In the event you’re new to Arduino and connecting Arduino to the web, the method might sound difficult at first. Many rookies face challenges in terms of web connectivity whereas coding with Arduino. And not using a user-friendly interface and built-in debugging instruments, it may be tough to determine and rectify errors. On this article, we are going to present a complete information on connecting your Arduino board to the web, together with the required code.
After I first started taking part in round with my Arduino Uno, I used to be very pleased with making LEDs blink and sensors beep. However I quickly realized that the true potential of an Arduino can solely be achieved when you join it to the web.
You possibly can examine the progressive Arduino Tasks.
Just about any intermediate to superior stage Arduino challenge would require you to hook up with the web for varied causes, be it logging information on the cloud equivalent to climate information, or passing on real-time instructions to your machine remotely equivalent to by way of an app in your telephone.
On this tutorial, we’re going to have a look at find out how to join your Arduino machine to the web comprehensively. Every little thing—from the {hardware} to the circuit and code—shall be lined.
Connecting Arduino to the Web with Ethernet
The primary possibility for connecting your Arduino to the web is by way of an Ethernet cable. In case you are utilizing an Arduino board that comes with a built-in Ethernet port equivalent to an Arduino Yún, you may skip the ‘{Hardware} necessities’ part and the circuit design description given beneath. Simply join the Ethernet cable to your machine and begin coding.
Nevertheless, if, like most individuals, you personal an easier model of Arduino equivalent to Arduino Uno that doesn’t have a built-in Ethernet port, you’ll have to purchase a separate machine, known as an Ethernet protect, to connect to your Arduino.
{Hardware} Necessities
You’ll require an Ethernet cable with the web, an Arduino Uno board, and an
Ethernet Protect. Right here’s find out how to join them:
- Join the Ethernet protect on high of the Arduino Uno.
- Join the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet protect.

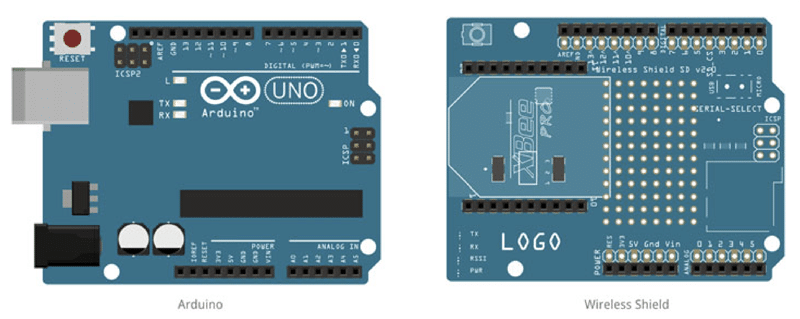
Fig. 1 reveals Arduino Uno and its Ethernet protect. After connecting the 2, your Arduino Uno ought to appear like the one in Fig. 2.
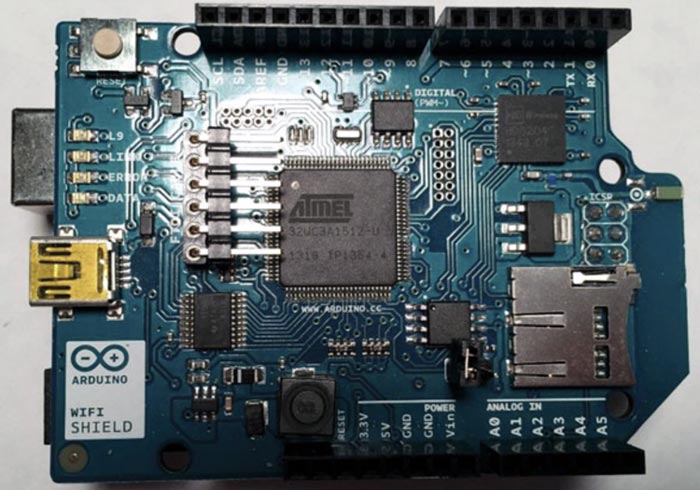

Arduino Code for Connecting to the Web by way of Ethernet
Earlier than getting began with the code for connecting Arduino to the web, we have to embrace an exterior library to be used in this system. This library will assist us set up a connection and ship/obtain information over the web.
Word: This library ought to come preinstalled along with your IDE. If for some purpose you run into errors, please obtain this library from the official GitHub repository of the Arduino Undertaking.
#embrace <Ethernet.h>Within the subsequent step, we shall be defining some constants and variables required for this program.
First, we’d like the MAC deal with. That is usually printed on a sticker on the Ethernet protect. Subsequent, we have to outline a static IP deal with.
