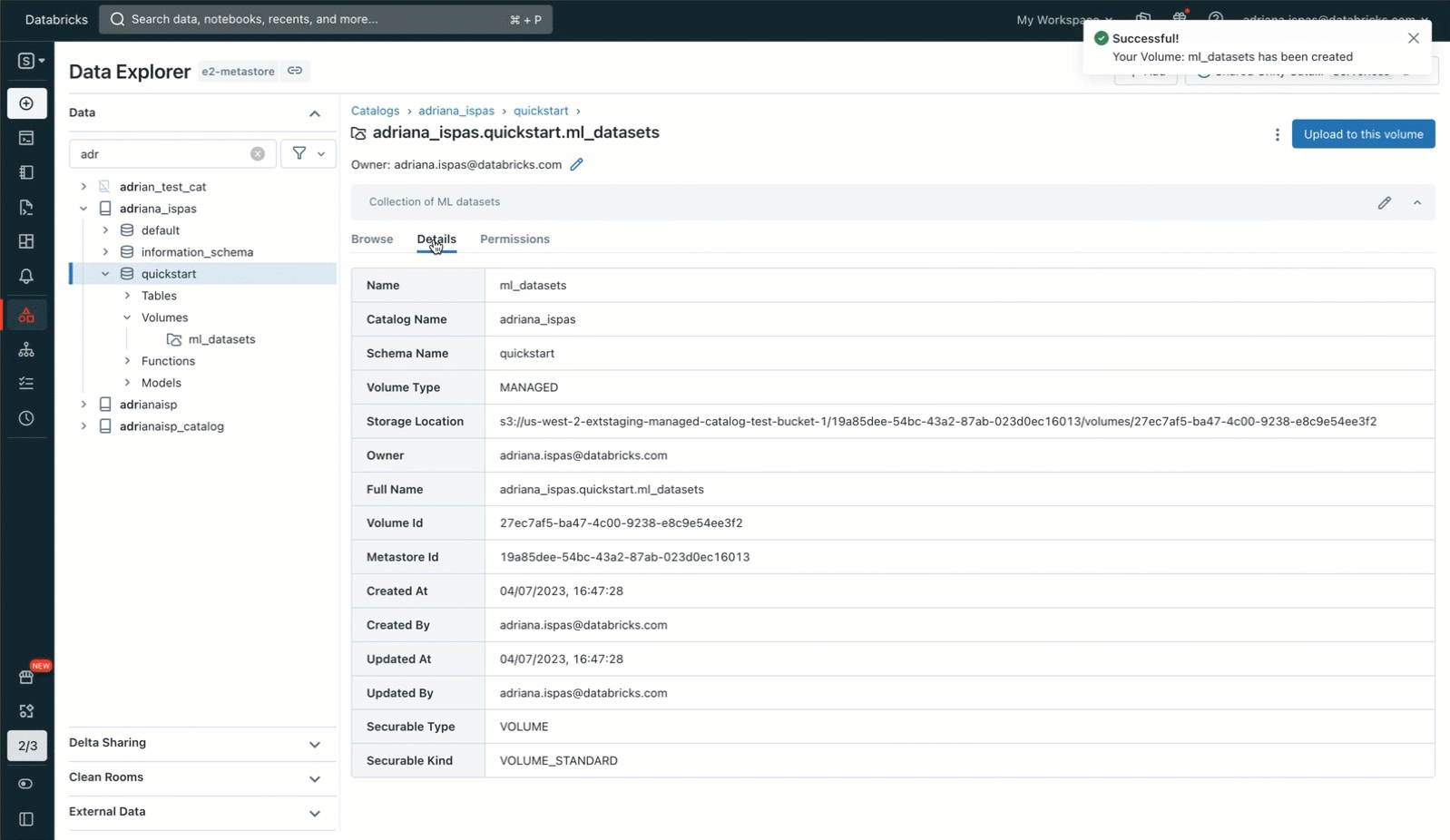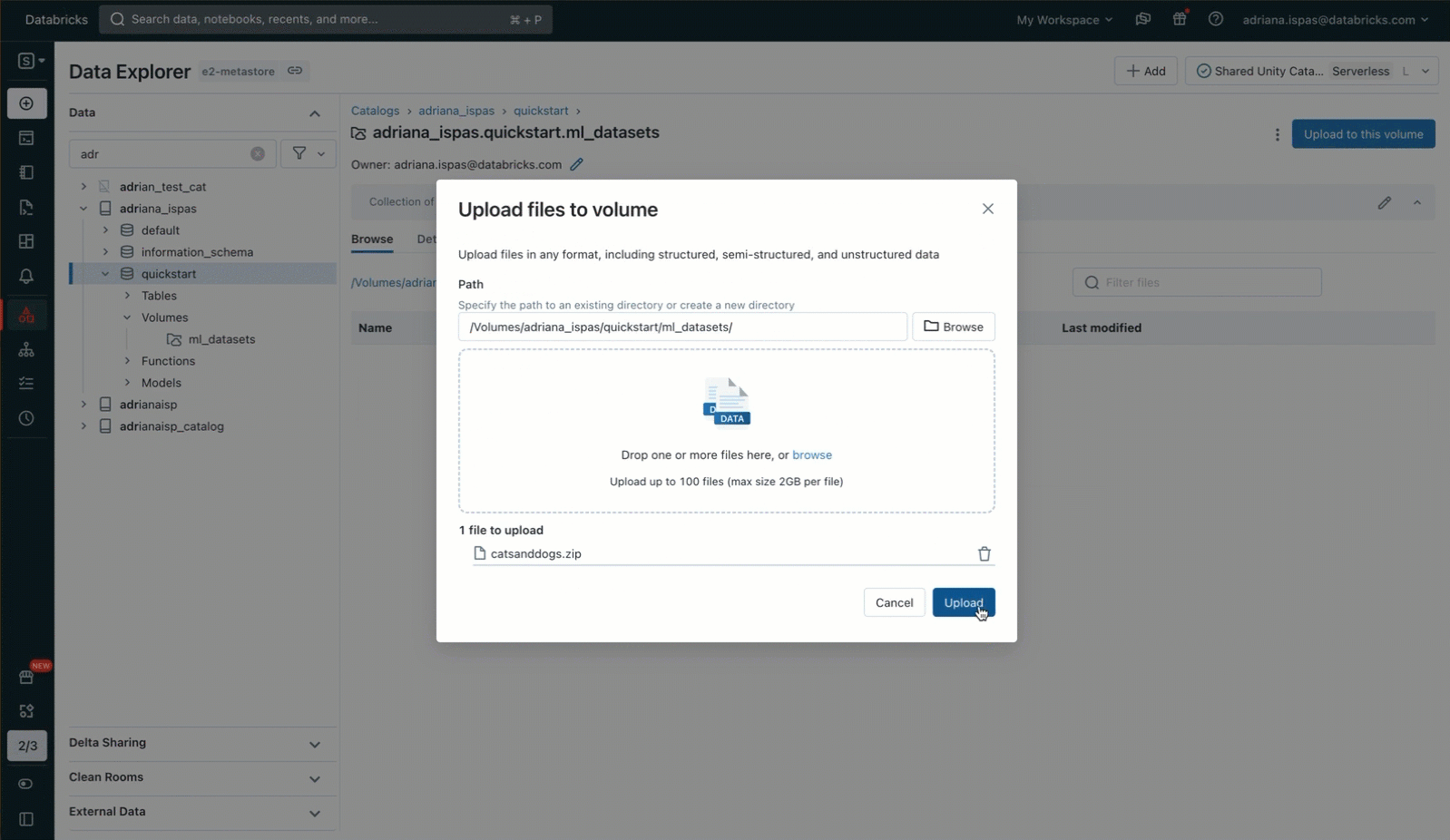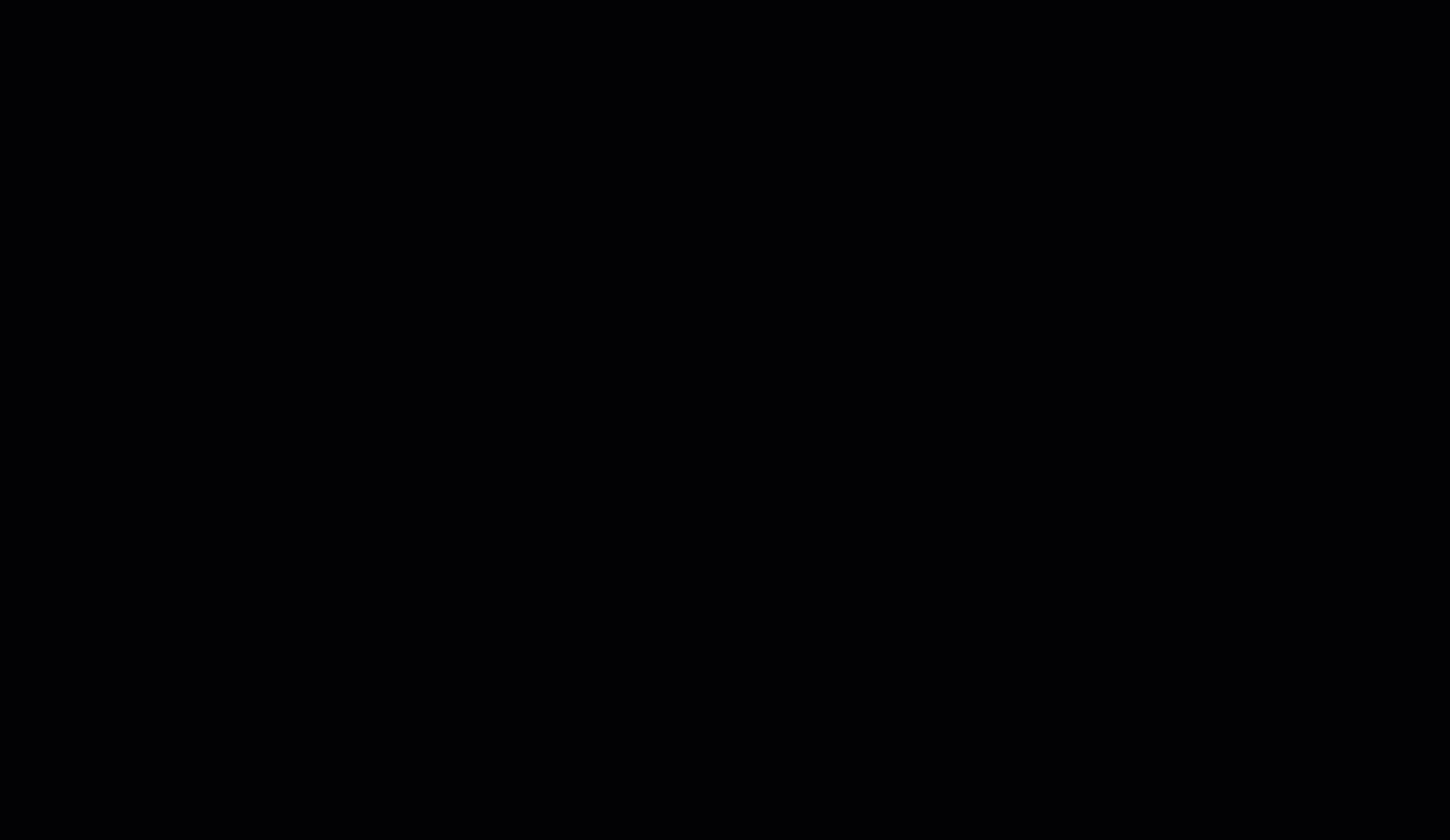
To perform this, we’ll leverage the Knowledge Explorer consumer interface. We’ll create a brand new Quantity inside a Unity Catalog schema, with us being the proprietor. Afterward, we’ll grant entry permissions to our collaborators and add an archive containing the picture recordsdata. It is necessary to notice that we even have the choice to add the recordsdata to an current Quantity the place now we have write permissions. Alternatively, we will create our personal Quantity and handle its permissions utilizing SQL instructions inside a pocket book or the SQL editor.
CREATE VOLUME my_catalog.my_schema.my_volume;
GRANT READ VOLUME, WRITE VOLUME
ON VOLUME my_volume
TO `consumer group`;
Now, we will proceed to extract the picture archive utilizing the generally used unzip utility. It is value noting that the command features a path that particularly pertains to our Quantity. This path corresponds to the Unity Catalog useful resource hierarchy and respects the permissions outlined in Unity Catalog.
