Whether or not you’re making a social media app or a productiveness software, the tab bar interface can improve the person expertise by making it extra intuitive and user-friendly. With SwiftUI’s TabView, making a seamless and customizable tab interface has by no means been simpler.
By default, iOS shows the tab bar in its commonplace kind, permitting customers to shortly change between totally different app capabilities with ease. Nevertheless, as a developer, you in all probability need to customise the tab bar to suit the particular wants of your app.
On this tutorial, you’ll discover ways to create a scrollable and animated tab bar which helps infinite tab gadgets utilizing SwiftUI. Check out the top outcome under to get a glimpse of what you’ll be capable of obtain by the top of the tutorial.
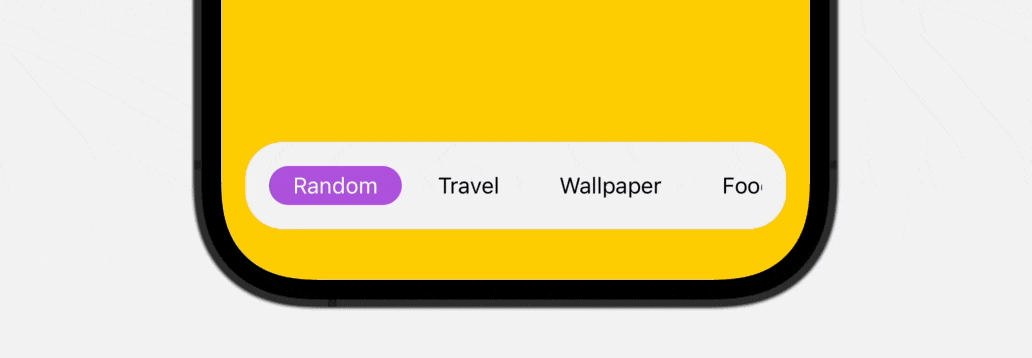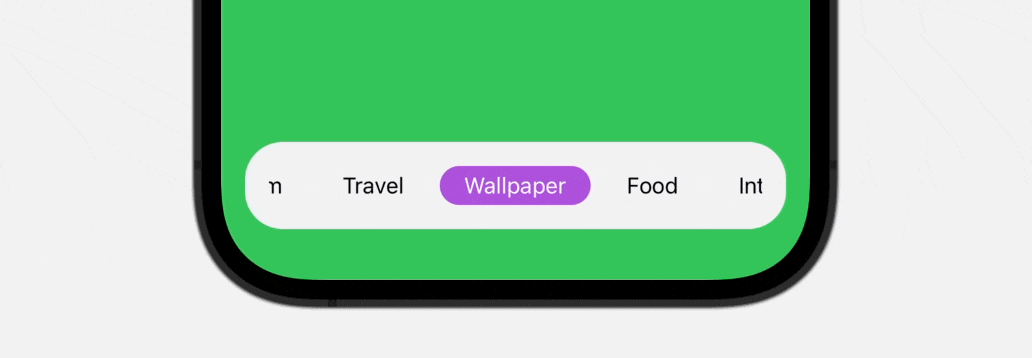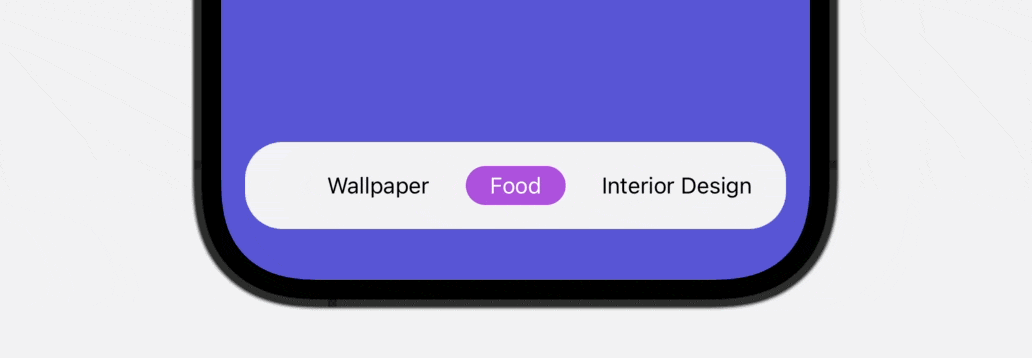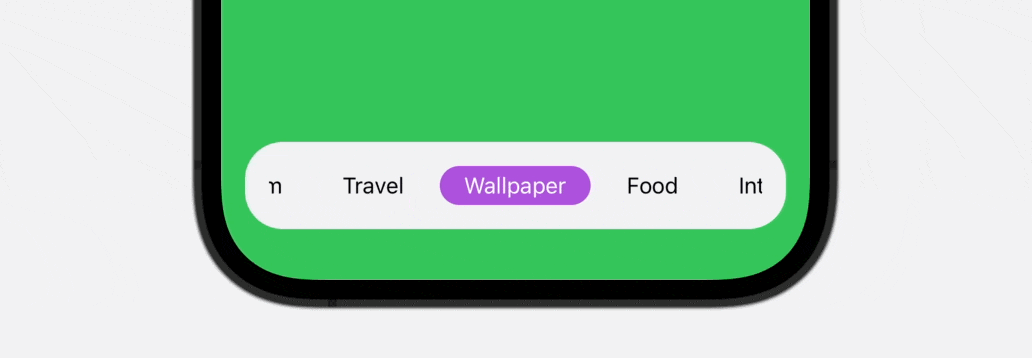
Introducing Tab View and Tab Bar
When you haven’t used TabView earlier than, let’s have a fast stroll via. To create a tab view, you simply want to make use of TabView and embed the kid views inside. For every of the kid views, you apply the tabItem modifier to specify the merchandise description. Right here is an instance:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
