A Microsoft Home windows coverage loophole has been noticed being exploited primarily by native Chinese language-speaking risk actors to forge signatures on kernel-mode drivers.
“Actors are leveraging a number of open-source instruments that alter the signing date of kernel mode drivers to load malicious and unverified drivers signed with expired certificates,” Cisco Talos mentioned in an exhaustive two-part report shared with The Hacker Information. “It is a main risk, as entry to the kernel gives full entry to a system, and due to this fact complete compromise.”
Following accountable disclosure, Microsoft mentioned it has taken steps to dam all certificates to mitigate the risk. It additional said that its investigation discovered “the exercise was restricted to the abuse of a number of developer program accounts and that no Microsoft account compromise has been recognized.”
The tech big, in addition to suspending developer program accounts concerned within the incident, emphasised that the risk actors had already gained administrative privileges on compromised techniques prior to make use of of the drivers.
It is price stating that the Home windows maker had rolled out related blocking protections in December 2022 to forestall ransomware attackers from utilizing Microsoft-signed drivers for post-exploitation exercise.
Driver signature enforcement, which requires kernel-mode drivers to be digitally signed with a certificates from Microsoft’s Dev Portal, is a essential line of protection towards malicious drivers, which might be doubtlessly weaponized to evade safety options, tamper with system processes, and preserve persistence.
The brand new weak spot found by Cisco Talos makes it attainable to forge signatures on kernel-mode drivers, thereby permitting Home windows certificates insurance policies to be bypassed.
That is made attainable on account of an exception carved out by Microsoft to keep up compatibility, which allows cross-signed drivers in the event that they have been “signed with an end-entity certificates issued previous to July twenty ninth 2015 that chains to a supported cross-signed [certificate authority].”
“The third exception creates a loophole that enables a newly compiled driver to be signed with non-revoked certificates issued previous to or expired earlier than July 29, 2015, supplied that the certificates chains to a supported cross-signed certificates authority,” the cybersecurity firm mentioned.
In consequence, a driver signed on this method is not going to be prevented from being loaded on a Home windows machine, thereby enabling risk actors to reap the benefits of the escape clause to deploy 1000’s of malicious, signed drivers with out submitting them to Microsoft for verification.
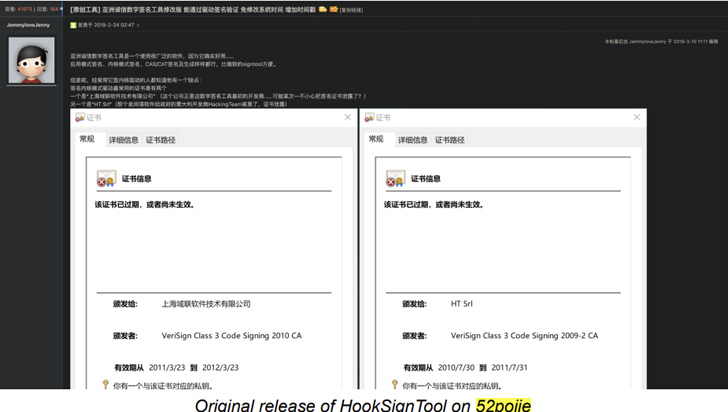
These rogue drivers are deployed utilizing signature timestamp forging software program resembling HookSignTool and FuckCertVerifyTimeValidity, which have been publicly obtainable since 2019 and 2018, respectively.
HookSignTool has been accessible through GitHub since January 7, 2020, whereas FuckCertVerifyTimeValidity was first dedicated to the code internet hosting service on December 14, 2018.
“HookSignTool is a driver signature forging device that alters the signing date of a driver through the signing course of by way of a mix of hooking into the Home windows API and manually altering the import desk of a official code signing device,” Cisco Talos defined.
Particularly, it includes hooking to the CertVerifyTimeValidity operate, which verifies the time validity of a certificates, to vary the signing timestamp throughout execution.
“This tiny undertaking prevents the signtool from verifing [sic] cert time validity and allow you to signal your bin with outdated cert with out altering system time manually,” the GitHub web page for FuckCertVerifyTimeValidity reads.
🔐 PAM Safety – Knowledgeable Options to Safe Your Delicate Accounts
This expert-led webinar will equip you with the data and techniques it’s worthwhile to rework your privileged entry safety technique.
“It set up hook into crypt32!CertVerifyTimeValidity and make it at all times return 0 and make kernel32!GetLocalTime return what you need as you’ll be able to add “-fuckyear 2011″ to signtool’s command line to signal a cert from 12 months 2011.”
That mentioned, pulling off a profitable forgery requires a non-revoked code signing certificates that was issued earlier than July 29, 2015, together with the certificates’s non-public key and passphrase.
Cisco Talos mentioned it found over a dozen code signing certificates with keys and passwords contained in a PFX file hosted on GitHub in a forked repository of FuckCertVerifyTimeValidity. It is not instantly clear how these certificates have been obtained.
What’s extra, it has been noticed that HookSignTool has been used to re-sign cracked drivers with a purpose to bypass digital rights administration (DRM) integrity checks, with an actor named “Juno_Jr” releasing a cracked model of PrimoCache, a official software program caching resolution, in a Chinese language software program cracking discussion board on November 9, 2022.
“Within the cracked model […], the patched driver was re-signed with a certificates initially issued to ‘Shenzhen Luyoudashi Expertise Co., Ltd.,’ which is contained within the PFX file on GitHub,” Talos researchers mentioned. “This potential to resign a cracked driver removes a major roadblock when making an attempt to bypass DRM checks in a signed driver.”
That is not all. HookSignTool can also be being utilized by a beforehand undocumented driver recognized as RedDriver to forge its signature timestamp. Lively since a minimum of 2021, it capabilities as a driver-based browser hijacker that leverages the Home windows Filtering Platform (WFP) to intercept browser visitors and reroute it to localhost (127.0.0.1).
The goal browser is chosen at random from a hard-coded listing containing the method names of many in style Chinese language language browsers like Liebao, QQ Browser, Sogou, and UC Browser, in addition to Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, and Mozilla Firefox.
“I initially discovered RedDriver whereas researching certificates timestamp forging on Home windows drivers,” Chris Neal, outreach researcher for Cisco Talos instructed The Hacker Information. “It was one of many first samples I bumped into that was instantly suspicious. What caught my consideration was the listing of internet browsers saved contained in the RedDriver file.”
The final word goal of this browser visitors redirection will not be clear, though it goes with out saying that such a functionality might be abused to tamper with browser visitors on the packet stage.
RedDriver an infection chains begin with the execution of a binary named “DnfClientShell32.exe,” which, in flip, initiates encrypted communications with a command-and-control (C2) server to obtain the malicious driver.
“We did not observe the supply of the preliminary file, but it surely’s very probably that the file was packaged to masquerade as a recreation file, and was hosted on a malicious obtain hyperlink,” Neal mentioned. “The sufferer most likely thought they have been downloading a file from a official supply and ran the executable. ‘DNFClient’ is the title of a file belonging to ‘Dungeon Fighter On-line’ which is an especially in style recreation in China and generally known as ‘DNF.'”
“RedDriver was probably developed by extremely expert risk actors as the educational curve for growing malicious drivers is steep,” Cisco Talos mentioned. “Whereas the risk seems to focus on native Chinese language audio system, the authors are probably Chinese language audio system as effectively.”
“The authors additionally demonstrated a familiarity or expertise with software program growth lifecycles, one other talent set that requires earlier growth expertise.”