%sh unzip /Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/catsanddogs.zip -d
/Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/catsanddogs/To execute this command, we will use a pocket book the place now we have the comfort of accessing the Quantity’s content material by means of the sidebar. Moreover, we will make use of the “Copy path” perform to expedite the method of typing file-related instructions resembling itemizing recordsdata or displaying photographs.
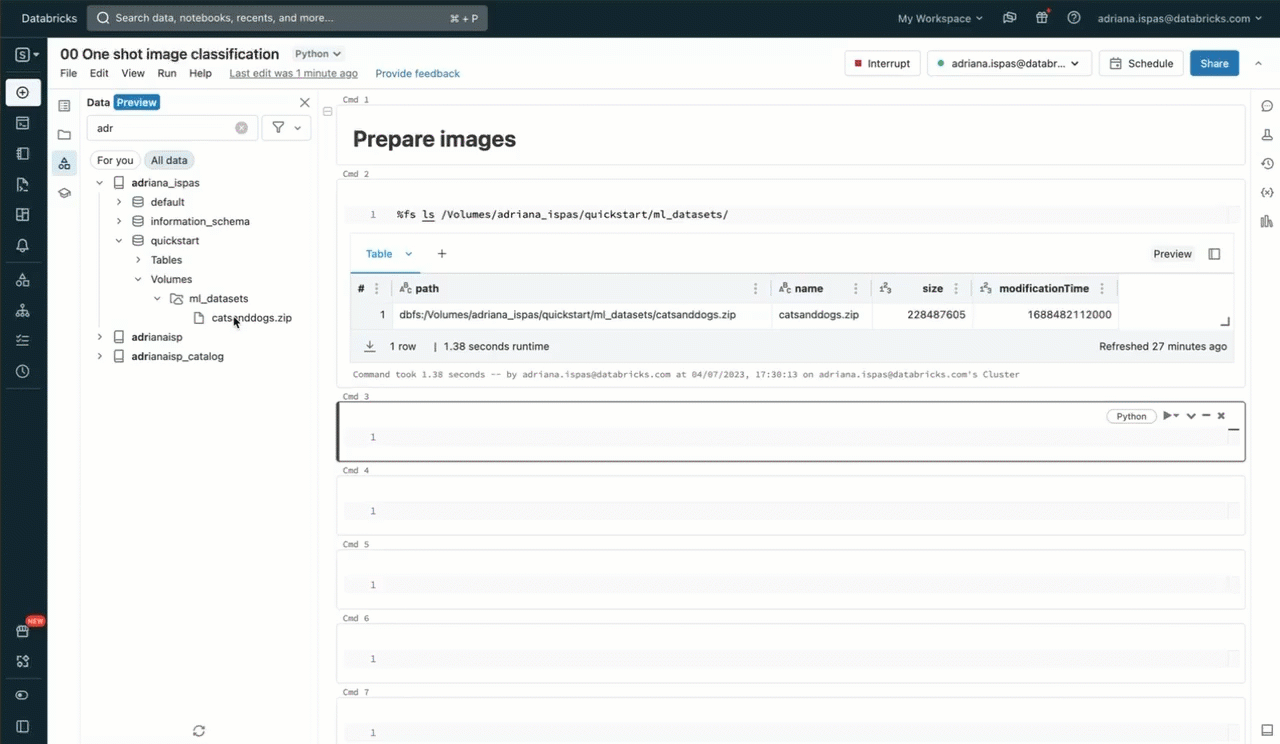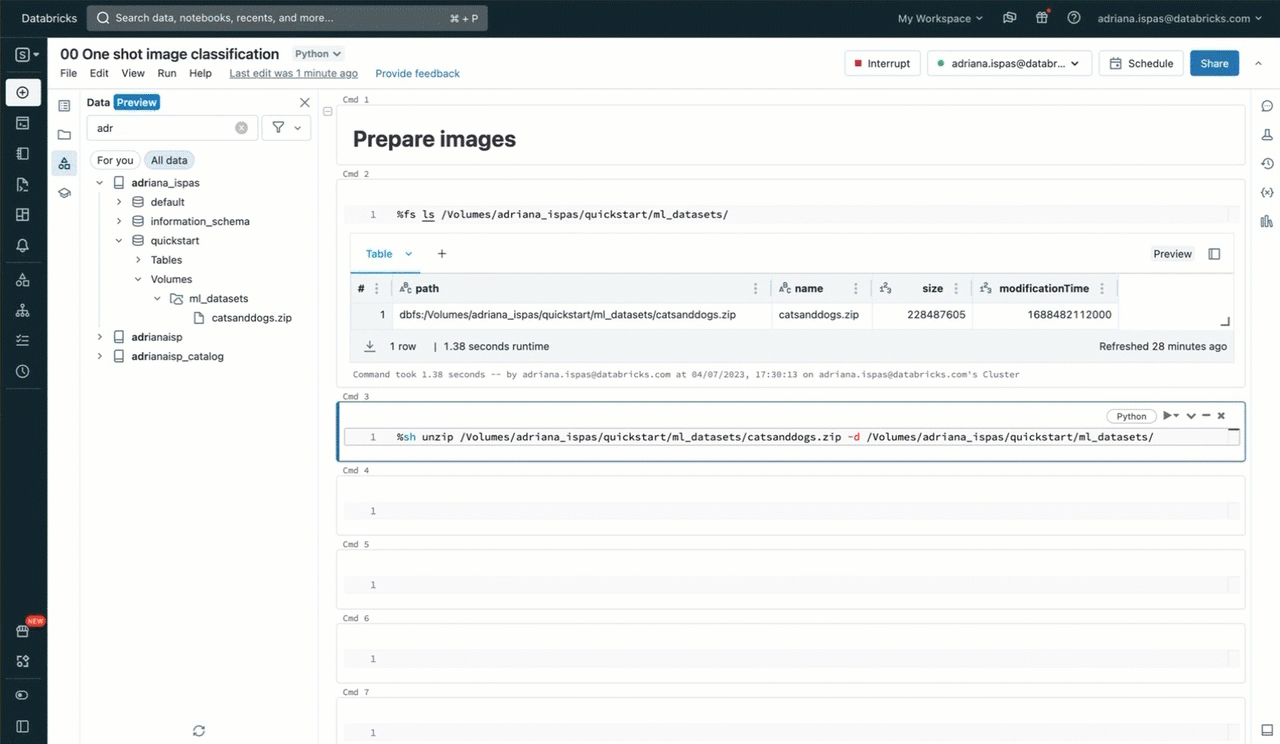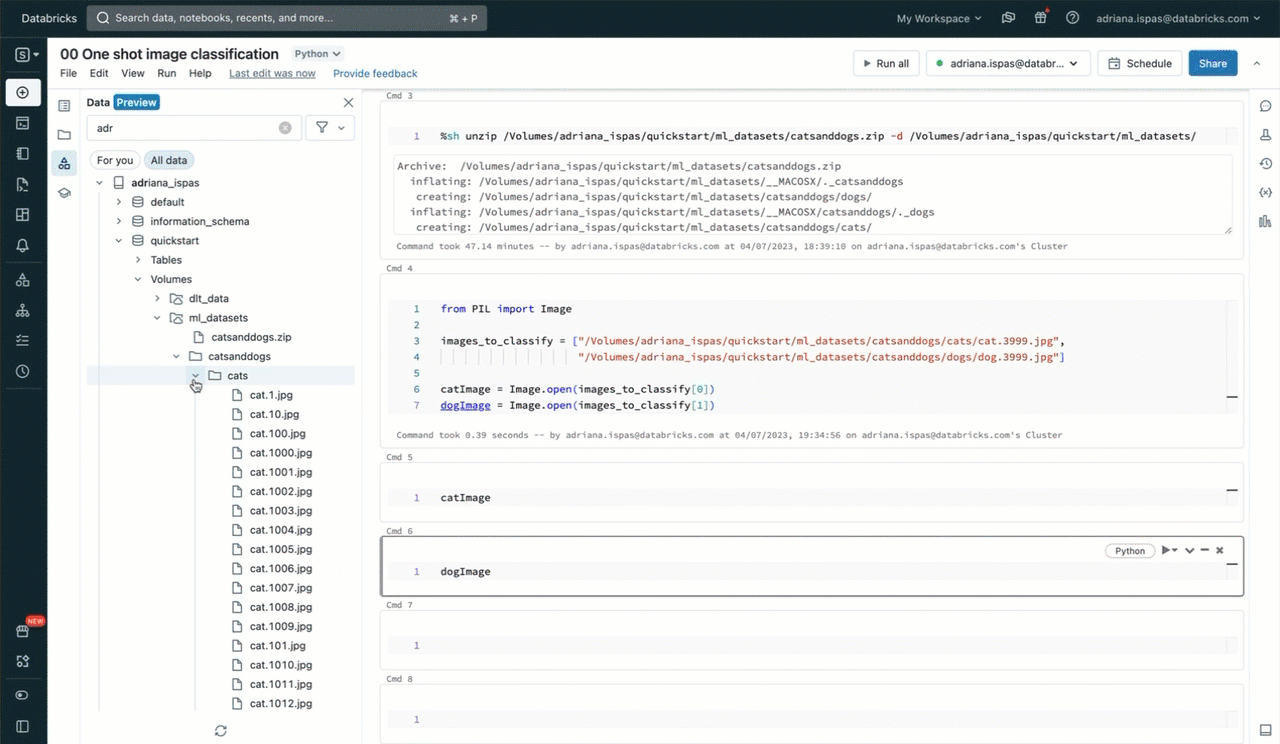