struct ContentView: View { let colours: [Color] = [ .yellow, .blue, .green, .indigo, .brown ] let tabbarItems = [ “Random”, “Travel”, “Wallpaper”, “Food”, “Interior Design” ]
var physique: some View { TabView { ForEach(colours.indices, id: .self) { index in colours[index] .body(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity) .tag(index) .tabItem { Picture(systemName: “(index + 1).circle”) Textual content(tabbarItems[index]) } } } } } |
The code above creates a easy tab view with 5 tab gadgets. You employ the Picture view to show the tab icon. When you’ve written the code in Xcode, it’s best to see a tab bar within the preview.
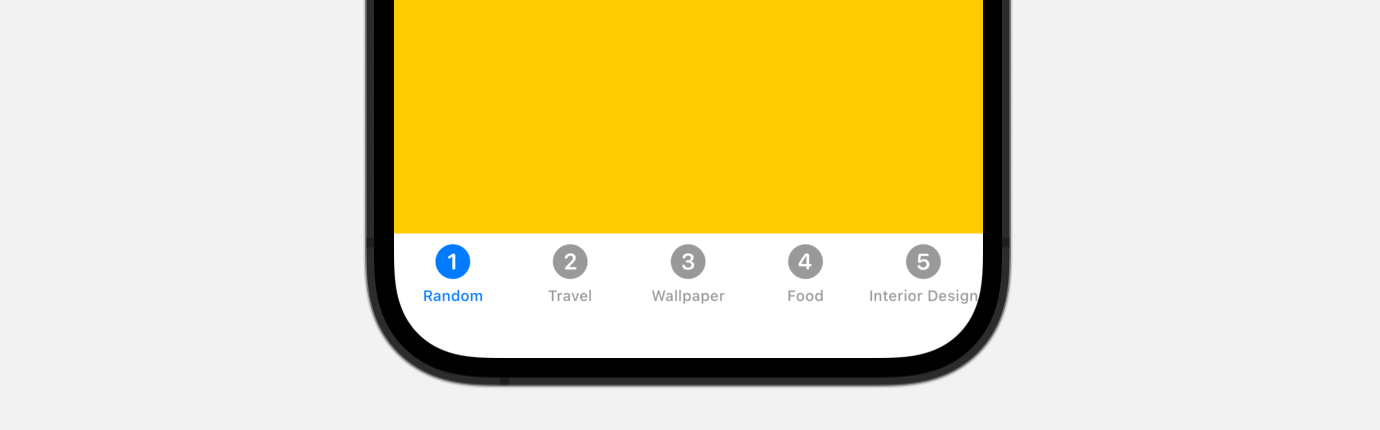
The TabView has one other init technique for this function. The tactic requires a state variable which incorporates the tag worth of the tab.
|
TabView(choice: $selectedIndex) |
For example, declare the next state variable in ContentView:
|
@State personal var selectedIndex = 0 |
Now in case you change the worth of selectedIndex, the tab view will routinely change to the corresponding tab. You might modify the code like this to try it out:
|
TabView(choice: $selectedIndex) { . . . } .onAppear { selectedIndex = 2 } |
When the tab view seems, the third tab is routinely chosen.
