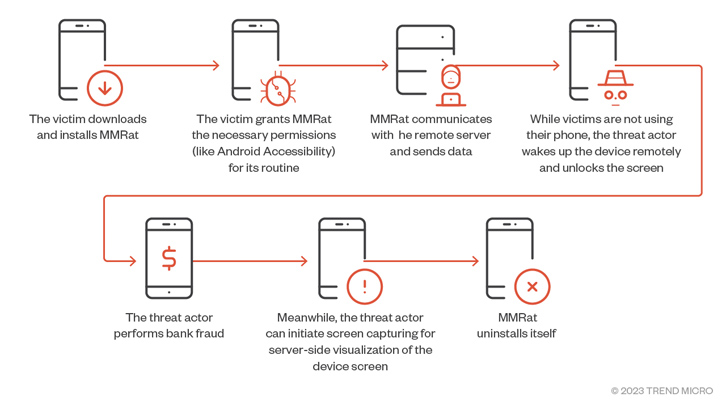
A beforehand undocumented Android banking trojan dubbed MMRat has been noticed concentrating on cell customers in Southeast Asia since late June 2023 to remotely commandeer the gadgets and carry out monetary fraud.
“The malware, named after its distinctive package deal title com.mm.person, can seize person enter and display content material, and can even remotely management sufferer gadgets by numerous strategies, enabling its operators to hold out financial institution fraud on the sufferer’s system,” Development Micro mentioned.
What makes MMRat stand other than others of its form is using a custom-made command-and-control (C2) protocol based mostly on protocol buffers (aka protobuf) to effectively switch giant volumes of knowledge from compromised handsets, demonstrating the rising sophistication of Android malware.
Doable targets based mostly on the language used within the phishing pages embrace Indonesia, Vietnam, Singapore, and the Philippines.

The entry level of the assaults is a community of phishing websites that mimic official app shops, though how victims are directed to those hyperlinks is presently unknown. MMRat usually masquerades as an official authorities or a courting app.
As soon as put in, the app leans closely on Android accessibility service and MediaProjection API, each of which have been leveraged by one other Android monetary trojan referred to as SpyNote, to hold out its actions. The malware can be able to abusing its accessibility permissions to grant itself different permissions and modify settings.
It additional units up persistence to outlive between reboots and initiates communications with a distant server to await directions and exfiltrate the outcomes of the execution of these instructions again to it. The trojan employs totally different combos of ports and protocols for features comparable to information exfiltration, video streaming, and C2 management.
MMRat possesses the power to gather a broad vary of system information and private data, together with sign energy, display standing, and battery stats, put in purposes, and speak to lists. It is suspected that the risk actor makes use of the small print to hold out some type of sufferer profiling earlier than shifting to the subsequent stage.
A few of the different options of MMRat embody recording real-time display content material and capturing the lock display sample in order to permit the risk actor to remotely acquire entry to the sufferer’s system when it’s locked and never actively in use.

“The MMRat malware abuses the Accessibility service to remotely management the sufferer’s system, performing actions comparable to gestures, unlocking screens, and inputting textual content, amongst others,” Development Micro mentioned.
“This can be utilized by risk actors — along side stolen credentials — to carry out financial institution fraud.”
The assaults finish with MMRat deleting itself upon receiving the C2 command UNINSTALL_APP, which usually takes place after a profitable fraudulent transaction, successfully eradicating all traces of an infection from the system.
To mitigate threats posed by such potent malware, it is really useful that customers solely obtain apps from official sources, scrutinize app evaluations, and examine the permissions an app requests for entry to earlier than utilization.