Distant epitaxy, a promising know-how for skinny movie progress and exfoliation, suffers from substrate harm underneath harsh circumstances. On this regard, researchers just lately investigated the impact of nano-sized pits on AlN template floor on GaN distant epitaxy. Whereas GaN skinny movie could possibly be exfoliated at 750 °C, it failed at 1050 °C. At increased temperatures, the nano pits broken the graphene layer between the template and the movie, inflicting alterations within the movie progress mode.
Picture Credit score: Distant epitaxy
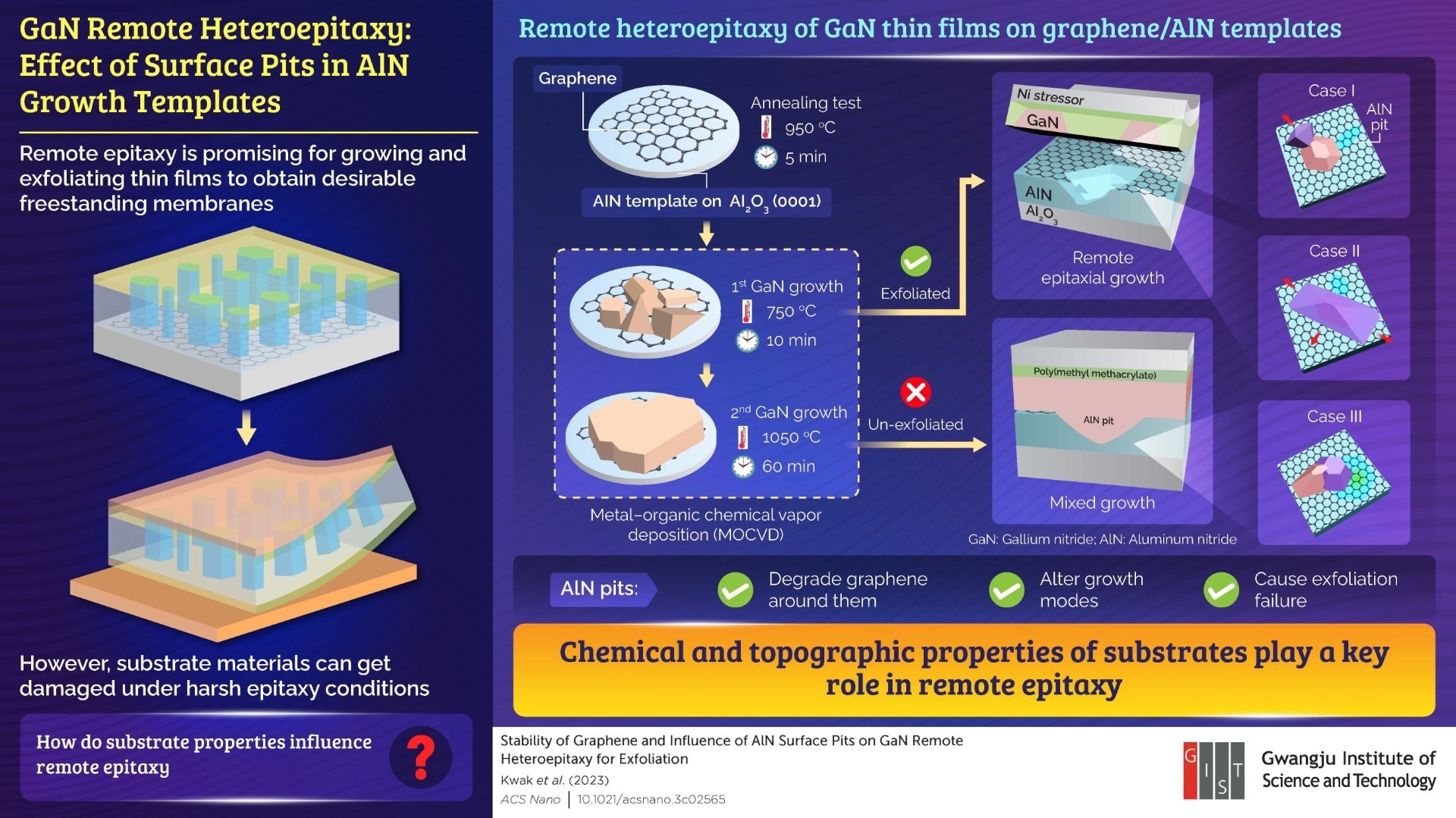
Distant epitaxy has been gaining consideration within the area of semiconductor manufacturing for rising skinny movies that replicate the crystal construction of the template, which may later be exfoliated to type freestanding membranes. Nonetheless, harsh epitaxy circumstances can usually trigger harm to the template supplies, equivalent to within the case of distant epitaxy of GaN skinny movies, promising supplies for light-emitting diodes, photodetectors, and energy digital gadgets, on graphene/AlN templates.
GaN distant heteroepitaxy has not been achieved by a normal steel–natural chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) approach as a result of excessive temperatures concerned within the course of. It has been reported that graphene positioned on a substrate in an excessive setting equivalent to excessive temperature or use of an energetic gasoline in MOCVD will get broken because of chemical instability, which causes failure to exfoliate grown GaN movies.
In opposition to this background, a group of researchers led by Dong-Seon Lee, Head of the Division of Semiconductor Engineering and Professor on the Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Pc Science on the Gwangju Institute of Science and Expertise, has just lately used distant epitaxy to develop GaN skinny movies on graphene/AlN templates by MOCVD and investigated the impact of floor pits in AlN on the expansion and exfoliation of those skinny movies. Their paper was made out there on-line on 6 June 2023 and printed in Quantity 17, Problem 12 of the journal ACS Nano on 27 June 2023.
The researchers first carried out an annealing check at 950 °C for five minutes to test the thermal stability of graphene on AlN. Primarily based on its outcomes, they developed a two-step course of to develop GaN skinny movies on the template by MOCVD. The primary GaN progress befell at 750 °C for 10 minutes, following which the second progress was carried out at 1050 °C for 60 minutes. The exfoliation of the thus-grown GaN skinny movies was used as a proof of success of the distant epitaxy course of. Whereas the movies grown at 750 °C could possibly be exfoliated efficiently, the separation failed after the second step progress.
Upon deeper evaluation, the group discovered that the nano-sized pits on AlN floor led to the degradation of graphene close to them at increased temperatures, which altered the expansion modes of GaN skinny movies. Because of this, GaN immediately bonded with the AlN substrate, inflicting the failure of movie exfoliation. “By means of this research, we revealed for the primary time that structural issues within the substrate can even trigger peeling failure. These outcomes exemplify the significance of chemical and topographic properties of templates for profitable distant epitaxy,” highlights Prof. Lee.
This research offers the first experimental knowledge that helps the secure implementation of the event of distant epitaxy. When requested in regards to the implications of the current work, Prof. Lee says: “Within the close to future, GaN distant epitaxy implementation is predicted to offer high-quality GaN semiconductors required for the electrical automobile business. Since substrate recycling is feasible, it’s anticipated to alter the large image of the prevailing semiconductor business. Additional, it is going to be attainable to beat Moore’s regulation.”
