Drugs is an inherently multimodal self-discipline. When offering care, clinicians routinely interpret information from a variety of modalities together with medical photographs, medical notes, lab exams, digital well being data, genomics, and extra. During the last decade or so, AI methods have achieved expert-level efficiency on particular duties inside particular modalities — some AI methods processing CT scans, whereas others analyzing excessive magnification pathology slides, and nonetheless others trying to find uncommon genetic variations. The inputs to those methods are typically advanced information corresponding to photographs, and so they usually present structured outputs, whether or not within the type of discrete grades or dense picture segmentation masks. In parallel, the capacities and capabilities of enormous language fashions (LLMs) have change into so superior that they’ve demonstrated comprehension and experience in medical information by each deciphering and responding in plain language. However how will we carry these capabilities collectively to construct medical AI methods that may leverage data from all these sources?
In in the present day’s weblog publish, we define a spectrum of approaches to bringing multimodal capabilities to LLMs and share some thrilling outcomes on the tractability of constructing multimodal medical LLMs, as described in three current analysis papers. The papers, in flip, define how one can introduce de novo modalities to an LLM, how one can graft a state-of-the-art medical imaging basis mannequin onto a conversational LLM, and first steps in direction of constructing a very generalist multimodal medical AI system. If efficiently matured, multimodal medical LLMs would possibly function the idea of recent assistive applied sciences spanning skilled drugs, medical analysis, and shopper functions. As with our prior work, we emphasize the necessity for cautious analysis of those applied sciences in collaboration with the medical neighborhood and healthcare ecosystem.
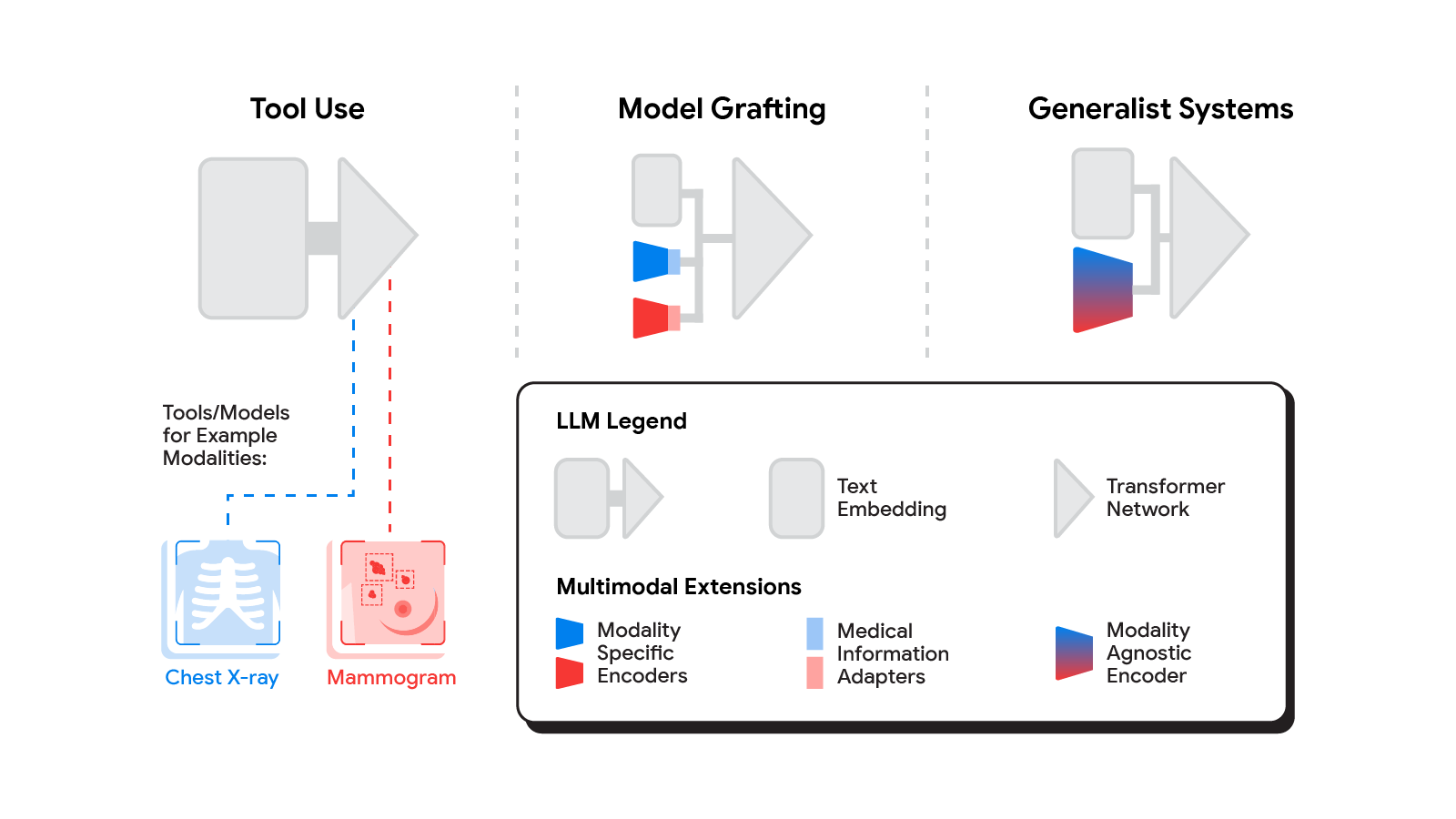
A spectrum of approaches
A number of strategies for constructing multimodal LLMs have been proposed in current months [1, 2, 3], and little question new strategies will proceed to emerge for a while. For the aim of understanding the alternatives to carry new modalities to medical AI methods, we’ll contemplate three broadly outlined approaches: device use, mannequin grafting, and generalist methods.
