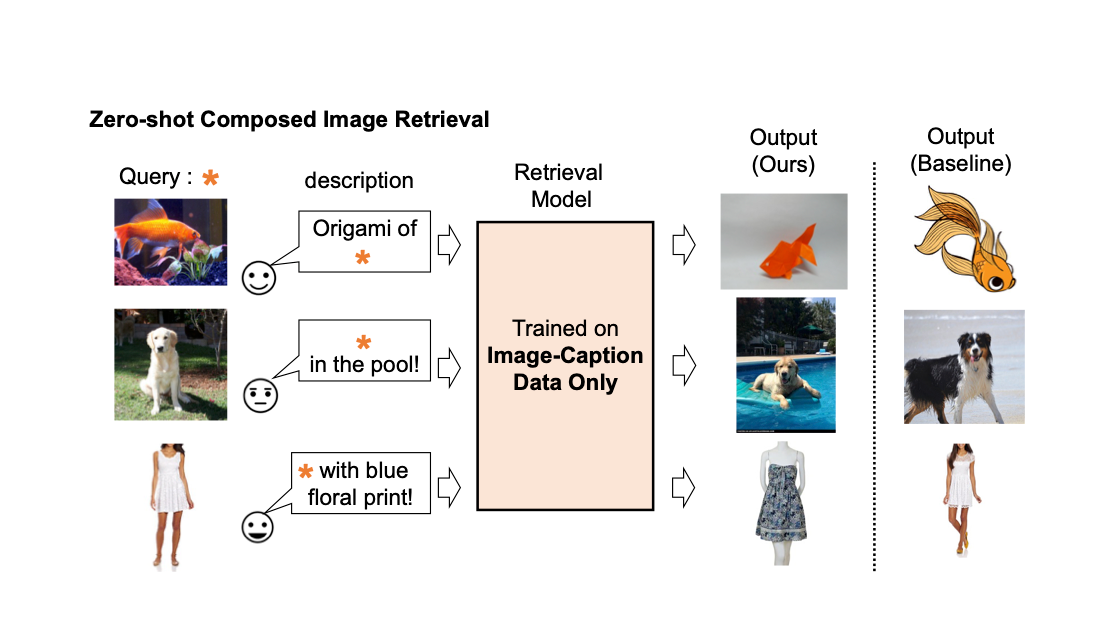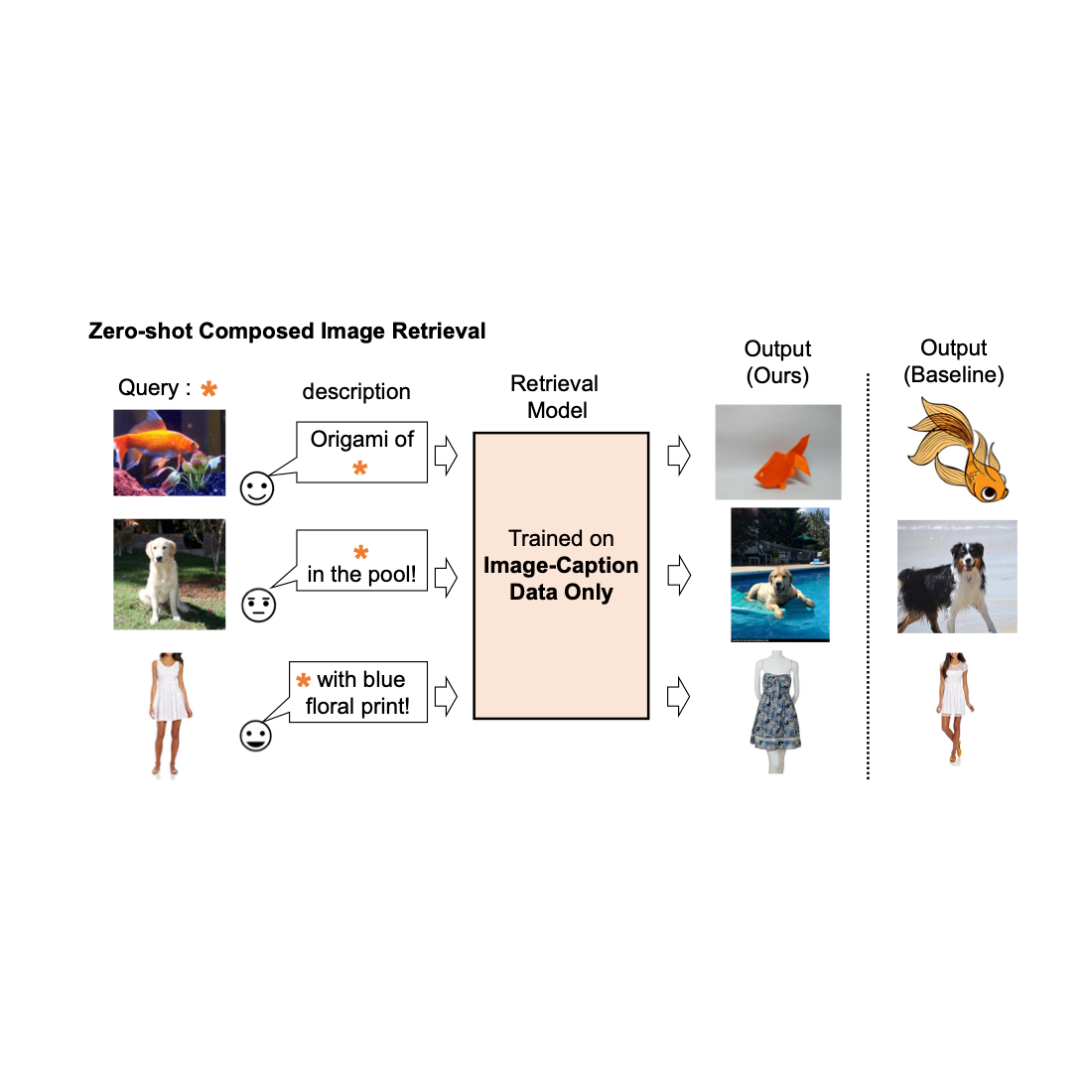
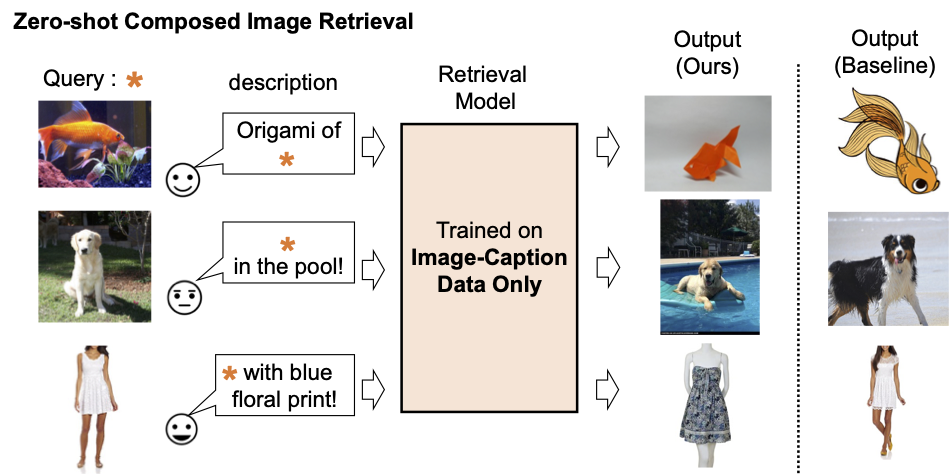
Picture retrieval performs a vital position in serps. Usually, their customers depend on both picture or textual content as a question to retrieve a desired goal picture. Nevertheless, text-based retrieval has its limitations, as describing the goal picture precisely utilizing phrases might be difficult. As an example, when looking for a style merchandise, customers might want an merchandise whose particular attribute, e.g., the colour of a emblem or the brand itself, is totally different from what they discover in an internet site. But looking for the merchandise in an current search engine isn’t trivial since exactly describing the style merchandise by textual content might be difficult. To handle this reality, composed picture retrieval (CIR) retrieves photos primarily based on a question that mixes each a picture and a textual content pattern that gives directions on learn how to modify the picture to suit the supposed retrieval goal. Thus, CIR permits exact retrieval of the goal picture by combining picture and textual content.