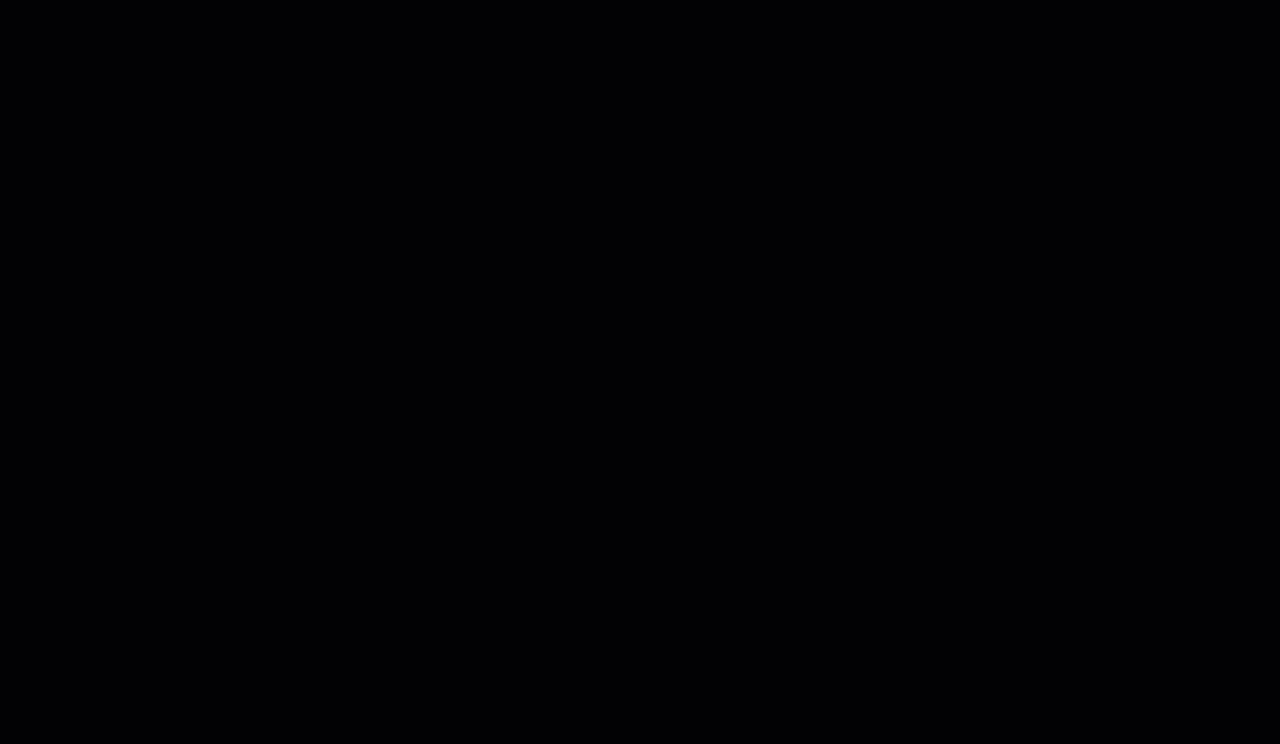
from PIL import Picture
image_to_classify = "/Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/catsanddogs/cat3999.jpg"
picture = Picture.open(image_to_classify)
show(picture)
The screencast beneath demonstrates the complete interplay stream.
