We first carried out structural characterization of synthesized CeO2 nanoparticles (CeO2 NPs). The form of CeO2 NPs was not uniform, and most of these noticed in TEM pictures had been granular (Further file 1: Determine S1). CeO2 nanostructures had been extremely crystalline, as evidenced by HR-TEM pictures exhibiting a steady lattice and sharp fringes. As well as, SAED patterns and steady lattices confirmed the crystalline traits and fluorite construction of CeO2 NPs. The O and Ce parts had been uniformly distributed on the floor of CeO2 NPs in response to the HAADF-STEM evaluation (Further file 1: Determine S2). XPS spectrum confirmed the presence of Ce, O and C as the principle elements and the Ce confirmed the combined oxidation state of Ce3+ and Ce4+, which was crucial for the simulated oxidase-like properties of CeO2 NPs (Further file 1: Determine S3). Meantime, the attribute diffraction peaks of the XRD spectrum at 2θ indicated the exceptional crystalline purity of the CeO2 NPs produced (Further file 1: Determine S4).
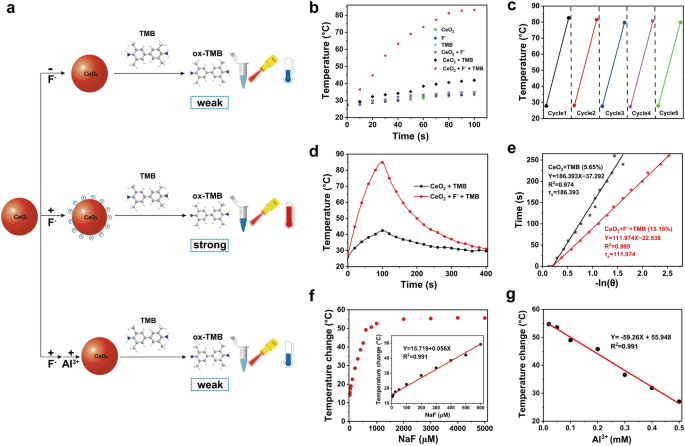
We then sought to find out whether or not fluoride ions might activate the photothermal exercise of CeO2 + TMB (Fig. 1a). As depicted in Further file 1: Determine S5, since CeO2 and TMB had basically no absorption within the NIR area, we noticed a minor temperature enhance of 5.7 °C and seven.4 °C following NIR irradiation (808 nm) for roughly 100 s. An identical temperature rise of seven.4 °C was recorded within the presence of CeO2 + F−. Because of the low oxidase catalytic exercise of the CeO2 nanozyme, solely a tiny quantity of TMB was catalyzed to be oxidized to oxTMB, leading to weak absorption within the NIR area. The temperature enhance of CeO2 + TMB below NIR irradiation was solely 14.6 °C. As anticipated, the presence of F− considerably elevated the exercise of CeO2 oxidase to oxidize TMB to oxTMB with sturdy absorption within the NIR area. Subsequently, the CeO2 + F− + TMB system confirmed a strong photothermal impact with a temperature enhance of 55.3 °C below NIR irradiation (Fig. 1b). Because of the good photothermal stability of oxTMB, no apparent photobleaching was detected within the CeO2 + F− + TMB system after 5 cycles of on/off NIR irradiation (Fig. 1c). Additional, the photothermal conversion effectivity (η) of CeO2 + TMB and CeO2 + F− + TMB was in contrast. The η of CeO2 + TMB and CeO2 + F− + TMB was decided to be 5.65% and 15.15%, validating our hypothesis that treating bare CeO2 NPs with fluoride ions facilitated the advance of the photothermal efficiency of CeO2 + TMB (Fig. 1d, e). Accordingly, the above findings indicated that F− might successfully stimulate the photothermal conversion effectivity of the CeO2 + TMB.
