
Floor cracks and biofilms on plastic particles would possibly assist unfold air pollution
Issues about microplastic air pollution come up not solely due to the particles themselves, but in addition from no matter cargo they may be carrying. A latest examine studies on their tendency to build up heavy metals.
Led by researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan College, the examine centered on polystyrene foam, amassing particles alongside the Tuul river operating via Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. Important ranges of heavy metals appear to build up on the particles, reflecting native land use and industries. Floor options reminiscent of holes and biofilms additionally improve this propensity to gather pollution.
Although microplastics are largely chemically inert, scientists at the moment are discovering that they can be efficient vectors for no matter may be absorbed on them, together with poisonous pollution. A lot analysis is underway on what kinds of poisons they could assist transport, and the way.
Concerning Ulaanbaatar, the main target of this examine, it’s clear that the town’s growth has given rise to plastic waste from building supplies, which appears to be ubiquitous, notably polystyrene foam utilized in insulation. The examine subjected these tiny fragments to a variety of diagnostics to determine how they’d modified, and what they now contained. They discovered a variety of metallic contaminants (i.e., not current within the unique materials), notably giant quantities of copper and chromium. Sturdy indicators have been discovered for metals related to particular land makes use of or industries within the metropolis, reminiscent of chemical compounds utilized in glass and ceramics manufacture and pollutant-enriched sediments from wastewater remedy vegetation.
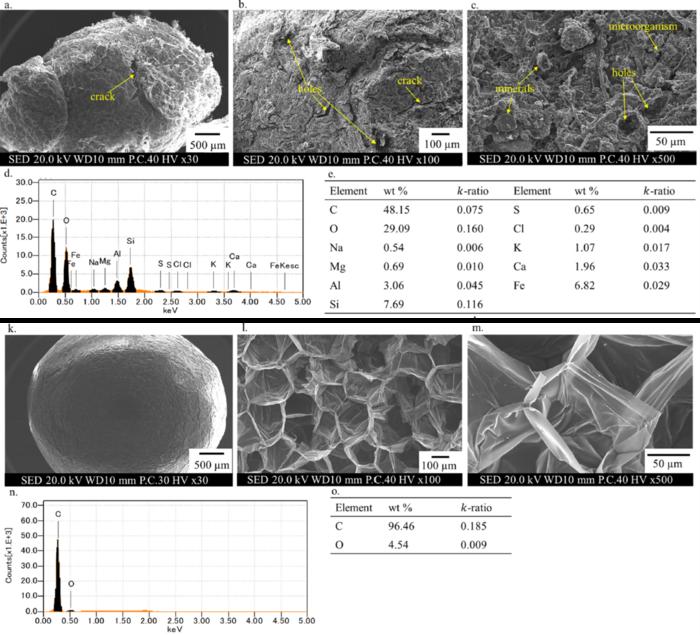
Additionally they seemed intimately on the bodily properties of the particles themselves. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) pictures of the particles confirmed that publicity to the atmosphere had considerably modified the floor properties of the particles, creating fractures, holes, and pits. Lots of the pictures additionally confirmed mineral crystal particles, exhibiting how the roughened floor may grow to be dwelling to inorganic pollution absorbed from the atmosphere.
Additionally they discovered traces of biofilms, layers of micro organism which adhere to surfaces. Such movies are identified to develop electrical costs and chemical teams on their surfaces which might successfully take up metallic contaminants. Mixed with the stronger accumulation of metals in meso-sized (5-20mm) particles than in micro-sized (<5mm) particles, the group concluded that these floor options performed a key function within the assortment of heavy metals on plastic particles.
By working to achieve perception into the mechanism by which metals are adsorbed onto plastic fragments, the group say they hope to become familiar with the scope of the affect of plastic pollution within the atmosphere.
This work was supported by a Tokyo Metropolitan Authorities Superior Analysis Grant.
