Google introduced a brand new method to run JavaScript that improves webpage responsiveness, serving to publishers who use it to beat their opponents efficiency in a brand new core net important metric.
The announcement gives a sneak peek at a method to turbocharge webpage efficiency.
If this trial is profitable then it could be one thing that publishers throughout all content material administration platforms and methods will need to use so as to get a leap forward of their opponents.
The Downside Google Is Fixing
Interplay to Subsequent Paint (INP) is a metric that may be a alternative for First Enter Delay (FID).
INP is scheduled to go reside as a Core Internet important metric on March 2024.
As a way to rating nicely on the approaching quickly INP core net important, a webpage must be responsive to each potential person interplay.
One of many issues that causes poor INP scores is a few JavaScript take a very long time to run.
When these scripts take a very long time to run, they’re referred to as Lengthy Duties.
The issue with Lengthy Duties is that they’re like a sluggish driver on a street that’s poking alongside within the quick lane, slowing down visitors.
What at the moment occurs is that the scripts that management person interplay are blocked by the lengthy process, inflicting the webpage to be unresponsive.
The person in that state of affairs waits and waits for the web page to do one thing after clicking a button.
What sometimes happens in lots of webpages right now is {that a} person interplay has to attend till the lengthy process finishes operating.
The picture under exhibits how an extended process blocks the vital person interplay process from operating.
Lengthy Activity Blocking Consumer Interplay Script
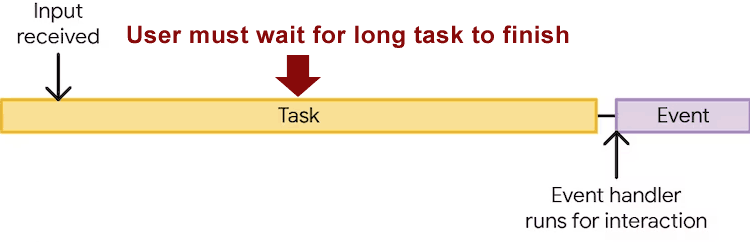
What Google is proposing is an answer to that downside that makes the lengthy process behave like a sluggish automotive that pulls over to the facet of the street to permit a hearth truck go by.
Current Methods Don’t Work
There are already coding workarounds that assist enhance person interplay scores.
However they don’t actually work nicely as a result of they have been designed to resolve different issues, not the person interplay downside.
Google’s explainer says that current methods pause the lengthy process however ship it to the again of the queue of all the opposite scripts, lots of which might not be as vital because the lengthy process.
In that typical state of affairs, the lengthy process that should end has to attend till much less vital scripts end as a result of it’s in the back of the road now.
Present coding workarounds can find yourself making a worse scenario as a substitute of serving to.
Resolution For Lengthy Duties is scheduler.yield
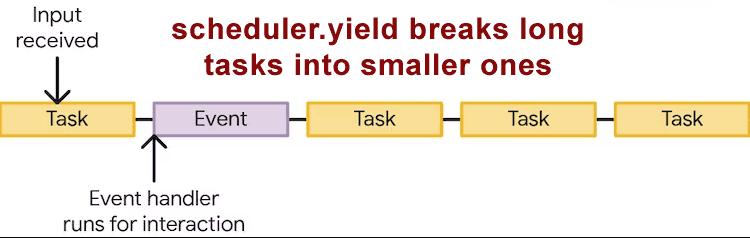
The answer to the lengthy process downside is an method that Google calls scheduler.yield.
What scheduler.yield does is to pause the lengthy process so as to yield to the person interplay process, which may begin operating.
As soon as the person interplay script is completed the lengthy process is ready to leap to the top of the queue and begin operating once more.
Right here’s an illustration printed by Google that exhibits how an extended process may be damaged into smaller duties so as to enable vital person interplay scripts to run.
Illustration Of How scheduler.yield Works
Origin Trials Of Scheduler.Yield
The flexibility to run scheduler.yield has been out there since Chrome 115, which launched on July thirteenth.
Google is asking for volunteers to check out the brand new characteristic in an “origin trial” so as to acquire suggestions to grasp the way it works in the true world earlier than finally making this an official characteristic.
An origin trial is a chance to take part in testing a brand new characteristic (info on origin trials right here).
Google’s announcement defined:
“In a continued effort to ship new APIs that assist net builders make their web sites as snappy as they are often, the Chrome Workforce is at the moment operating an origin trial for scheduler.yield beginning in model 115 of Chrome.
scheduler.yield is a proposed new addition to the scheduler API that permits for each a neater and higher method to yield management again to the primary thread than the strategies which were historically relied upon.”
One of many potential points with operating scheduler.yield on a reside website is {that a} fallback will must be coded in for non-Chrome 115 browsers in order that the web site will work usually for website guests not on Chrome 115 that don’t assist the brand new characteristic.
There’s additionally a method to run it regionally for testing:
“If you wish to experiment with scheduler.yield regionally, kind and enter chrome://flags in Chrome’s tackle bar and choose Allow from the dropdown within the Experimental Internet Platform Options part.
It will make scheduler.yield (and another experimental options) out there in solely your occasion of Chrome.”
A Probability To Leap Forward Of Rivals
This new characteristic is at the moment in testing mode.
However provided that INP is scheduled to grow to be an official core net important metric in March 2024, it could be helpful to keep watch over this new Chrome characteristic and undertake it sooner somewhat than later as soon as it’s out of the experimental part.
Adopting it now could also be a great way to get forward of opponents, so long as a fallback is in place for browsers that haven’t but adopted the brand new characteristic.
Learn the official announcement:
Introducing the scheduler.yield origin trial
https://developer.chrome.com/weblog/introducing-scheduler-yield-origin-trial/
Signing up for the scheduler.yield origin trial: may be accomplished right here.
Learn an explainer about optimizing for lengthy duties:
Go to the GitHub explainer web page for the scheduler.yield api:
Featured picture by Shutterstock/Catalyst Labs