a Schematic illustrations of the affect of fluoride ions on the photothermal exercise of CeO2 + TMB response. b Photothermal heating curves of CeO2, F−, TMB, CeO2 + F−, CeO2 + TMB, and CeO2 + F− + TMB below 808 nm NIR laser irradiation at 2.3 W/cm2. Focus: CeO2 (30 µg/mL), F− (5 mM), TMB (1 mM), acetate buffer (pH 4, 20 mM). c Heating and cooling cycles of CeO2 + F− + TMB system (CeO2: 30 µg/mL, F−: 5 mM, TMB: 1 mM) below on–off cycles. d Photothermal results, and e corresponding curve becoming of cooling time versus the destructive pure logarithm of the driving pressure temperature throughout the cooling part of CeO2 + TMB (CeO2: 30 µg/mL, TMB: 1 mM) with and with out fluoride ions. f The linear calibration plots of temperature readings towards the varied fluoride ions concentrations (0–5000 µM). g Relationship between temperature change values from the NIR laser irradiation (808 nm, 2.3 W/cm2) below totally different circumstances of Al3+ focus
To optimize the efficiency of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system, the photothermal assay investigated the impression of a number of parameters, together with the focus of CeO2 NPs, buffer resolution, and lightweight energy depth. The optimized circumstances had been decided as CeO2 NPs focus of 30 μg/mL, pH of 4.0, and energy depth of two.3 W/cm2 (Further file 1: Determine S6). Moreover, we validated the position of every module within the CeO2 + F− + TMB system. In response to the glutathione (GSH), the oxidase exercise was wholly eradicated owing to the discount of CeO2 NPs (Further file 1: Determine S7), and the CeO2 + F− + TMB system recorded a notable change of photothermal impact with the temperature change worth from 56.2 °C to 7.7 °C (Further file 1: Determine S8). Equally, with the addition of 8-hydroxyquinoline (8-HQ, blocking the oxidation of TMB) to the CeO2 + F− + TMB system, the temperature change worth from 56.2 °C to 7.8 °C was noticed, verifying the photothermal transformation mediated by oxTMB. Al3+, a chelating agent for F−, prevents F− from adhering to the floor of CeO2 NPs. As predicted, a temperature change worth from 56.2 °C to 12.8 °C was seen by the CeO2 + F− + TMB system with the addition of Al3+ (Further file 1: Determine S9), which additional proved the F− might successfully activate the photothermal conversion effectivity of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system.
Based mostly on the above outcomes, we additional investigated whether or not the NIR photothermal system of CeO2 + F− + TMB might obtain programmed temperature by adjusting the focus of F−. As proven in Fig. 1f, including F− at concentrations starting from 1 μM to three mM elicited a fast dynamic response from the temperature output. The temperature rose linearly with F− focus from 1 μM to 600 μM. Quite the opposite, the temperature change values dropped linearly with Al3+ focus from 0.02 mM to 0.5 mM (Fig. 1g). The potential interferences of Cl−, Br−, I−, CO32−, H2PO4−, NO3−, and CH3COO− had been explored to evaluate additional the particular identification capability of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system for F−. As demonstrated in Further file 1: Determine S10, the addition of potential interferences had no considerable impact on the temperature change relative to the F−, demonstrating the excellent selectivity of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system towards F−. Subsequently, herein, we constructed a NIR photothermal system of CeO2 + F− + TMB that would acquire programmed temperature by various the focus of F−.