Nevertheless, CIR strategies require massive quantities of labeled information, i.e., triplets of a 1) question picture, 2) description, and three) goal picture. Accumulating such labeled information is expensive, and fashions educated on this information are sometimes tailor-made to a particular use case, limiting their capacity to generalize to totally different datasets.
To handle these challenges, in “Pic2Word: Mapping Footage to Phrases for Zero-shot Composed Picture Retrieval”, we suggest a job known as zero-shot CIR (ZS-CIR). In ZS-CIR, we goal to construct a single CIR mannequin that performs quite a lot of CIR duties, akin to object composition, attribute enhancing, or area conversion, with out requiring labeled triplet information. As an alternative, we suggest to coach a retrieval mannequin utilizing large-scale image-caption pairs and unlabeled photos, that are significantly simpler to gather than supervised CIR datasets at scale. To encourage reproducibility and additional advance this house, we additionally launch the code.
 |
| Description of current composed picture retrieval mannequin. |
 |
| We practice a composed picture retrieval mannequin utilizing image-caption information solely. Our mannequin retrieves photos aligned with the composition of the question picture and textual content. |
Technique overview
We suggest to leverage the language capabilities of the language encoder within the contrastive language-image pre-trained mannequin (CLIP), which excels at producing semantically significant language embeddings for a variety of textual ideas and attributes. To that finish, we use a light-weight mapping sub-module in CLIP that’s designed to map an enter image (e.g., a photograph of a cat) from the picture embedding house to a phrase token (e.g., “cat”) within the textual enter house. The entire community is optimized with the vision-language contrastive loss to once more make sure the visible and textual content embedding areas are as shut as attainable given a pair of a picture and its textual description. Then, the question picture might be handled as if it’s a phrase. This allows the versatile and seamless composition of question picture options and textual content descriptions by the language encoder. We name our methodology Pic2Word and supply an outline of its coaching course of within the determine under. We wish the mapped token s to characterize the enter picture within the type of phrase token. Then, we practice the mapping community to reconstruct the picture embedding within the language embedding, p. Particularly, we optimize the contrastive loss proposed in CLIP computed between the visible embedding v and the textual embedding p.
 |
| Coaching of the mapping community (fM) utilizing unlabeled photos solely. We optimize solely the mapping community with a frozen visible and textual content encoder. |
Given the educated mapping community, we will regard a picture as a phrase token and pair it with the textual content description to flexibly compose the joint image-text question as proven within the determine under.
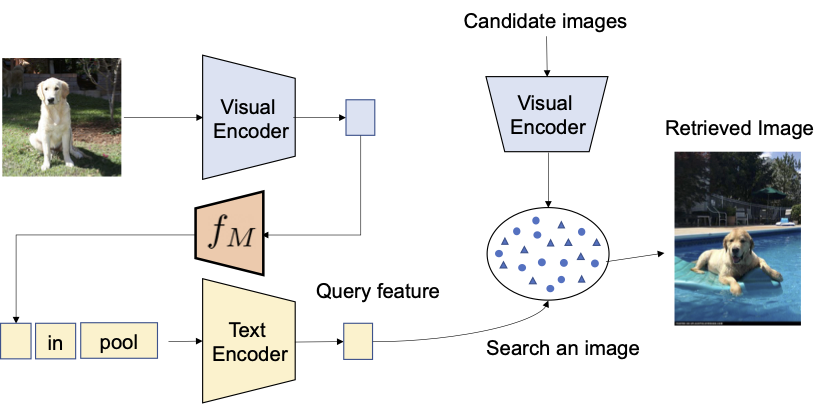 |
| With the educated mapping community, we regard the picture as a phrase token and pair it with the textual content description to flexibly compose the joint image-text question. |
Analysis
We conduct quite a lot of experiments to guage Pic2Word’s efficiency on quite a lot of CIR duties.