Instrument use
Within the device use method, one central medical LLM outsources evaluation of knowledge in numerous modalities to a set of software program subsystems independently optimized for these duties: the instruments. The frequent mnemonic instance of device use is educating an LLM to make use of a calculator reasonably than do arithmetic by itself. Within the medical house, a medical LLM confronted with a chest X-ray might ahead that picture to a radiology AI system and combine that response. This could possibly be completed through utility programming interfaces (APIs) provided by subsystems, or extra fancifully, two medical AI methods with completely different specializations partaking in a dialog.
This method has some vital advantages. It permits most flexibility and independence between subsystems, enabling well being methods to combine and match merchandise between tech suppliers based mostly on validated efficiency traits of subsystems. Furthermore, human-readable communication channels between subsystems maximize auditability and debuggability. That mentioned, getting the communication proper between unbiased subsystems may be difficult, narrowing the data switch, or exposing a threat of miscommunication and data loss.
Mannequin grafting
A extra built-in method can be to take a neural community specialised for every related area, and adapt it to plug immediately into the LLM — grafting the visible mannequin onto the core reasoning agent. In distinction to device use the place the particular device(s) used are decided by the LLM, in mannequin grafting the researchers might select to make use of, refine, or develop particular fashions throughout improvement. In two current papers from Google Analysis, we present that that is in truth possible. Neural LLMs usually course of textual content by first mapping phrases right into a vector embedding house. Each papers construct on the thought of mapping information from a brand new modality into the enter phrase embedding house already acquainted to the LLM. The primary paper, “Multimodal LLMs for well being grounded in individual-specific information”, exhibits that bronchial asthma threat prediction within the UK Biobank may be improved if we first practice a neural community classifier to interpret spirograms (a modality used to evaluate respiratory capability) after which adapt the output of that community to function enter into the LLM.
The second paper, “ELIXR: In direction of a basic objective X-ray synthetic intelligence system by alignment of enormous language fashions and radiology imaginative and prescient encoders”, takes this identical tack, however applies it to full-scale picture encoder fashions in radiology. Beginning with a basis mannequin for understanding chest X-rays, already proven to be a great foundation for constructing quite a lot of classifiers on this modality, this paper describes coaching a light-weight medical data adapter that re-expresses the highest layer output of the inspiration mannequin as a sequence of tokens within the LLM’s enter embeddings house. Regardless of fine-tuning neither the visible encoder nor the language mannequin, the ensuing system shows capabilities it wasn’t educated for, together with semantic search and visible query answering.
 |
| Our method to grafting a mannequin works by coaching a medical data adapter that maps the output of an present or refined picture encoder into an LLM-understandable kind. |
Mannequin grafting has a number of benefits. It makes use of comparatively modest computational sources to coach the adapter layers however permits the LLM to construct on present highly-optimized and validated fashions in every information area. The modularization of the issue into encoder, adapter, and LLM elements may facilitate testing and debugging of particular person software program elements when creating and deploying such a system. The corresponding disadvantages are that the communication between the specialist encoder and the LLM is not human readable (being a sequence of excessive dimensional vectors), and the grafting process requires constructing a brand new adapter for not simply each domain-specific encoder, but additionally each revision of every of these encoders.
Generalist methods
Probably the most radical method to multimodal medical AI is to construct one built-in, totally generalist system natively able to absorbing data from all sources. In our third paper on this space, “In direction of Generalist Biomedical AI”, reasonably than having separate encoders and adapters for every information modality, we construct on PaLM-E, a lately printed multimodal mannequin that’s itself a mixture of a single LLM (PaLM) and a single imaginative and prescient encoder (ViT). On this arrange, textual content and tabular information modalities are coated by the LLM textual content encoder, however now all different information are handled as a picture and fed to the imaginative and prescient encoder.
We specialize PaLM-E to the medical area by fine-tuning the whole set of mannequin parameters on medical datasets described within the paper. The ensuing generalist medical AI system is a multimodal model of Med-PaLM that we name Med-PaLM M. The versatile multimodal sequence-to-sequence structure permits us to interleave numerous sorts of multimodal biomedical data in a single interplay. To the very best of our information, it’s the first demonstration of a single unified mannequin that may interpret multimodal biomedical information and deal with a various vary of duties utilizing the identical set of mannequin weights throughout all duties (detailed evaluations within the paper).
This generalist-system method to multimodality is each essentially the most bold and concurrently most elegant of the approaches we describe. In precept, this direct method maximizes flexibility and data switch between modalities. With no APIs to keep up compatibility throughout and no proliferation of adapter layers, the generalist method has arguably the best design. However that very same magnificence can also be the supply of a few of its disadvantages. Computational prices are sometimes increased, and with a unitary imaginative and prescient encoder serving a variety of modalities, area specialization or system debuggability might endure.
The fact of multimodal medical AI
To profit from AI in drugs, we’ll want to mix the power of knowledgeable methods educated with predictive AI with the flexibleness made attainable by generative AI. Which method (or mixture of approaches) will likely be most helpful within the subject depends upon a large number of as-yet unassessed elements. Is the flexibleness and ease of a generalist mannequin extra invaluable than the modularity of mannequin grafting or device use? Which method provides the best high quality outcomes for a selected real-world use case? Is the popular method completely different for supporting medical analysis or medical training vs. augmenting medical follow? Answering these questions would require ongoing rigorous empirical analysis and continued direct collaboration with healthcare suppliers, medical establishments, authorities entities, and healthcare business companions broadly. We expect to find the solutions collectively.