Constructing a Customized Scrollable Tab Bar
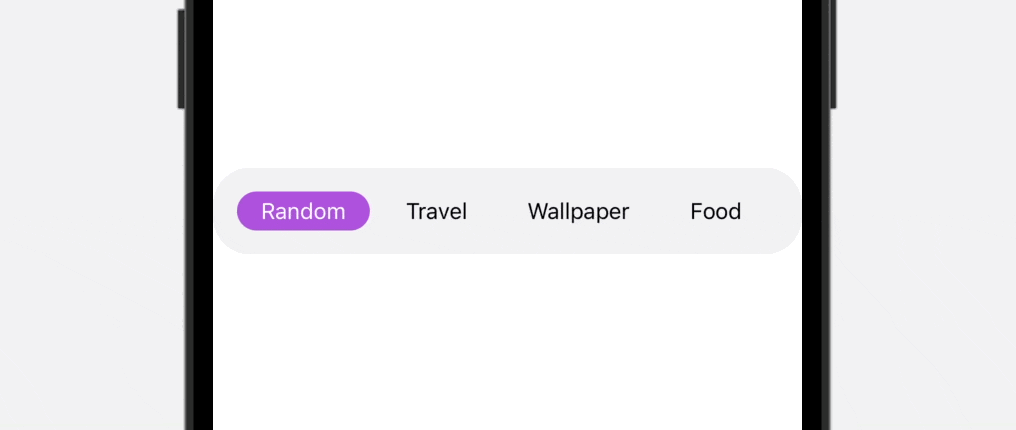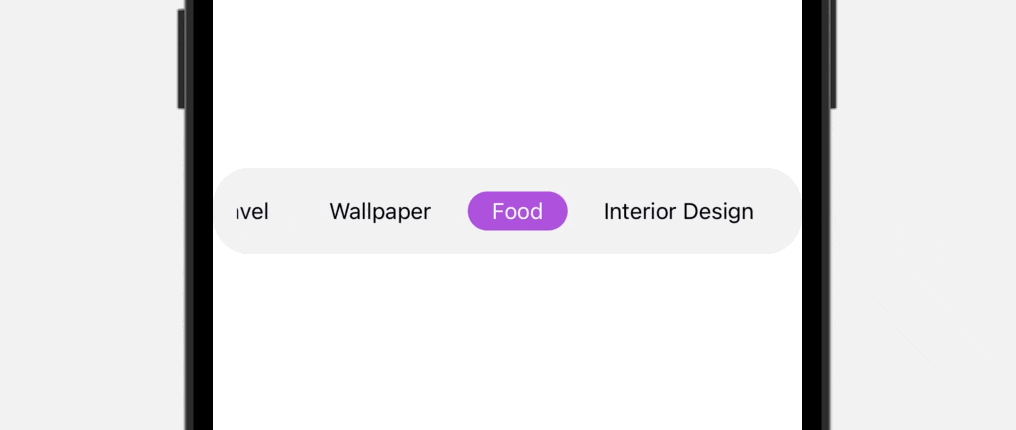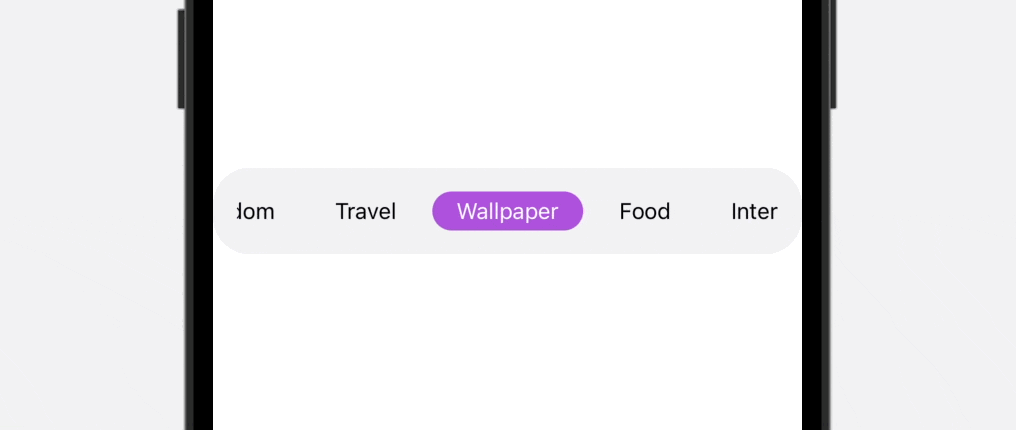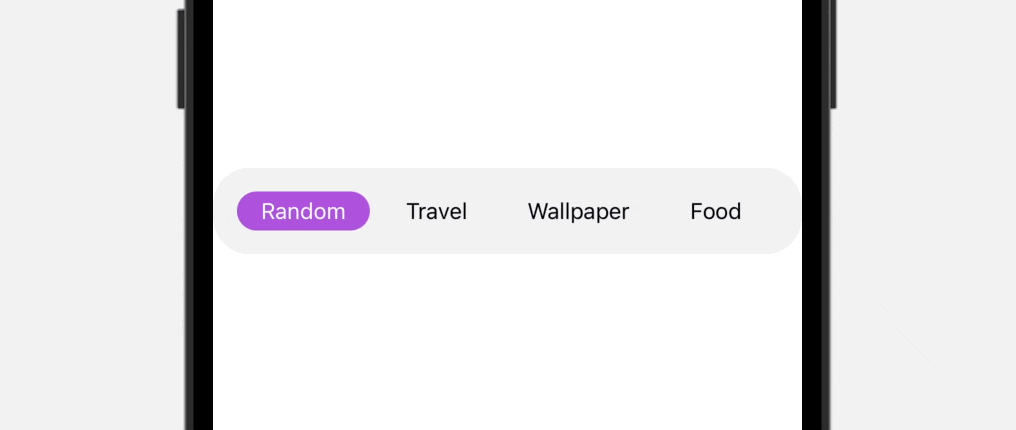
As you’ll be able to see within the ultimate outcome above, the tab bar is scrollable, which is especially helpful when it’s essential to accomodate greater than 5 gadgets. To construct this practice tab bar, we’ll use each ScrollView and ScrollViewReader to create our personal view.
Let’s identify our tab bar view TabBarView and create it like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
struct TabBarView: View { var tabbarItems: [String]
@State var selectedIndex = 0
var physique: some View { ScrollViewReader { scrollView in ScrollView(.horizontal, showsIndicators: false) { HStack { ForEach(tabbarItems.indices, id: .self) { index in
Textual content(tabbarItems[index]) .font(.subheadline) .padding(.horizontal) .padding(.vertical, 4) .foregroundColor(selectedIndex == index ? .white : .black) .background(Capsule().foregroundColor(selectedIndex == index ? .purple : .clear)) .onTapGesture { withAnimation(.easeInOut) { selectedIndex = index } } } } } .padding() .background(Coloration(.systemGray6)) .cornerRadius(25)
}
} } |
This tradition tab view accepts an array of tab bar gadgets. For demo functions, we’re utilizing a String array. Nevertheless, in real-world purposes, you might need to create your individual customized kind for the tab merchandise.
To allow scrolling throughout the tab bar, we’ve embedded all the tab gadgets in a scroll view. Moreover, we’ve wrapped the scroll view with a scroll view reader to make sure that the chosen tab merchandise is all the time seen.
When a particular tab merchandise is chosen, we replace the selectedIndex variable to mirror the chosen index. This allows us to spotlight the lively tab merchandise and supply suggestions to the person.