Area conversion
We first consider the potential of compositionality of the proposed methodology on area conversion — given a picture and the specified new picture area (e.g., sculpture, origami, cartoon, toy), the output of the system must be a picture with the identical content material however within the new desired picture area or fashion. As illustrated under, we consider the flexibility to compose the class info and area description given as a picture and textual content, respectively. We consider the conversion from actual photos to 4 domains utilizing ImageNet and ImageNet-R.
To check with approaches that don’t require supervised coaching information, we choose three approaches: (i) picture solely performs retrieval solely with visible embedding, (ii) textual content solely employs solely textual content embedding, and (iii) picture + textual content averages the visible and textual content embedding to compose the question. The comparability with (iii) exhibits the significance of composing picture and textual content utilizing a language encoder. We additionally examine with Combiner, which trains the CIR mannequin on Trend-IQ or CIRR.
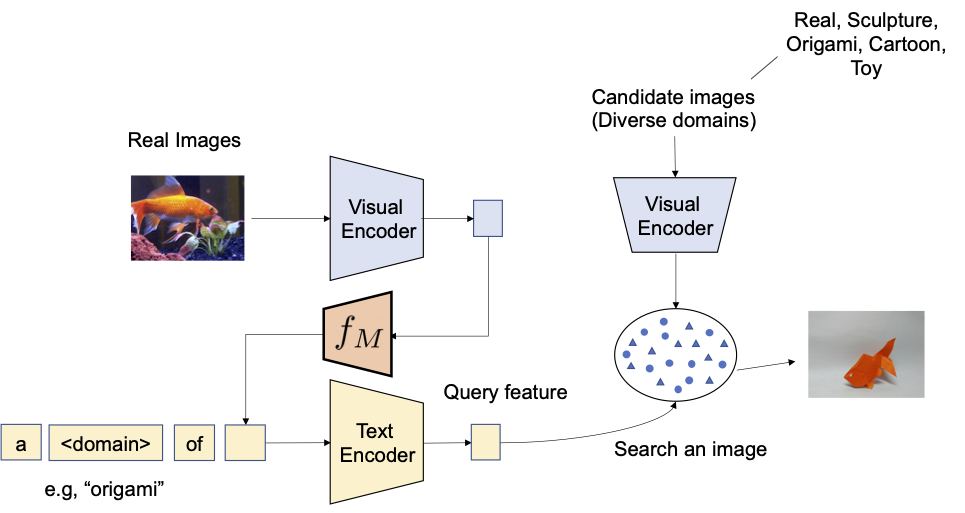 |
| We goal to transform the area of the enter question picture into the one described with textual content, e.g., origami. |
As proven in determine under, our proposed method outperforms baselines by a big margin.