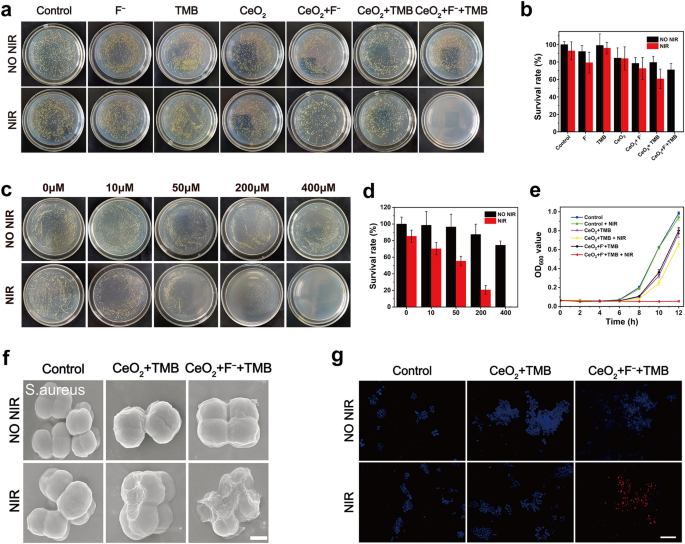
Inspired by the above information, to this finish, we evaluated the antibacterial exercise of CeO2 + F− + TMB system for PTT in vitro. S. aureus (gram-positive organism) and E. coli (gram-negative creature) had been chosen as typical strains to function mannequin micro organism. No statistically vital distinction within the variety of colonies was noticed between the NIR illumination and darkish settings of the management teams for each S. aureus and E. coli (Fig. 2a and Further file 1: Determine S11a), proving that NIR illumination alone had no impression on microorganisms. In darkish circumstances, for the CeO2 and TMB group, the survival charges of S. aureus (Fig. 2b) had been 84.6% and 99.1%, and the survival charges of E. coli (Further file 1: Determine S11b) had been near the management group. Because of the poor photothermal effectivity of CeO2 and TMB, the CeO2 and TMB group exhibited negligible antibacterial exercise when uncovered to 808 nm NIR illumination for about 7 min, with survival charges of 83.9% and 95.9% for S. aureus, and 101.6% and 81.2% for E. coli, respectively. This incidence proved that CeO2 and TMB didn’t show obvious antibacterial exercise below darkish and NIR gentle settings relating to the variety of S. aureus and E. coli colonies. Within the CeO2 + TMB group, no substantial antibacterial impact was noticed for S. aureus and E. coli in darkish circumstances. Beneath NIR irradiation (2.3 W/cm2, 7 min), the CeO2 + TMB group displayed a poor antibacterial impact with a 60.8% survival charge of S. aureus and 63.0% survival charge of E. coli, attributing to a low photothermal impact of CeO2 + TMB. The S. aureus and E. coli within the F− teams exhibited survival charges of 79.3% and 89.9% when uncovered to 808 nm gentle, which indicated that the F− barely impacted the micro organism exercise. In distinction, below an identical circumstances for NIR irradiation, the antibacterial charges of the CeO2 + F− + TMB group considerably boosted to 99.8% (S. aureus) and 99.3% (E. coli) compared to the CeO2 + TMB group, exhibiting that the F− might considerably improve the photothermal conversion effectivity of the CeO2 + TMB for PTT. To search out out the affiliation between F− dosage and micro organism sterilization effectivity, the F− focus was altered to 0, 10, 50, 200, and 400 μM. Notably, below NIR illumination, the antibacterial exercise of the CeO2 + TMB group towards S. aureus elevated step by step with rising F− focus (Fig. 2c). For following antibacterial and wound therapeutic research, the optimum focus of F− for PTT was established to be 400 μM as a result of ultra-high antibacterial effectiveness (99.7%) and optimum photothermal temperature to ensure good security (minimal invasion) and environment friendly bacterial breakdown (Fig. 2d). Equally, the antibacterial impact of CeO2 + TMB towards E. coli step by step elevated with the rise of F− focus below NIR irradiation (Further file 1: Determine S12a), and the optimum antibacterial focus of F− was additionally 400 μM (Further file 1: Determine S12b). The negligible OD600 values of S. aureus (Fig. 2e) and E. coli (Further file 1: Determine S13) handled within the CeO2 + F− + TMB group below NIR irradiation, just like the agar plate outcomes, additional revealed the potent antibacterial exercise of CeO2 + TMB may very well be successfully boosted by F−.
