Researchers on the McKelvey College of Engineering at Washington College in St. Louis have pioneered a brand new method that may allow higher-resolution imaging of very small objects like neurons. The method, which improves on an current methodology known as enlargement microscopy, is described in a brand new paper revealed within the journal Nano Letters.
Most individuals are conversant in microscopes that use lenses to make an object seem bigger and simpler to see with the human eye. However enlargement microscopy (ExM) works in virtually the alternative method—by making the item itself bigger. Scientists coat the pattern—a cell, for instance—with tiny light-emitting markers known as fluorophores, then embed the pattern inside a gel that expands when it comes into contact with water. Because the pattern grows bigger, the fluorescent labels hint the outlines of options too small to see, like the skinny branches, or dendrites, that develop from mind cells.
However enlargement microscopy has a serious shortcoming. The sunshine sign emitted by standard fluorophores loses a lot of its depth (greater than 50%) in the course of the preparation and enlargement steps.
“While you make issues larger, it is not essentially good, as a result of if you happen to do not change the quantity of sign that’s already current, that sign will get weaker,” stated Barani Raman, professor of biomedical engineering.
Raman and Srikanth Singamaneni, the Lilyan & E. Lisle Hughes Professor within the Division of Mechanical Engineering & Supplies Science, have addressed this problem through the use of ultrabright fluorescent markers known as plasmonic-fluors (PFs). Singamaneni developed the PFs for different purposes in 2020.
“It is a good instance of two folks with fully completely different experience having an opportunity dialog and saying “Okay, this drawback is right here in a single subject, however the resolution is there in one other subject,'” Raman stated. The crew has dubbed its new method “plasmon-enhanced enlargement microscopy,” or p-ExM.
The plasmonic-fluor is constructed from a core particle of gold wrapped in a silver shell, which is then coated with a layer of different supplies, together with standard fluorophores. The construction is designed to guard the fluorophores from the tough chemical compounds used within the course of and to make the sunshine sign from the fluorophores a lot brighter. The method will help researchers in mapping neural networks, or the connections between neurons.
“The metallic nanoparticle serves as an antenna, which signifies that it is ready to pull extra gentle into the fluorophores,” Singamaneni stated. The interplay between the gold-silver nanoparticle and the fluorophores additionally causes the fluorophores to emit extra photons than they usually would. Because of this, the plasmonic-fluor is sort of 4 orders of magnitude brighter than the fluorescent markers could be on their very own. Plasmonic fluors additionally resolve the issue of sign dilution as a result of the fluorescent markers are connected on to the nanoparticle, so they do not unfold aside when the pattern expands.
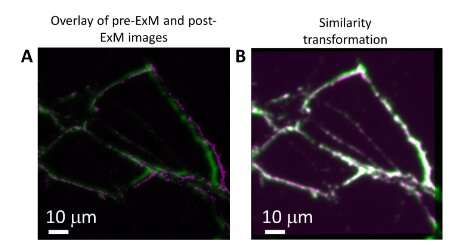
To display the potential of plasmon-enhanced enlargement microscopy, the researchers used it to check a pattern of neurons from the hippocampus area of the mind. In some instances, the neuron’s budding branches, known as neurites, are too shut to one another to make out with out the assistance of strategies like enlargement microscopy.
“When two neurites are too shut to one another, we can not resolve them. The software program thinks that they’re only one neurite,” Singamaneni stated.
After labeling the cells with the ultrabright plasmonic-fluors and increasing the pattern, the crew was capable of depend the variety of neurites, quantify the full space of the neurites and measure the size of particular person neurites. They recognized 2.5 instances extra neurite terminal factors than had been seen earlier than the pattern was expanded.
When the crew in contrast the plasmonic-fluor’s efficiency to the fluorophores by themselves, they discovered that the plasmonic-fluor retained about 76% of the sunshine sign whereas the fluorophores retained lower than 16%. The crew’s outcomes additionally confirmed that plasmon-enhanced enlargement microscopy is appropriate with current enlargement microscopy protocols, which implies plasmonic fluors can be utilized instead of standard fluorophores in future research. PFs will also be created from any given fluorophore that fits researchers’ wants.
Extra info:
Priya Rathi et al, Plasmon-Enhanced Growth Microscopy, Nano Letters (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.3c01256
Supplied by
Washington College in St. Louis
Quotation:
Brighter fluorescent markers permit for finer imaging (2023, July 20)
retrieved 20 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-brighter-fluorescent-markers-finer-imaging.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

