The Web of Issues (IoT) is remodeling effectivity in varied sectors like healthcare and logistics however has additionally launched new safety dangers, significantly IoT-driven DDoS assaults. This text explores how these assaults work, why they’re uniquely problematic, and learn how to mitigate them.
What Is IoT?
IoT (Web of Issues) refers to on-line, interconnected units that gather and change information. This broad class of units consists of sensors, cameras, community routers, and superior equipment, and their integration into on a regular basis life and work processes ends in an ecosystem that may automate operations, enhance decision-making, and improve person expertise.
IoT: A Breeding Floor for Botnets
IoT’s speedy adoption amplifies its vulnerability, as poorly secured units change into simple prey for attackers and should change into a part of a botnet. Managed by attackers, botnets can scale and quickly execute varied assaults, together with DDoS, information theft, advert fraud, cryptocurrency mining, spam and phishing, information harvesting, and snooping—with out system homeowners’ data.
Why are IoT Botnets a Rising Concern?
Botnets are nothing new, however IoT botnets pose a particular menace. The variety of IoT units reached 16 billion in 2022 and is anticipated to exceed 30 billion by 2025. These units usually undergo from rare updates or insecure default settings, or are merely left unattended, making them much less safe than conventional computer systems and are vulnerable to being hijacked with relative ease to type potent botnets.
The dimensions and complexity of IoT-driven assaults are set to rise attributable to their growing use. Amongst these dangers, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults stand out as significantly difficult to mitigate. The distributed nature of IoT units renders them supreme platforms for these assaults, making it troublesome to establish and block malicious visitors and thereby compounding the challenges of DDoS mitigation.
Anatomy of IoT-Pushed botnet DDoS Assaults
Let’s focus on how IoT DDoS assaults occur and the way new IoT units be part of the ranks of bots.
How Are IoT DDoS Assaults Launched?
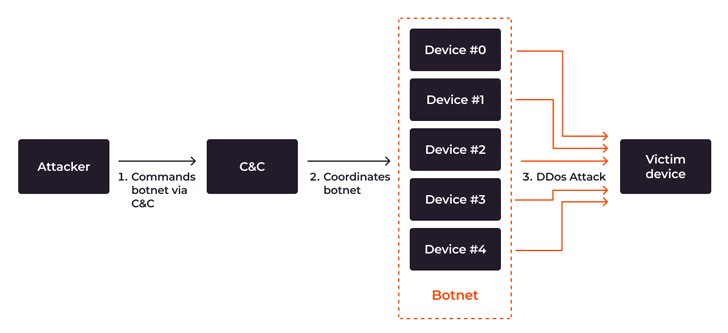
There are a number of key entities concerned in a DDoS botnet assault:
- The attacker is the one who controls the botnet. They’re often known as the bot herder or botmaster.
- A command-and-control (C&C) server is a pc managed by the attacker and used to speak with the contaminated units. The C&C orchestrates the botnet’s actions, sending out international instructions for duties like initiating an assault or scanning a brand new system for vulnerabilities.
- A botnet is a community of units which have been contaminated with malware and are managed by a single attacker.
- The sufferer or goal is the main target of a particular botnet-driven assault.
 |
| DDoS botnet assault circulation from attacker’s command to DDoS assault |
The assault course of is comparatively simple:
- The attacker targets the botnet to a sufferer. The botnet operator identifies the goal—often a tool, web site, or on-line service—that they wish to take down.
- The C&C server orchestrates the DDoS assault. The C&C server sends the attacker’s directions to all of the bots within the community to begin sending requests to the goal, and coordinates the botnet’s conduct.
- A flood of visitors happens. All of the bots within the community begin sending a lot of requests to the goal web site or server.
When the botnet floods the goal with extreme requests, service failures happen which jeopardize the provision of the focused system and even put the integrity of the entire infrastructure in danger. When aimed towards important infrastructures similar to healthcare or transportation, the hazards transcend monetary and reputational hurt to endangering individuals’s lives.
Incorporating IoT Gadgets into Botnets
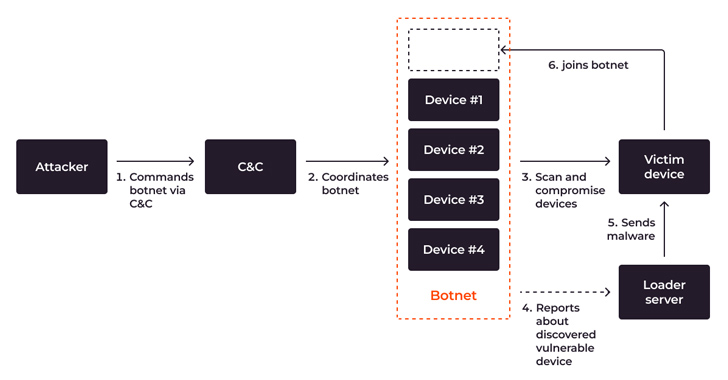
IoT units which can be unpatched, unattended, or misconfigured, or are already underneath botnet DDoS assault, are vulnerable to being included right into a botnet. To broaden the botnet, an attacker hacks new IoT units. This course of entails two entities: the botnet itself and the loader server, a particular server that infects different units.
