| Aug 14, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Rice College chemists have found that tiny gold “seed” particles, a key ingredient in one of the vital frequent nanoparticle recipes, are one and the identical as gold buckyballs, 32-atom spherical molecules which are cousins of the carbon buckyballs found at Rice in 1985.
|
|
Carbon buckyballs are hole 60-atom molecules that had been co-discovered and named by the late Rice chemist Richard Smalley. He dubbed them “buckminsterfullerenes” as a result of their atomic construction reminded him of architect Buckminster Fuller’s geodesic domes, and the “fullerene” household has grown to incorporate dozens of hole molecules.
|
|
In 2019, Rice chemists Matthew Jones and Liang Qiao found that golden fullerenes are the gold “seed” particles chemists have lengthy used to make gold nanoparticles. The discover got here only a few months after the primary reported synthesis of gold buckyballs, and it revealed chemists had unknowingly been utilizing the golden molecules for many years.
|
|
“What we’re speaking about is, arguably, essentially the most ubiquitous methodology for producing any nanomaterial,” Jones stated. “And the reason being that it’s simply so extremely easy. You don’t want specialised gear for this. Highschool college students can do it.”
|
|
Jones, Qiao and coauthors from Rice, Johns Hopkins College, George Mason College and Princeton College spent years compiling proof to confirm the invention, and lately revealed their ends in Nature Communications (“Atomically exact nanoclusters predominantly seed gold nanoparticle syntheses”).
|
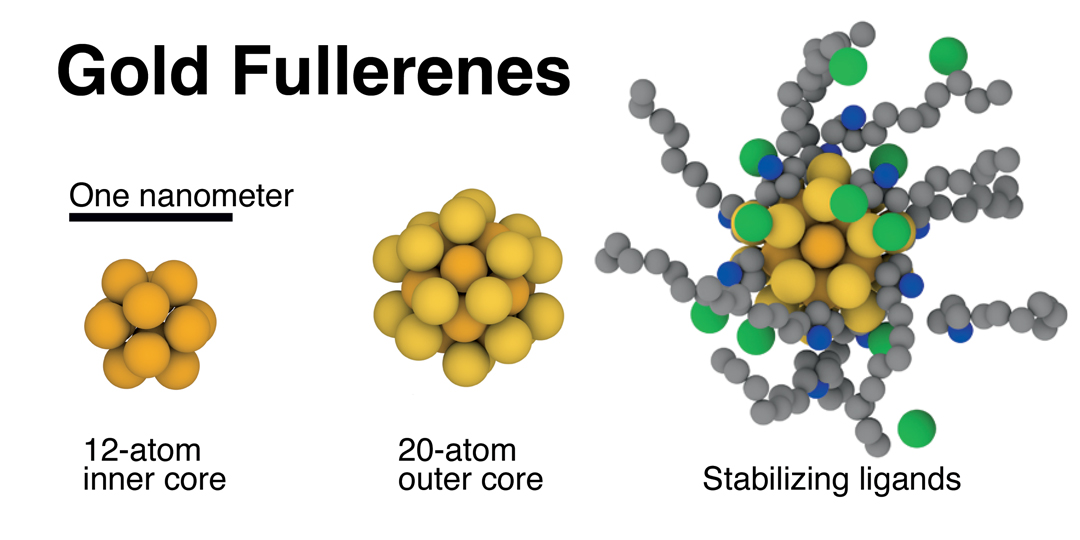 |
| Gold buckball fullerenes every include a hole interior core of 12 gold atoms (left) and a 20-atom gold outer core (middle). Hooked up natural ligands (proper) that stabilize the construction. (Picture: Jones lab/Rice College)
|
|
Jones, an assistant professor in chemistry and supplies science and nanoengineering at Rice, stated the information that gold nanoparticles are synthesized from molecules may assist chemists uncover the mechanisms of these syntheses.
|
|
“That’s the large image for why this work is vital,” he stated.
|
|
Jones stated researchers found within the early-2000s learn how to use gold seed particles in chemical syntheses that produced many shapes of gold nanoparticles, together with rods, cubes and pyramids.
