| Jul 13, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) New analysis sheds mild on the mechanism behind how a particular materials adjustments from an electrically conducting steel to an electrical insulator. The researchers studied lanthanum strontium nickel oxide (La1.67Sr0.33NiO4) derived from a quantum materials La2NiO4.
|
|
Quantum supplies have uncommon properties that end result from how their electrons work together. Beneath a vital temperature, the strontium doped materials is an insulator. That is as a result of separation of launched holes from the magnetic areas, forming “stripes.” Because the temperature will increase, these stripes fluctuate and soften at 240K. At this temperature, researchers anticipated the fabric to turn out to be a conducting steel. As an alternative, it stays an insulating materials.
|
|
Neutron scattering sheds mild on this intriguing phenomenon. The outcomes point out that the fabric stays an insulator due to sure atomic vibrations that lure electrons and thus impede electrical conduction.
|
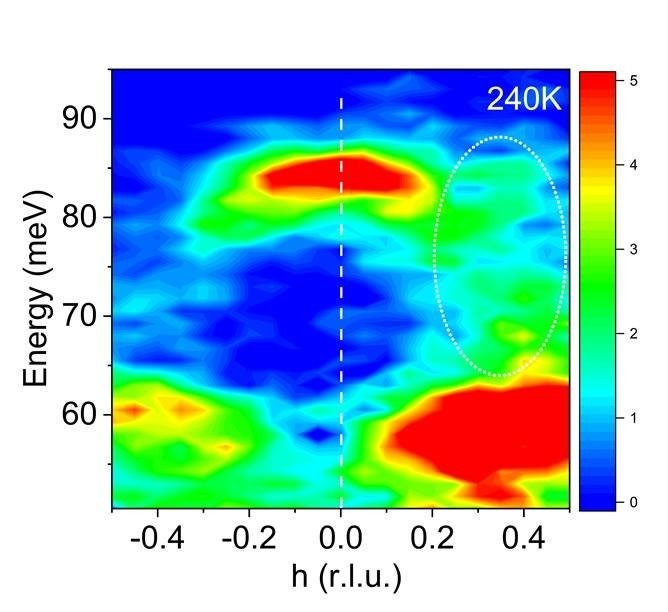 |
| Neutron scattering depth by momentum and power at 240K for a quantum materials. Excessive depth purple areas point out regular atomic vibrations. Decrease depth inexperienced areas (oval) point out sturdy interactions between vibrations & electrons within the materials. (Picture: Dmitry Reznik)
|
|
This analysis has been revealed in Scientific Analysis (“Big electron–phonon coupling of the respiratory airplane oxygen phonons within the dynamic stripe part of La1.67Sr0.33NiO4“).
|
|
Quantum supplies have properties that aren’t predicted by the elements that make up these supplies. For instance, they will transition from metals to insulators or act as superconductors. They maintain great promise for purposes in science and expertise. This analysis describes the tunability of electron-phonon interplay on the metal-insulator transition in a single quantum materials. The outcomes will assist validate theoretical fashions of supplies which have strongly interacting electrons. These theories will assist scientists design new quantum supplies for future applied sciences.
|
|
In metals, electrons might be thought of as free particles flying alongside trajectories enforced by the crystal construction. In latest many years, scientists found new supplies the place electrons strongly repel one another and bounce off atomic vibrations within the host crystal. These supplies exhibit uncommon and technologically helpful properties. These properties can embody dramatic electrical resistance drop in magnetic fields, electron conduction solely on the floor, and excessive temperature superconductivity. Understanding these properties in several supplies stays a grand problem for the scientific group.
|
|
This work used excessive depth neutron beams on the Spallation Neutron Supply, a Division of Vitality consumer facility at Oak Ridge Nationwide Laboratory (ORNL), to look deep inside an archetype quantum materials La2NiO4 wherein one sixth of the lanthanum (La) atoms are changed with strontium (Sr) atoms (La1.67Sr0.33NiO4).
|
|
The crew included researchers from the College of Colorado Boulder, ORNL, Brookhaven Nationwide Laboratory, and the RIKEN Middle for Emergent Matter Science in Japan. These supplies are insulating at low temperatures as a result of so-called “stripe” order that outcomes from the advanced interaction between digital spins and the holes launched because of strontium doping. The doped materials is predicted to turn out to be metallic above 240K when the stripes soften.
|
|
Nevertheless, the fabric stays insulating. The collaboration uncovered sturdy friction between the holes and sure vibrations of oxygen ions and located proof for this interplay in different supplies of comparable construction. The microscopic mechanism may pave approach for the design of recent supplies with uncommon properties helpful for numerous quantum applied sciences.
|