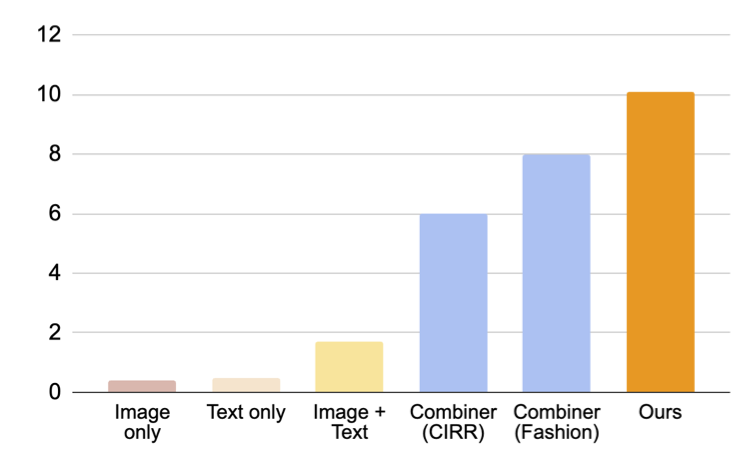 |
| Outcomes (recall@10, i.e., the proportion of related cases within the first 10 photos retrieved.) on composed picture retrieval for area conversion. |
Trend attribute composition
Subsequent, we consider the composition of style attributes, akin to the colour of material, emblem, and size of sleeve, utilizing the Trend-IQ dataset. The determine under illustrates the specified output given the question.
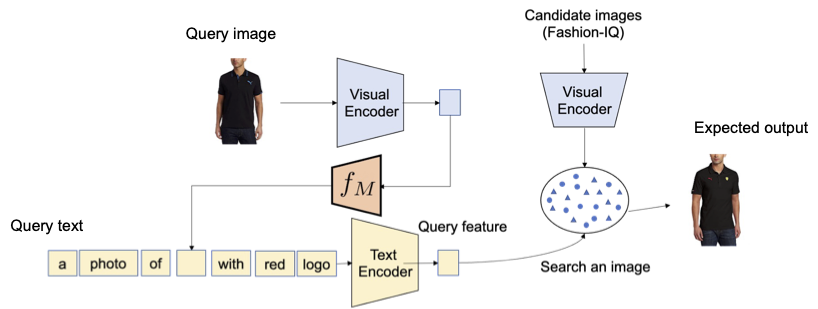 |
| Overview of CIR for style attributes. |
Within the determine under, we current a comparability with baselines, together with supervised baselines that utilized triplets for coaching the CIR mannequin: (i) CB makes use of the identical structure as our method, (ii) CIRPLANT, ALTEMIS, MAAF use a smaller spine, akin to ResNet50. Comparability to those approaches will give us the understanding on how nicely our zero-shot method performs on this job.
Though CB outperforms our method, our methodology performs higher than supervised baselines with smaller backbones. This consequence means that by using a strong CLIP mannequin, we will practice a extremely efficient CIR mannequin with out requiring annotated triplets.
 |
| Outcomes (recall@10, i.e., the proportion of related cases within the first 10 photos retrieved.) on composed picture retrieval for Trend-IQ dataset (larger is best). Gentle blue bars practice the mannequin utilizing triplets. Word that our method performs on par with these supervised baselines with shallow (smaller) backbones. |
Qualitative outcomes
We present a number of examples within the determine under. In comparison with a baseline methodology that doesn’t require supervised coaching information (textual content + picture function averaging), our method does a greater job of appropriately retrieving the goal picture.
 |
| Qualitative outcomes on numerous question photos and textual content description. |
Conclusion and future work
On this article, we introduce Pic2Word, a technique for mapping photos to phrases for ZS-CIR. We suggest to transform the picture right into a phrase token to realize a CIR mannequin utilizing solely an image-caption dataset. By means of quite a lot of experiments, we confirm the effectiveness of the educated mannequin on numerous CIR duties, indicating that coaching on an image-caption dataset can construct a robust CIR mannequin. One potential future analysis path is using caption information to coach the mapping community, though we use solely picture information within the current work.
Acknowledgements
This analysis was performed by Kuniaki Saito, Kihyuk Sohn, Xiang Zhang, Chun-Liang Li, Chen-Yu Lee, Kate Saenko, and Tomas Pfister. Additionally because of Zizhao Zhang and Sergey Ioffe for his or her precious suggestions.