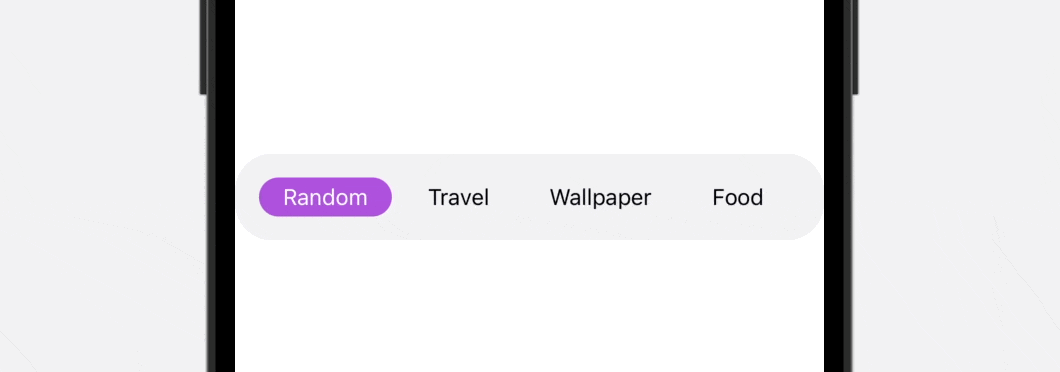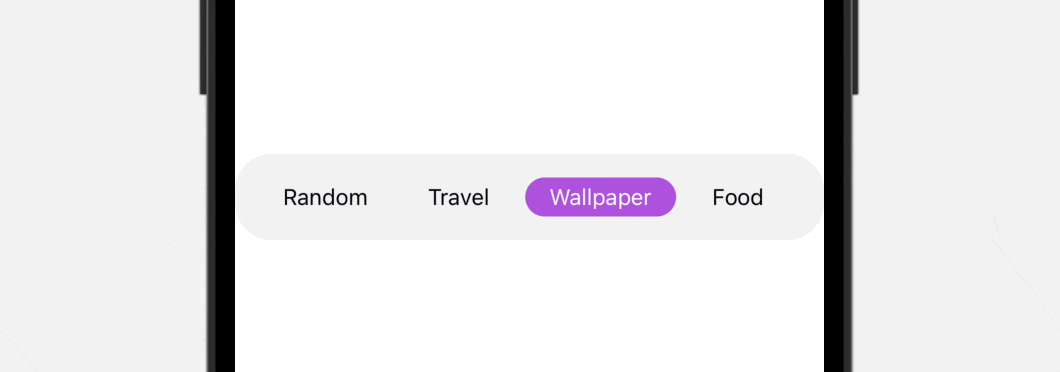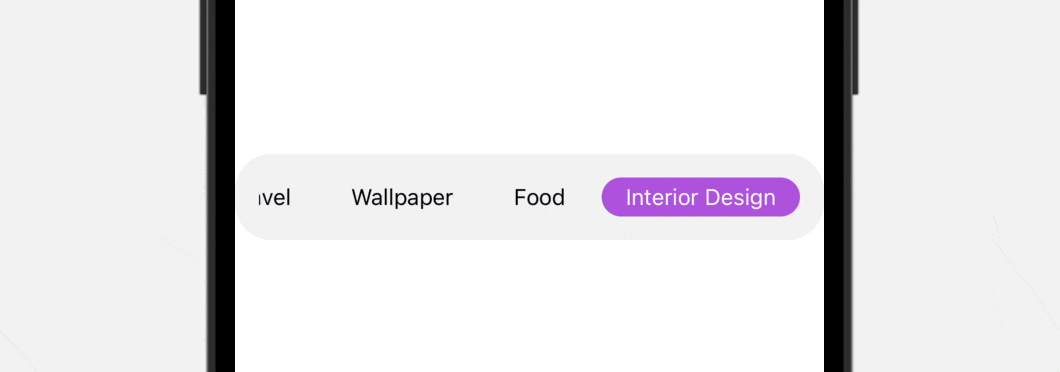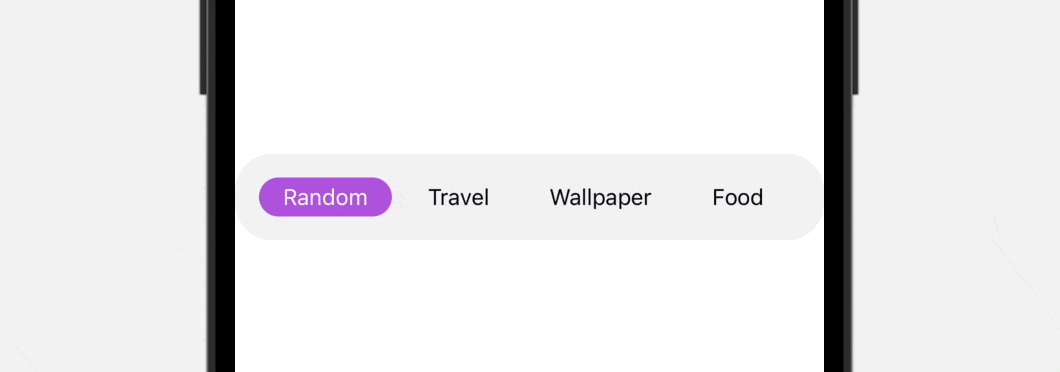
To preview this practice tab bar, you’ll be able to add the TabBarView to the preview like this:
|
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider { static var previews: some View { ContentView()
TabBarView(tabbarItems: [ “Random”, “Travel”, “Wallpaper”, “Food”, “Interior Design” ]).previewDisplayName(“TabBarView”) } } |
Proper now, the customized tab bar works fairly good. Nevertheless, you might discover that it’s essential to manually scroll the tab bar with the intention to reveal the final merchandise. To repair this problem, you’ll be able to connect the next code to the ScrollView:
|
.onChange(of: selectedIndex) { index in withAnimation { scrollView.scrollTo(index, anchor: .heart) } } |
When the chosen index is up to date, we name the scrollTo technique to maneuver the scroll view.