So as to classify the photographs utilizing labels from a predefined listing, we make the most of a zero-shot picture classification mannequin that has been registered prematurely to the MLflow Mannequin Registry inside Unity Catalog. The code snippet offered beneath demonstrates the best way to load the mannequin, carry out the classification, and show the ensuing predictions. The accompanying screencast proven beneath offers a visible illustration of those interactions.
classification_labels = ["fox", "bear", "dog", "cat"]
import mlflow
mlflow.set_registry_uri("databricks-uc")
registered_model_name = "my_catalog.my_schema.my_model_name"
model_uri = f"fashions:/{registered_model_name}/1"
loaded_model = mlflow.transformers.load_model(model_uri)
predictions = loaded_model(image_to_classify, candidate_labels = classification_labels)
print(f"Image has classification end result: {predictions[i]}")
Important Quantity Capabilities in Unity Catalog
Govern Non-tabular information with Unity Catalog. Volumes are cataloged inside schemas in Unity Catalog alongside tables, fashions, and features and observe the core rules of the Unity Catalog object mannequin, that means that information is safe by default. Knowledge stewards with adequate privileges can create Volumes, turning into the Quantity’s proprietor and the one principal in a position to entry its content material. They will then grant different customers and teams permission to learn and write the Quantity’s content material. Information saved inside a Quantity may be accessed throughout workspaces, with the choice to limit Quantity entry to particular workspaces by binding their dad or mum catalog to the specified workspaces.
Versatile Storage Configuration with Managed or Exterior Volumes. You will have the choice to configure both managed or exterior Volumes. Managed Volumes retailer recordsdata within the default storage location for the Unity Catalog schema and are a handy answer if you need a ruled location for recordsdata with out the overhead of first configuring entry to Cloud storage, e.g., for fast information explorations ranging from recordsdata uploaded out of your native machine. Exterior Volumes retailer recordsdata in an exterior storage location referenced when creating the Quantity and are useful when recordsdata produced by different methods must be staged for entry from inside Databricks. For instance, you possibly can present direct entry to a Cloud storage location the place giant collections of picture and video information generated by IoT or medical gadgets are deposited.
Course of Knowledge at Cloud Storage Efficiency and Scale. Volumes are backed by Cloud object storage, therefore benefiting from the sturdiness, availability, scalability, and stability of Cloud storage. You need to use Volumes to run high-traffic workloads at Cloud storage efficiency and course of information at scale – petabytes or extra.
Enhance Productiveness with State-of-the-Artwork Consumer Interface: Volumes are seamlessly built-in throughout the Databricks Platform expertise, together with the Knowledge Explorer, notebooks, Lineage, the Add Knowledge, or the cluster library configuration consumer interfaces. You need to use the consumer interface for a variety of actions: handle Quantity permissions and possession; handle a Quantity’s lifecycle by means of actions resembling creating, renaming, or deleting Quantity entities; handle a Quantity’s content material, together with searching, importing, or downloading recordsdata; browse Volumes and their content material alongside notebooks; examine lineage; configure the supply for cluster or job libraries; and plenty of extra.