In short, the method goes like this: The botnet hacks the system and features entry, after which the loader server installs malware on it. The attacker then features everlasting entry to the system and attaches it to the botnet. Listed here are the levels of infecting IoT units and connecting them to a botnet primarily based the Mirai case:
- Preliminary command: The attacker makes use of the C&C server to ship a command to the botnet for attacking and incorporating new units.
- Orchestration: The C&C server coordinates the botnet’s actions.
- Scanning and compromise: The botnet scans and compromises sufferer units to realize privileged entry by brute-forcing weak passwords or exploiting outdated firmware or insecure configurations.
- Knowledge reporting: The botnet relays the sufferer’s IP handle and entry credentials to the loader server as soon as the system is hacked.
- Malware supply and an infection: The loader server sends malware or malicious directions, that are then executed by a compromised system, turning it right into a bot.
- Becoming a member of the botnet: The newly contaminated system turns into a part of the botnet and awaits additional instructions, usually working undetected.
 |
| Course of circulation, demonstrating scanning, compromising, infecting and becoming a member of a brand new system to a botnet |
Superior botnets can self-propagate, compromising extra units autonomously, bringing increasingly more units into the botnet, increasing the botnet’s measurement and amplifying the dimensions of future assaults.
How Harmful Is the Present IoT DDoS Risk?
IoT-driven DDoS assaults elevated by 300% within the first half of 2023 alone, inflicting an estimated international monetary lack of $2.5 billion. In 2023, 90% of complicated, multi-vector DDoS assaults had been primarily based on botnets. The development reveals no indicators of slowing down: the variety of IoT units engaged in botnet-driven DDoS assaults rose from round 200,000 a 12 months in the past to roughly 1 million units, whereas there are twice as many vulnerabilities being focused by botnet malware.
General, DDoS assault capability is on the rise. In response to Gcore’s Radar 2023, the highest energy of a singular DDoS assault reached a staggering 800 Gbps within the first half of 2023. Simply two years earlier, it peaked at 300 Gbps. Whereas most assaults hit 1–2 Tbps speeds, essentially the most potent can attain 100 Tbps.
Alarming Projections for 2023–2024
We’re witnessing a important improve in particular DDoS assault vectors, similar to UDP reflection and HTTP request flooding, primarily focusing on the expertise and monetary industries. Sectors closely reliant on on-line providers and real-time information processing are essentially the most engaging targets, going through instant monetary losses and long-term reputational injury.
IoT’s development, whereas driving innovation, additionally brings alarming future traits in cybersecurity: it fuels innovation but in addition raises important cybersecurity issues. With an anticipated 18% development in IoT units to 14.4 billion in 2023, and a projected improve to 27 billion by 2025, consultants anticipate a corresponding surge in botnet assaults. With each IoT and DDoS on the rise, IoT DDoS are posed to change into an more and more substantial menace within the instant future.
Defensive Measures: Methods and Greatest Practices
The rise of extra refined and highly effective assaults makes instant consideration to safety important. Here is how varied stakeholders can contribute to a safer digital ecosystem:
1. Defend your IoT from being contaminated.
- Educate on protected IoT practices: Encourage residence and company customers to alter default passwords, replace firmware, and cling to finest practices to stop units from being compromised. Many firms, like SANS Institute, supply coaching on IoT safety and penetration testing.
- Collaborate and menace share: Initiatives just like the Cyber Risk Alliance and the Joint Cyber Protection Collaborative unite governments, tech firms, and cybersecurity corporations to quickly detect and neutralize rising threats, strengthening collective international defenses.
- Commonly replace units: Guarantee IoT units are up to date with the newest firmware and patches to stop recognized vulnerabilities from being exploited.
2. Defend towards IoT-driven botnet DDoS assaults.
- Implement multi-layer safety protocols: Deploy a complete safety technique, from firewalls and intrusion detection methods to internet software safety options.
- Put money into Specialised DDoS Safety Options: Corporations like Gcore have developed options explicitly designed to fight even huge, IoT-driven DDoS assaults. These DDoS safety options have been pivotal in decreasing dangers by leveraging real-time analytics.
Conclusion
The problem of defending towards IoT-driven DDoS assaults is an ongoing battle. By understanding present options, investing in specialised applied sciences like Gcore’s DDoS safety, and fostering a tradition of vigilance and collaboration, you may considerably cut back organizational dangers and assist pave the best way for a safer digital panorama within the face of escalating threats.