Rework the Animation with matchedGeometryEffect
You’ve constructed a dynamic and scrollable tab bar, however wouldn’t or not it’s nice if we will make the animation even higher? Presently, the tab bar makes use of a fade animation when switching between tab gadgets. By incorporating matchedGeometryEffect into the tab bar, you’ll be able to create a a lot smoother and visually interesting animation. Let’s see learn how to implement it.
First, let’s create a brand new struct known as TabbarItem for the tab bar merchandise like this:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
struct TabbarItem: View { var identify: String var isActive: Bool = false let namespace: Namespace.ID
var physique: some View { if isActive { Textual content(identify) .font(.subheadline) .padding(.horizontal) .padding(.vertical, 4) .foregroundColor(.white) .background(Capsule().foregroundColor(.purple)) .matchedGeometryEffect(id: “highlightmenuitem”, in: namespace) } else { Textual content(identify) .font(.subheadline) .padding(.horizontal) .padding(.vertical, 4) .foregroundColor(.black) }
} } |
With matchedGeometryEffect, all you want is describe the looks of two views. The modifier will then compute the distinction between these two views and routinely animates the scale/place modifications. So within the code above, we spotlight the tab merchandise in purple when it’s lively. In any other case, we show a traditional textual content type.
Within the TabBarView, declare a brand new namespace variable:
|
@Namespace personal var menuItemTransition |
After which, rewrite the code of the ForEach loop like this:
|
ForEach(tabbarItems.indices, id: .self) { index in
TabbarItem(identify: tabbarItems[index], isActive: selectedIndex == index, namespace: menuItemTransition) .onTapGesture { withAnimation(.easeInOut) { selectedIndex = index } } } |
When you made the change, it’s best to discover a significantly better animation when switching between tab gadgets.

Utilizing the Customized Tab Bar
We’ve got to make a minor change within the TabBarView earlier than we will apply it to our ContentView. In TabBarView, modify the state variable to a binding variable like this:
|
@Binding var selectedIndex: Int |
Now you’re prepared to make use of this practice tab bar in different views. In ContentView, replace the physique half like this:
|
ZStack(alignment: .backside) { TabView(choice: $selectedIndex) { ForEach(colours.indices, id: .self) { index in colours[index] .body(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity) .tag(index) .ignoresSafeArea() } } .ignoresSafeArea()
TabBarView(tabbarItems: tabbarItems, selectedIndex: $selectedIndex) .padding(.horizontal) } |
Incorporating the customized tab bar into your app is a simple course of. By wrapping the TabView in a ZStack and overlaying the TabBarView on prime of it, you’ll be able to simply combine the tab bar into the tab UI.
To make the undertaking run easily, you additionally have to replace the preview struct like this:
|
struct ContentView_Previews: PreviewProvider { static var previews: some View { ContentView()
TabBarView(tabbarItems: [ “Random”, “Travel”, “Wallpaper”, “Food”, “Interior Design” ], selectedIndex: .fixed(0)).previewDisplayName(“TabBarView”) } } |
Now you’re prepared to check the tab UI.

Wrap Up
The tab bar interface is a vital part of many fashionable cellular apps, offering customers with fast and easy accessibility to varied app capabilities. Whereas the usual tab bar usually suffices for many situations, there could also be events whenever you need to create a customized tab bar to reinforce the person expertise.
On this tutorial, you’ve discovered learn how to create a dynamic and scrollable tab bar that may accommodate an infinite variety of tab gadgets. By incorporating matchedGeometryEffect, you can too take your tab bar’s animation to the following stage. With the methods coated, you’ll be capable of design a seamless and intuitive customized tab bar that matches your app’s particular wants.
If you wish to dive deeper into SwiftUI, you’ll be able to take a look at our Mastering SwiftUI e book.