a Images of bacterial colonies fashioned by S. aureus after publicity to acetate buffer (Management), F−, TMB, CeO2, CeO2 + F−, CeO2 + TMB and CeO2 + F− + TMB with out/with NIR irradiation. Focus: CeO2 (30 µg/mL), F− (400 µM), TMB (1 mM), acetate buffer (pH 4, 20 mM). b The statistical evaluation of survival charges of S. aureus uncovered to totally different samples with out and with NIR irradiation. c Colony pictures of CeO2 + TMB (CeO2: 30 µg/mL, TMB: 1 mM) handled S. aureus with totally different F− concentrations (0, 10 µM, 50 µM, 200 µM, 400 µM) below darkish and NIR gentle circumstances. d The statistical evaluation of survival charges of S. aureus uncovered to CeO2 + TMB with various F− concentrations with out and with NIR irradiation. e The OD600 worth of the supernatant as a perform with the time after being handled with varied circumstances with S. aureus. f SEM (Scale bar: 500 nm), and g Fluorescence pictures of S. aureus samples after remedies with Management (acetate buffer), CeO2 + TMB, CeO2 + F− + TMB with out/with NIR irradiation (Scale bar: 20 μm). Focus: CeO2 (30 µg/mL), F− (400 µM), TMB (1 mM), acetate buffer (pH 4, 20 mM). Error bars symbolize the usual deviation from the imply (n = 3)
To look at the mechanism of antimicrobial motion, bacterial SEM testing and bacterial live-dead fluorescence staining below gentle and darkish settings had been carried out. As proven in Fig. 2f and Further file 1: Determine S14, for management teams below the NIR illumination and darkish settings, S. aureus and E. coli exhibited typical spherical and rod morphologies with easy surfaces and undamaged cell partitions, respectively just like these of native dwelling micro organism. After therapy with CeO2 + TMB + NIR, just a few disturbances may very well be seen on the cell wall, indicating minimal harm to the integrity of cell partitions. Nonetheless, the therapy of CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group induced various levels of harm to the morphology of the bacterial cells, leading to compression in addition to a roughening of the bacterial floor. The effectiveness of the antibacterial therapy was additional evaluated utilizing dwell/useless fluorescence assays. The dwelling micro organism had been stained with blue dye throughout these checks, whereas the useless micro organism had been stained with pink dye. As evidenced by the absence of pink fluorescence in Fig. 2g and Further file 1: Determine S15, most S. aureus and E. coli had been alive below NIR illumination and darkish circumstances for the management teams. Just a few pink luminous cells had been discovered for micro organism handled with CeO2 + TMB + NIR group, implying a partial sterilization impact. Notably, therapy with CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group triggered a big enhance within the variety of useless cells, as seen by the sturdy pink fluorescence sign, indicating a considerable enchancment in antibacterial effectiveness. In brief, the potent antibacterial exercise of CeO2 + TMB may very well be effectively activated by F− below NIR illumination.
After totally confirming the excellent antimicrobial effectivity of CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR in vitro, we additional investigated the potential in disinfecting and treating animal wounds. It was important to evaluate the biosafety of antibacterial wound therapeutic brokers. Earlier than developing an infectious mannequin in vivo, the cytotoxicity and hemocompatibility of CeO2 + F− + TMB had been evaluated. We employed NIH3T3 fibroblasts derived from mouse embryos to evaluate the cytotoxicity. Based on the outcomes of the cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) experiment, CeO2 + F− + TMB displayed little cytotoxicity over the 24 h statement interval (Further file 1: Determine S16). To additional assess its biocompatibility, the hemolytic efficiency of CeO2 + F− + TMB was measured after it had been grown with mouse pink blood cells (RBCs). Optimistic and destructive management RBCs had been distributed individually in deionized water and regular saline to judge the hemolysis charge. The supernatant (water) from the optimistic management group had a deep pink colour (Further file 1: Determine S17), whereas the supernatant (regular saline) from the destructive management group and all different teams was clear. Lower than 5 % hemolysis was recognized within the group handled with CeO2 + F− + TMB, indicating glorious blood compatibility. Collectively, the CeO2 + F− + TMB system with glorious biocompatibility was possible for in vivo anti-infective therapy.