Ensure that the IP deal with that you’re including isn’t being utilized by another person. Lastly, we will outline the EthernetClient variable.
byte mac[] = { oxDE, oxAD, oxBE, oxEF,
oxFE, oxED };
IPAddress staticIP(10, 0, 0, 20);
EthernetClient consumer;We are able to now write the tactic for connecting to the web. There are two steps right here. First, we attempt to get an IP by way of the DHCP (dynamic host configuration protocol), i.e., attempt to fetch your dynamic IP. If that step fails, then we fall again to the static IP that we have now outlined above.
void connectToInternet()
{
// Step 1 - Strive connecting
with DHCP
If (Ethernet.start(mac) == 0)
{
Serial.print(“[ERROR]
Failed to attach by way of DHCP”);
Ethernet.start(mac,
staticIP); // Join by way of static IP
outlined earlier
}
// Add a delay for initialization
delay(1000);
Serial.println(“[INFO] Connection
Profitable”);
Serial.print(“”);
printConnectionInformation(); // Customized
technique
Serial.print
ln(“---------------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
}As you may see within the code above, we used a customized technique printConnectionInformation() for displaying the connection data. So allow us to go forward and write the code for that.
void printConnectionInformation()
{
// Print IP Deal with
Serial.print(“[INFO] IP Deal with: ”);
Serial.println(Ethernet.localIP());
// Print Subnet Masks
Serial.print(“[INFO] Subnet Masks: ”);
Serial.println(Ethernet.
subnetMask());
// Print Gateway
Serial.print(“[INFO] Gateway: ”);
Serial.println(Ethernet.gatewayIP());
// Print DNS
Serial.print(“[INFO] DNS: ”);
Serial.println(Ethernet.
dnsServerIP());
}Lastly, we will write the usual capabilities for this system, i.e. setup() and loop().
void setup()
{
Serial.start(9600);
// Connect with the web
connectToInternet();
}
void loop()
{
// Nothing a lot to do right here.
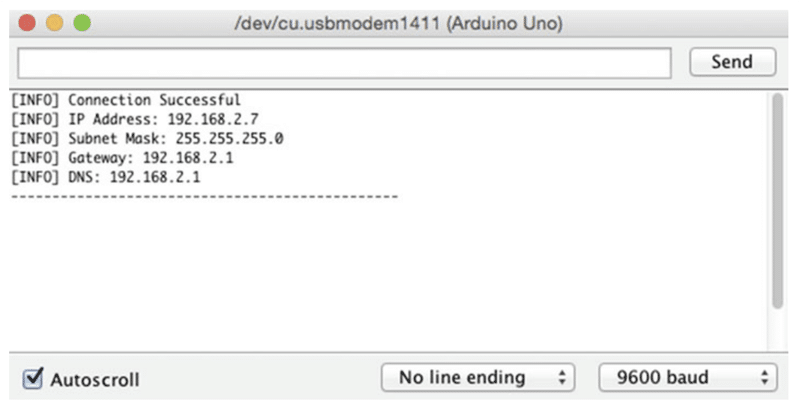
}If all the things checks out, you have to be seeing an output much like Fig. 3 on the serial monitor window.
Connecting Arduino to the Web by way of Wi-Fi
The second possibility is to attach your Arduino to the web wirelessly by way of Wi-Fi. If, like most individuals, you personal an Arduino Uno or another Arduino board that doesn’t have a built-in Wi-Fi functionality, you’ll have to purchase a wi-fi protect individually, just like the Ethernet protect.
In the event you personal an Arduino Yún or another Arduino board with built-in wi-fi functionality, you may skip the ‘{Hardware} necessities’ and the outline on the following web page and get began with the code straight away.
{Hardware} Necessities
You will want an Arduino Uno and a wi-fi protect. Right here’s find out how to join them:
- Join the wi-fi protect on high of the Arduino Uno.
- Join the Arduino Uno to your laptop by way of the USB port.
Fig. 4 reveals the Arduino Uno and the wi-fi protect. If all the things is linked correctly, your Arduino Uno board ought to appear like the one in Fig. 5.
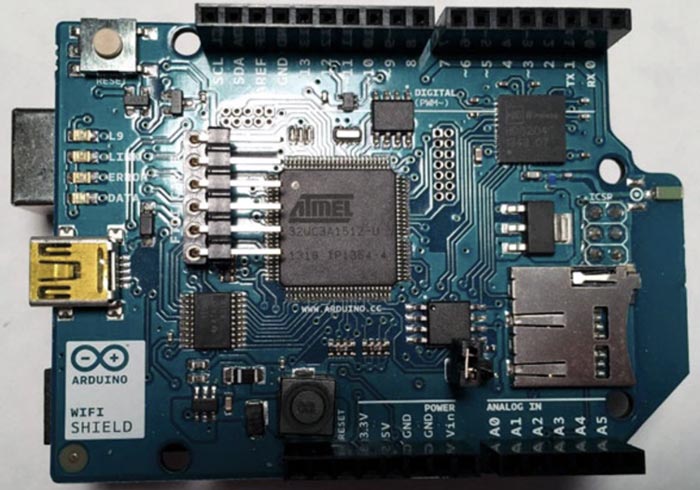

Arduino Code for Connecting to the Web by way of Wi-Fi
When connecting to the web by way of Ethernet, we used the exterior library. Equally, for connecting to the web wirelessly, we will be utilizing the exterior library.