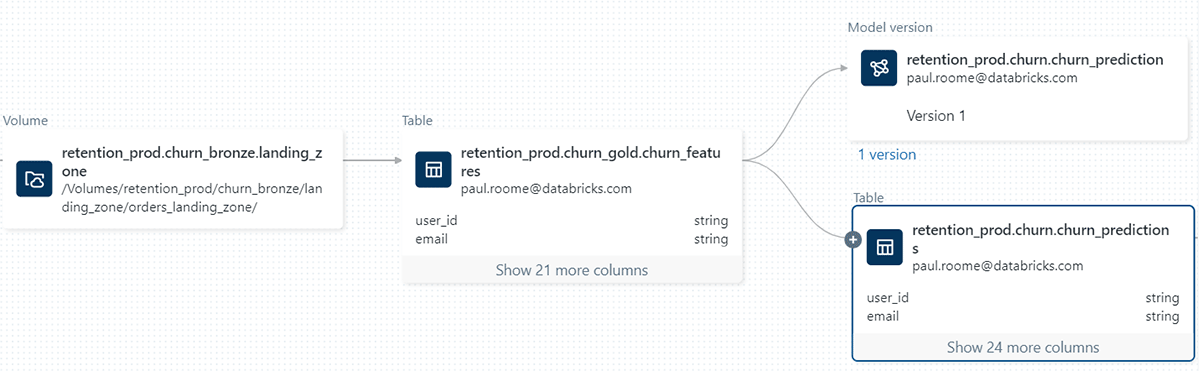
Leverage Acquainted Instruments for Working with Information. Volumes introduce a devoted path format to entry recordsdata that displays the Unity Catalog hierarchy and respects outlined permissions when used throughout Databricks:
/Volumes/<catalog>/<schema>/<quantity>/<path_to_file>You need to use the trail to reference recordsdata inside Apache Spark™ and SQL instructions, REST APIs, Databricks file system utilities (dbutils.fs), the Databricks CLI, Terraform, or when utilizing numerous working system libraries and file utilities. Beneath is a non-exhaustive listing with utilization examples.
| Utilization | Instance |
|---|---|
| Databricks file system utilities | dbutils.fs.ls("/Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/") |
| Apache Spark™ APIs | spark.learn.textual content("/Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/information.txt").present() |
| Apache Spark™ SQL / DBSQL | SELECT * FROM csv.`/Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/information.csv` |
| Pandas | import pandas as pd |
| Shell instructions through %sh | %sh curl http://<tackle>/textual content.zip > /Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/tmp/textual content.zip |
| Library installs utilizing %pip | %pip set up /Volumes/my_catalog/my_schema/my_volume/my_library.whl |
| Working system file utilities | import os |
Unlock New Processing Capabilities for Knowledge Managed by Unity Catalog. Volumes present an abstraction over Cloud-specific APIs and Hadoop connectors, resembling s3a://, abfss://, or gs://, which makes it simpler to work with Cloud-stored information recordsdata in Apache Spark™ Spark purposes, in addition to instruments that do not natively help object storage APIs. Utilizing the devoted Quantity file paths, you possibly can entry, traverse and course of a Quantity’s content material as if recordsdata have been native to the cluster nodes whereas file operations map to underlying Cloud storage operations. That is significantly helpful for working with numerous information science and ML libraries, resembling Pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow keras, and plenty of extra.
Getting began with Volumes in Unity Catalog
Unity Catalog Volumes are actually obtainable within the Databricks Enterprise and Professional tiers, ranging from Databricks Runtime 13.2 and above. That will help you get began with Volumes, now we have ready a complete step-by-step information. If you have already got a Databricks account, you possibly can observe our documentation, which offers detailed directions on creating your first Quantity (AWS | Azure | GCP). As soon as you have created a Quantity, you possibly can leverage the Knowledge Explorer (AWS | Azure | GCP) to discover its contents or be taught the SQL syntax for Quantity administration (AWS | Azure | GCP). We additionally encourage you to evaluate our greatest practices (AWS | Azure | GCP) to take advantage of out of your Volumes. When you’re new to Databricks and do not have an account but, you possibly can join a free trial to expertise the advantages of Volumes in Unity Catalog firsthand.
Keep tuned for an array of thrilling Volumes options, together with the power to share Volumes utilizing Delta Sharing and a REST API for file administration operations like importing, downloading, and deleting recordsdata.
You may also watch the Knowledge and AI Summit Periods on What’s new with Unity Catalog, deep dive session for greatest implementation practices and Every little thing You Must Know to Handle LLMs.