|
|
“It is actually interesting to have the ability to management particle form, as a result of that modifications lots of the properties,” stated Jones, an assistant professor in chemistry and supplies science and nanoengineering at Rice. “That is the synthesis that just about everybody makes use of. It’s been used for 20 years, and for that entire time period, these seeds had been merely described as ‘particles.’”
|
|
Jones and Qiao, a former postdoctoral researcher in Jones’ lab, weren’t searching for gold-32 in 2019, however they observed it in mass spectrometry readings. The invention of carbon-60 buckyballs occurred in an analogous means. And the coincidences don’t cease there. Jones is the Norman and Gene Hackerman Assistant Professor in Chemistry at Rice. Smalley, who shared the 1996 Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Rice’s Robert Curl and the UK’s Harold Kroto, was a Hackerman chair in chemistry at Rice for a few years previous to his demise in 2005.
|
|
Confirming that the widely-used seeds had been gold-32 molecules moderately than nanoparticles took years of effort, together with state-of-the-art imaging by Yimo Han’s analysis group at Rice and detailed theoretical analyses by the teams of each Rigoberto Hernandez at Johns Hopkins and Andre Clayborne at George Mason.
|
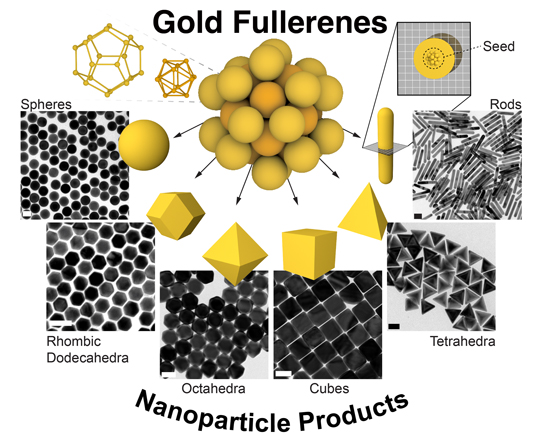 |
| Chemists in Matthew Jones’ lab at Rice College found that gold fullerenes (middle) are one and the identical as “seed” particles (prime proper) that scientists have lengthy used to synthesize myriad styles and sizes of gold nanoparticles (left, proper and backside). Every fullerene seed comprises 32 atoms of gold organized in a 12-atom, icosahedral interior core (prime left) and a 20-atom dodecahedral outer core (prime far left). (Picture: Jones lab/Rice College)
|
|
Jones stated the excellence between nanoparticle and molecule is vital and a key to understanding the research’s potential impression.
|
|
“Nanoparticles are usually related in dimension and form, however they don’t seem to be similar,” Jones stated. “If I make a batch of 7-nanometer spherical gold nanoparticles, a few of them could have precisely 10,000 atoms, however others may need 10,023 or 9,092.
|
|
“Molecules, alternatively, are excellent,” he stated. “I can write out a components for a molecule. I can draw a molecule. And if I make an answer of molecules, they’re all precisely the identical within the quantity, sort and connectivity of their atoms.”
|
|
Jones stated nanoscientists have realized learn how to synthesize many helpful nanoparticles, however progress has usually come through trial and error as a result of “there may be just about no mechanistic understanding” of their synthesis.
|
|
“The issue right here is fairly simple,” he stated. “It’s like saying, ‘I would like you to bake me a cake, and I am gonna provide you with a bunch of white powders, however I am not going to let you know what they’re.’ Even if in case you have a recipe, if you do not know what the beginning supplies are, it’s a nightmare to determine what elements are doing what.
|
|
“I would like nanoscience to be like natural chemistry, the place you may make primarily no matter you need, with no matter properties you need,” Jones stated.
|
|
He stated natural chemists have beautiful management over matter “as a result of chemists earlier than them did extremely detailed mechanistic work to grasp all the exact methods by which these reactions function. We’re very, very removed from that in nanoscience, however the one means we’ll ever get there may be by doing work like this and understanding, mechanistically, what we’re beginning with and the way issues type. That’s the final word objective.”
|