Word: This library ought to come preinstalled along with your IDE. If for some purpose you run into errors, please obtain this library from the official GitHub repository of the Arduino Undertaking.
#embrace <SPI.h>
#embrace <WiFi.h>Subsequent, we will outline the constants and variables required for connecting wirelessly. For connecting with the Wi-Fi, we require the ssid and password of the Wi-Fi that we will be utilizing. We will additionally create a WiFiClient variable for connecting to the web.
char ssid[] = “Write WiFi SSID right here”;
char go[] = “Write WiFi password
right here”;
int keyIndex - 0;
int standing = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
WiFiClient consumer;Now we will outline some customized strategies for connecting and sending/receiving information over the Web. First, allow us to create the tactic connectToInternet() for connecting with the Web.
void connectToInternet()
{
standing = WiFi.standing();
if (standing == WL_NO_SHIELD)
{
Serial.println(“[ERROR] WiFi Protect
Not Current”);
whereas (true);
}
whereas ( standing != WL_CONNECTED)
{
Serial.print(“[INFO] Making an attempt
Connection - WPA SSID: ”);
Serial.println(ssid);
standing = WiFi.start(ssid, go);
}
Serial.print(“[INFO] Connection
Profitable”);
Serial.print(“”);
printConnectionInformation();
Serial.print
ln(“-------------------------”);
Serial.println(“”);
}As you may see within the code above, we have now known as the customized technique printConnectionInformation() to show the details about our Wi-Fi connection. So allow us to go forward and write that technique:
void printConnectionInformation()
{
Serial.print(“[INFO] SSID: ”);
Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
// Print Router’s MAC deal with
byte bssid[6];
WiFi.BSSID(bssid);
Serial.print(“[INFO] BSSID: ”);
Serial.print(bssid[5], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(bssid[4], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(bssid[3], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(bssid[2], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(bssid[1], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.println(bssid[0], HEX);
// Print Sign Power
lengthy rssi = WiFi.RSSI();
Serial.print(“[INFO] Sign Power
(RSSI) : ”);
Serial.println(rssi);
// Print Encryption kind
byte encryption = WiFi.encryption
Kind();
Serial.print(“[INFO] Encryption Kind
: ”);
Serial.println(encryption, HEX);
// Print WiFi Protect’s IP deal with
IPAddress ip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print(“[INFO] IP Deal with : ”);
Serial.println(ip);
// Print MAC deal with
byte mac[6];
WiFi.macAddress(mac);
Serial.print(“[INFO] MAC Deal with: ”);
Serial.print(mac[5], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(mac[4], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(mac[3], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(mac[2], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.print(mac[1], HEX);
Serial.print(“:”);
Serial.println(mac[0], HEX);
}Lastly, allow us to write down the usual capabilities, i.e. setup() and loop():
void setup()
{
Serial.start(9600);
// Connect with the web
connectToInternet();
}
void loop()
{
// Nothing to do right here
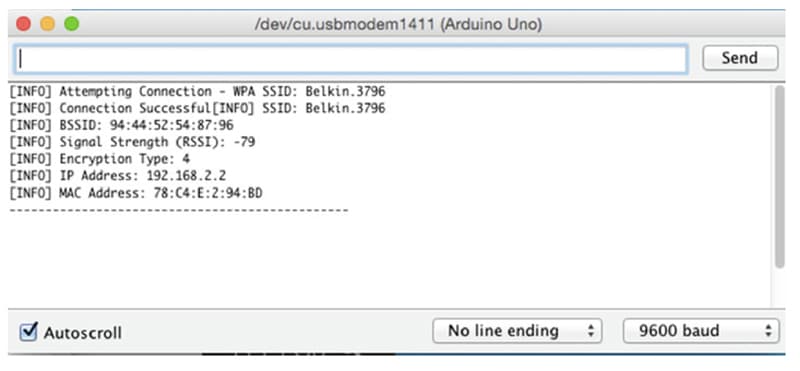
}Hurray! We’re finished with the Arduino code for connecting to the web by way of Wi-Fi. In case there aren’t any errors, the output in your serial monitor window ought to appear like the output in Fig. 6.
This text was first revealed within the December 2022 subject of Open Supply For You journal.
Mir H.S. Quadri is a analysis analyst with a specialization in synthetic intelligence and machine studying. He’s the founding father of Arkinfo, which focuses on the analysis and improvement of tech merchandise utilizing new-age applied sciences. He shares a deep love for evaluation of technological tendencies and understanding their implications. Being a FOSS fanatic, he has contributed to a number of open-source initiatives