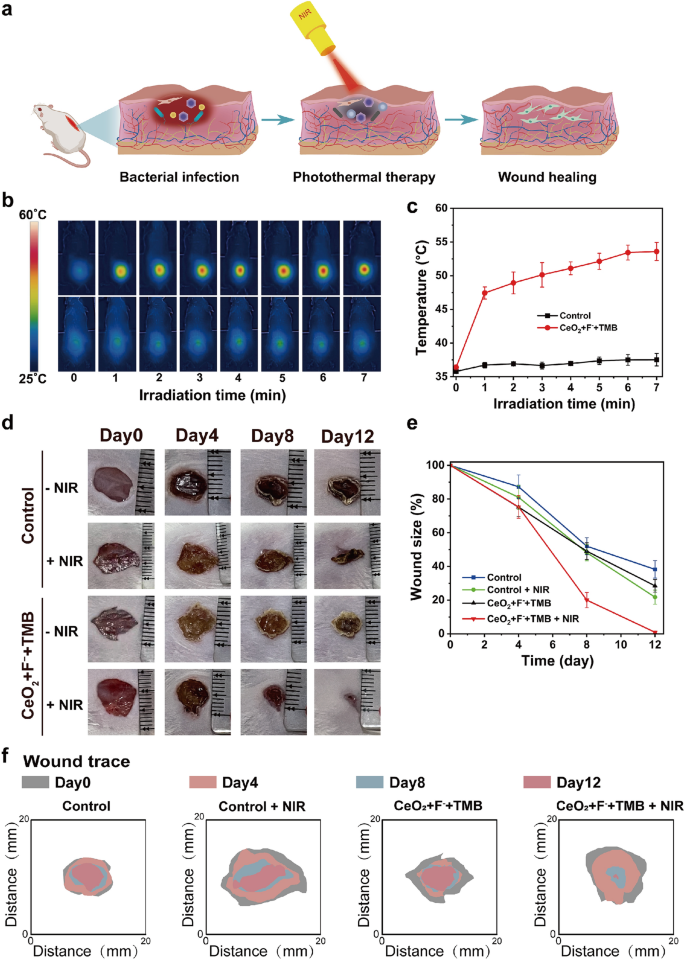
Impressed by the exceptional antibacterial efficacy and glorious biocompatibility of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system, we undertook wound administration experiments in vivo. To find out the disinfects abscesses of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system, we first established a pores and skin mannequin by injecting 100 μL of S. aureus (1 × 108 CFU/mL) into the dermis of a Balb/c mouse. The phototherapy mechanism for wound therapy was proven in Fig. 3a. We proceed to make use of the CeO2 + F− + TMB system as a optimistic management and acetate buffer as a destructive management for in vivo wound therapeutic investigations, which divided the mice into 4 teams, together with management, management + NIR, CeO2 + F− + TMB, and CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR. The wound receiving NIR phototherapy was monitored utilizing a thermal imaging digital camera (Fig. 3b). After administering CeO2 + F− + TMB injections to mice, the contaminated space confirmed a big photothermal response when uncovered to NIR gentle (808 nm, 2.3 W/cm2). The temperature rose quickly and remained secure at 53.6 °C after about 7 min (Fig. 3c). The photothermal temperature of 53.6 °C within the contaminated website assured good security (minimal invasion) and environment friendly bacterial breakdown. In distinction, there was only a minor temperature change within the management group following acetate buffer therapy below the identical circumstances. Images of wound therapeutic had been obtained each 4 days throughout totally different therapy teams (Fig. 3d). The calculation of wound contraction was depicted in Fig. 3e. In all examined teams, the scale of the wound decreased over time. Sometimes, among the many 4 teams, the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group displayed, on common, the quickest wound therapeutic (Fig. 3f). In the meantime, the in vivo photothermal response and wound therapeutic investigations of the CeO2 + TMB + NIR group had been performed to additional display the position of F− in CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR photothermal system. As proven in Further file 1: Determine S18, the temperature slowly elevated over time and remained secure at 39.5 °C after about 7 min. The wound measurement diminished the wound space to 72.2% after 12 days, which was far decrease than the 99.1% discount in wound space by treatemnt of the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group (Further file 1: Determine S19). Subsequently, introducing F− might considerably improve the wound therapeutic impact of the CeO2 + TMB + NIR in vivo. For evaluating the sterilization effectivity, micro organism from wound tissue on 2 h and day 7, had been cultivated in a single day on LB agar plates (Further file 1: Determine S20). On day 7, the micro organism within the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group diminished considerably in comparison with the opposite teams. Furthermore, to additional