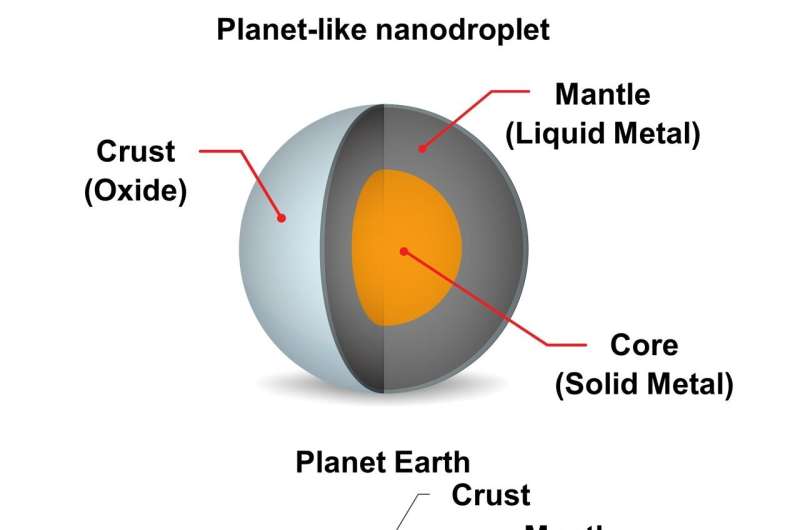
Liquid steel, planet-like nanodroplets have been efficiently fashioned with a brand new approach developed at RMIT College, Australia. Like our personal planet Earth, the nanodroplets function an outer “crust,” a liquid steel “mantle,” and a strong “core.”
The strong intermetallic core is the important thing to attaining a extra homogenous combine, “locking up” the identical quantity of solute (i.e., the “goal” metals) in every alloyed droplet.
The analysis group achieved homogeneity by way of full dissolution throughout the liquid-metal media, made attainable by high-temperature molten salt. Their article, “Synthesis of planet-like liquid steel nanodroplets with promising properties for catalysis,” was revealed in Superior Practical Supplies in July 2023.
The invention creates new analysis alternatives in basic liquid-metal chemistry in addition to purposes as numerous as versatile electronics, phase-change supplies, catalysts and gas cells, and silver-based antimicrobials.
Liquid steel nanodroplets shake aside
Liquid metals have emerged as a promising new frontier of chemical analysis in recent times, appearing as a novel response interface for solvents and catalysts.
They will additionally act as a practical materials providing excessive conductivity, attributable to delocalized metallic bonds, and a delicate, fluid inside.
With rising catalysis, sensing and nano-electronic purposes counting on attaining giant floor areas, synthesis of liquid steel nanodroplets has develop into an necessary focus.
There are various combos attainable when alloying for particular purposes, for instance dissolving copper (the solute) in liquid gallium (the metallic solvent).
The liquid-metal nanodroplets are created by mechanical agitation utilizing sound waves in a solvent similar to ethanol or water.
Nevertheless, throughout this “sonication” course of, liquid-metal alloys have tended to “de-alloy,” i.e., to interrupt aside into their constituent metals.
It is a results of earlier strategies making an attempt to dissolve the metals at comparatively low temperatures, close to room temperature. “Simply because it’s attainable to dissolve extra sugar in heat water than in chilly water, extra copper will be dissolved in hotter gallium,” says lead creator Caiden Parker, a Ph.D. candidate at RMIT.
At low temperatures, among the solute steel re-forms into bigger, strong particles earlier than full dissolution.
The ensuing composition has inconsistent, inhomogeneous properties, with the composition of particular person nanodroplets various significantly. “In excessive circumstances, many and even most nanodroplets could also be basically devoid of the solute steel, which finally ends up being concentrated in solely only a few particles,” says corresponding creator Dr. Torben Daeneke, additionally at RMIT.
This inhomogeneity and the presence of intermetallic compounds poses appreciable difficulties for researchers wishing to grasp the elemental mechanisms at work in liquid steel chemistry.
Excessive-temperatures and salts type homogenous, planet-like nanodroplets
Within the new examine, RMIT researchers resolved the issue of dealloying by considerably heating the synthesis course of (as excessive as 400°C) to make sure the solute steel is totally dissolved and introducing a fastidiously chosen molten-salt suspension fluid.
Sodium acetate was chosen as a result of it stays steady at excessive temperature and will be simply eliminated afterwards.
The ensuing nanodroplets function an fascinating planet-like construction consisting of an outer (oxide) shell, a liquid (steel) mantle and a suspended, strong central core (intermetallic).
“We have been instantly struck by the nanodroplets’ similarity to an Earth-like planet, with a strong outer shell, a liquid steel mantle, and a strong steel core,” says Caiden.
That strong core is the important thing to the success of the brand new approach, “locking up” the identical quantity of solute in every alloyed droplet.
“We have been additionally delighted to see that our new metallic planet-like nanodroplets have been all over the place,” continues Caiden.
The system was homogenously unfold, with output yield considerably improved. Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) evaluation confirmed the core construction is noticed in nearly each droplet.
The presence of the strong core additionally promotes a really fascinating use for the planet-like nanodroplets in catalytic reactions, dashing up chemical reactions.
The copper-gallium nanodroplets studied supplied promising ends in electrocatalytic oxidation of ethanol, which could possibly be utilized in ethanol gas cells.
Elimination of the sodium acetate is necessary previous to this catalytic response, with the salt simply cleaned away in easy water baths.
What’s subsequent?
The promising new approach opens up the potential use of high-surface space nanodroplets in a variety of future purposes, together with, however not restricted to, electronics or catalytic supplies.
The bodily scale of the nanodroplets (i.e., nano somewhat than micro) may even help basic research of liquid-metal chemistry, together with trying into the exact nature of bond formation inside liquid metals, solvation capabilities, crystallization dynamics and the final colloidal chemistry that will happen inside numerous molten steel techniques.
“The planet-like constructions are like little miniature laboratories, permitting us to review how molten metals behave at an atomic degree,” says Torben.
Whereas the examine proved viability of the brand new approach utilizing a copper-gallium system, the authors count on additional work to substantiate that the approach will likely be profitable utilizing different combos of solute and solvent alloy techniques, starting with silver, zinc, or bismuth in liquid gallium, tin or indium.
“A key benefit of liquid-metal techniques is the power to regulate the steel combine for sure purposes, depending on the properties of the constituent metals,” says Caiden.
“For instance, copper is a good electrical conductor. After we mix copper with gallium, we not solely save vital value in materials consumption, but additionally open the way in which to versatile electronics, similar to what you might need seen in sci-fi films.”
Doubtlessly, copper may also be utilized for its thermal properties, with potential utility of copper-based nanodroplets in warmth dissipation techniques.
Nanodroplet catalysis purposes based mostly on the power of copper to hurry up reactions has already been examined within the new examine, with improved active-site space along with materials synthesis financial savings.
Taking a look at one other steel, silver has beforehand discovered purposes based mostly on its anti-microbial properties, and as soon as mixed with gallium may create a extra bioavailable various.
“Thus the potential purposes of the brand new know-how are extraordinarily large. Any industries in want of nanomaterials can make the most of the system, with constituent metals various based on utility,” says Torben.
Extra data:
Caiden J. Parker et al, Synthesis of Planet‐Like Liquid Steel Nanodroplets with Promising Properties for Catalysis, Superior Practical Supplies (2023). DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202304248
Quotation:
Liquid steel nanodroplets fashioned with new approach have promising properties for catalysis (2023, July 14)
retrieved 14 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-liquid-metal-nanodroplets-technique-properties.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

