| Aug 23, 2023 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk Information) The powers of synthetic intelligence (AI) and robotic experiment techniques have come collectively in pioneering proof-of-concept work on the Nationwide Institute for Supplies Science (NIMS) in Japan.
|
|
The researchers describe the event and demonstration of their “closed loop” automation software program within the journal Science and Expertise of Superior Supplies: Strategies (“NIMS-OS: an automation software program to implement a closed loop between synthetic intelligence and robotic experiments in supplies science”).
|
|
“The general goal of our work is to permit experiments exploring supplies science to be designed after which proceed routinely, with no human intervention,” says physicist and software program engineer Ryo Tamura on the NIMS Heart for Fundamental Analysis on Supplies. The AI first performs the knowledge gathering and experimental design duties usually performed by people, after which controls the robotic techniques that may execute the required bodily duties.
|
|
The staff demonstrated the potential of their system through the use of it to establish electrolytes that might be appropriate for mediating the motion of ions in lithium-metal batteries.
|
|
The software program, known as the NIMS Orchestration System (NIMS-OS), comprises two fundamental sorts of modules. The primary makes use of AI algorithms to discover archived information on the properties of supplies. It selects promising supplies and proposes experimental procedures that might enable them to realize a desired goal. The second kind of module generates the directions wanted to manage a robotic system that can put the directions into observe.
|
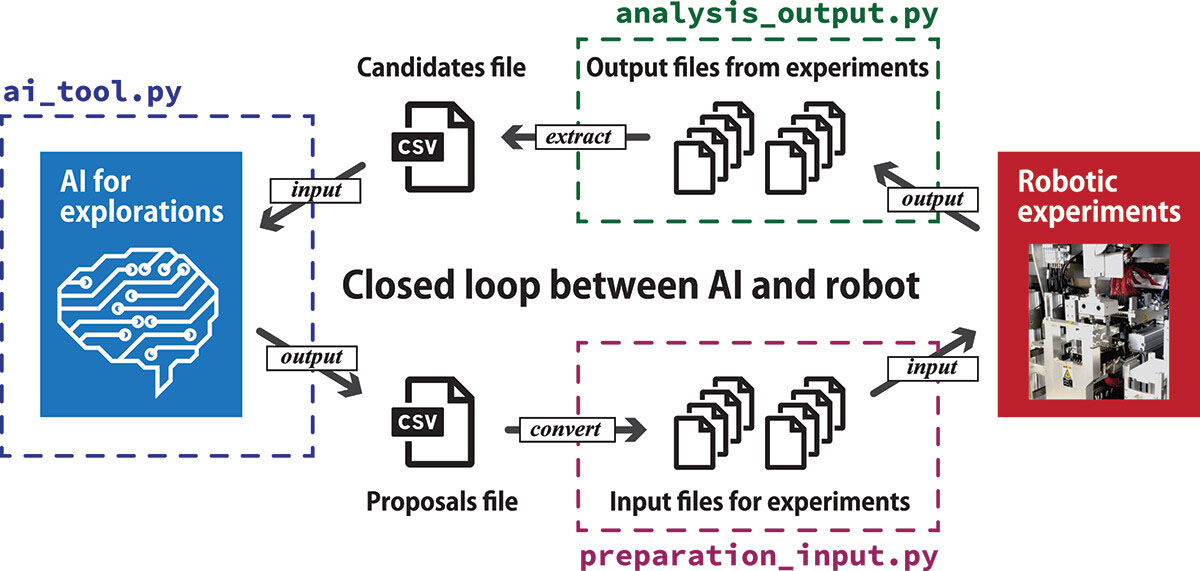 |
| Procedures in NIMS-OS and roles of every Python scripts. (Picture: NIMS)
|
|
To make the entire course of as simple to make use of as doable for a variety of researchers the staff additionally designed an easy-to-use graphical person interface to manage it.
|
|
“The outcomes of preliminary work by the robotic system through NIMS-OS might be fed again to refine the AI algorithms that management it, by a number of cycles of check and enchancment,” says Tamura.
|
|
Within the proof-of-concept job that explored choices for making electrolytes that maximize the efficiency of an electrode in a lithium-metal battery, NIMS-OS utilized techniques that had been robotically assembled into electrochemical cells and subjected to charging and discharging cycles to research their efficiency. The outcomes clearly recognized the higher electrolyte composition and indicated there’s room for enchancment on the electrolytes which are at the moment broadly used commercially.
|
|
“Our NIMS-OS is now publicly obtainable as open-source software program on the broadly used GitHub web site,” says Tamura. “We now plan to develop it additional to permit it to work along with many various kinds of robotic experiment techniques.”
|