consider the impact of wound therapeutic, we chosen the widespread antibiotic penicillin G as a comparability. The leads to Further file 1: Determine S21 confirmed that the wound measurement of thepenicillin G handled group and CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR handled group diminished the wound space to 94.1% and 99.1% after 12 days, respectively. Judging from the above information, the CeO2 + F− + TMB NIR photothermal system might considerably enhance bacteria-infected wound therapeutic.
a Schematic representations of wound an infection mannequin and therapy technique primarily based on CeO2 + F− + TMB therapeutic platform. b Infrared thermal photos, and c the rise in temperature on the wound websites of mice on the designated intervals below 808 nm NIR illumination (2.3 W cm2) for management (acetate buffer (pH 4, 20 mM)).and CeO2 + F− + TMB (CeO2: 30 µg/mL, F−: 400 µM, TMB: 1 mM) teams. d Photos depicting the development of wound contraction from day 0 to day 12 in response to numerous remedies. e Quantitative evaluation of the wound measurement in every group after totally different remedies. f The dynamic course of diagram of wound hint for every therapy inside 12 days. Error bars symbolize the usual deviation from the imply (n = 3)
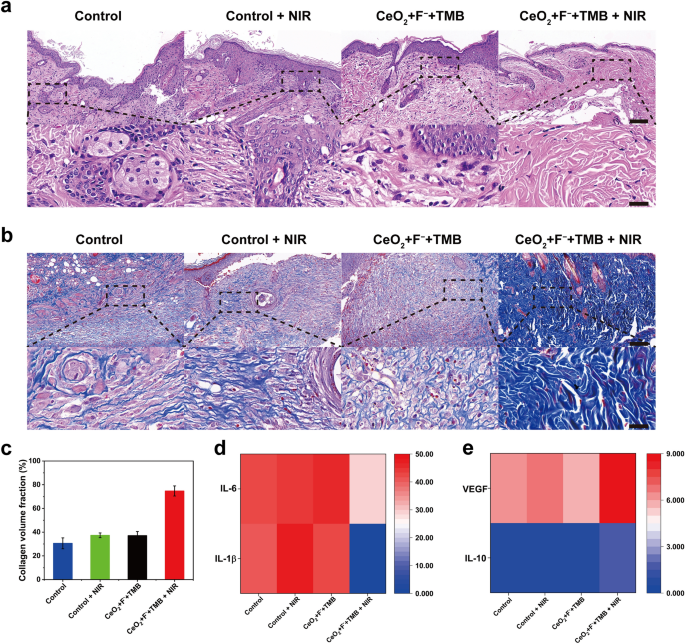
Moreover, alteration in pores and skin tissue was evaluated to corroborate the element of the aforementioned wound therapeutic. The histological investigation was carried out utilizing the H&E (hematoxylin and eosin) staining and Masson’s trichrome staining. At a sure interval after therapy, mice had been euthanized, and tissues had been obtained from the management, management + NIR, CeO2 + F− + TMB, and CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR teams. Outcomes from H&E staining revealed that on day 8, on the wound handled with CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group, the epidermal layer was intact, and there have been fewer inflammatory cells (blood cells and neutrophils), whereas the epidermal layer was compromised, and there have been extra inflammatory cells emerged within the pores and skin tissue of management, management + NIR, and CeO2 + F− + TMB teams (Fig. 4a). As well as, ample fibroblasts and blood vessels had been seen in CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group, indicating improved tissue regeneration and wound therapeutic. Masson’s trichrome staining revealed that on day 8, the wound handled with CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group had well-established collagen fibers and a dermal layer. In distinction, the injuries within the different therapy teams included many collagen fibers that had not been repaired (Fig. 4b). Moreover, in comparison with different teams, scar width handled with the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group decreased quickly (Further file 1: Determine S22). Moreover, extra collagen fibers had been noticed within the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group than in different therapy teams (Fig. 4c). Quite a few inflammatory cytokines are important within the initiation and development of inflammatory illness. As demonstrated in Fig. 4d, e, the degrees of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 within the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group had been considerably decrease than within the different therapy teams, whereas the degrees of anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and development components VEGF had been considerably greater. The information on inflammatory cytokines revealed that the therapy of the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group might successfully lower the expression of IL-1β and IL-6 whereas up-regulating the expression of IL-10 and VEGF, therefore lowering the inflammatory response. In brief, wounds handled with CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR demonstrated minimal irritation, good hemostasis, a excessive collagen fiber content material, thick granulation tissue and fast wound therapeutic. Consequently, CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR might speed up the part transition from hemostasis to irritation, proliferation, and transforming, facilitating wound therapeutic.
a H&E (Scale bar: the highest of 100 µm and the underside of 25 µm), and b Masson staining of wound tissues handled with Management, Management + NIR, CeO2 + F− + TMB, and CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR (Scale bar: the highest of 100 µm and the underside of 25 µm). Focus: CeO2 (30 µg/mL), F− (400 µM), TMB (1 mM), acetate buffer (pH 4, 20 mM). c Quantification of collagen quantity fraction. d Ranges of IL-1β and IL-6 (pg/mg), e IL-10 and VEGF (pg/mg). Error bars symbolize the usual deviation from the imply (n = 3)
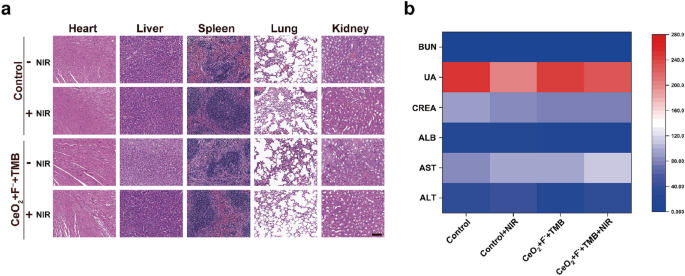
In the meantime, the in vivo biosafety of our proposed CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR antimicrobial system was additional investigated to display its potential for future bacterial suppression purposes. Monitoring the mice’s physique weight all through the experimental remedies indicated no vital weight reduction in both the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group or different therapy teams, proving that these remedies weren’t systemically poisonous to mice (Further file 1: Determine S23). Moreover, the first organs of the handled mice had been taken for H&E staining, together with the guts, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney, and no abnormalities or lesions had been seen on the biopsy pictures (Fig. 5a). Moreover, the routine blood checks and blood biochemical analyses of the mice within the CeO2 + F− + TMB + NIR group and different therapy teams confirmed no vital variations in any of the parameters, proving that the kidney and liver capabilities had been unhurt (Fig. 5b). Collectively, these findings repeatedly validated the nice organic safety of antimicrobial remedy using the CeO2 + F− + TMB NIR photothermal system, revealing the good potential in medical translation.