Researchers on the Dalian College of Expertise have constructed a design of copper nanowire assemblies that may significantly enhance the defrosting and de-icing effectivity with no predictable power enter. Particularly, the defrosting effectivity reaches 100%, a record-high worth in comparison with reported research.
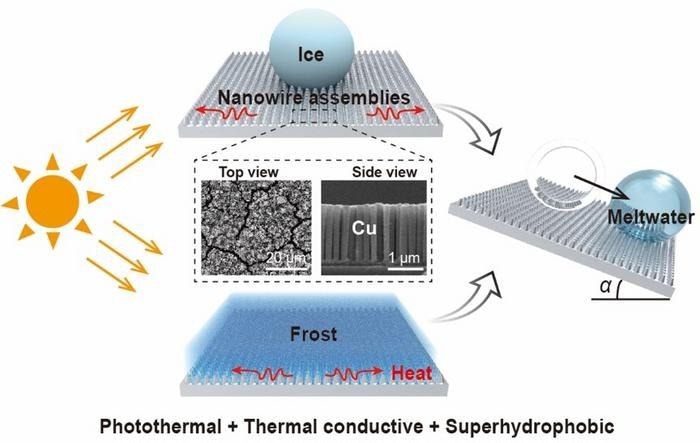
The analysis was revealed in Worldwide Journal of Excessive Manufacturing. It shows an easy electrochemical method for fabricating nanowire assemblies utilizing a managed sample, dimension, and hierarchy. This facilitates the concurrent presentation of thermally conductive, photothermal, and superhydrophobic properties, that are unattainable for standard surfaces in any other case.
The photothermal property ensures environment friendly daylight absorption, the thermal conductive property bestows fast lateral warmth conduction following daylight absorption, and the superhydrophobic property forces the rolling or sliding away of frost/ice upon melting from the floor.
Frost and ice buildup pose appreciable challenges in lots of purposes.
Conventional de-icing/defrosting options primarily depend on mechanical, thermal, and chemical approaches, but, all of that are both energy-intensive, labor-intensive, or environmentally unfriendly. Moreover, a few of these lively approaches required direct contact with the fabric floor, posing dangers to delicate coatings. To realize energy-saving and eco-friendly deicing/defrosting with out compromising the floor performance, most efforts have shifted in the direction of passive approaches by way of floor modifications.
Siyan Yangthe Research First Creator and Postdoc, Hong Kong Polytechnic College
Current consideration has targeted on photothermal surfaces with superhydrophobicity that may very well be heated with daylight, a inexperienced power supply. Most surfaces, nevertheless, endure from uneven and localized heating owing to inferior thermal conductivity. Therefore, additional assembling such floor properties utilizing thermally conductive supplies, significantly metals, comes with an awesome risk for defrosting and de-icing, which is massively unexplored.
To handle the above points, we develop a facile fabrication method to provide controllable copper nanowire assemblies. We discovered the morphology, top, and scale of the assemblies may be nicely tuned by adjusting the electrochemical parameters. By way of wettability and photothermal checks, we discovered that the majority of nanowire assemblies may be handled superhydrophobic, with a daylight absorption price bigger than 95%. Due to the excessive conductivity of copper supplies, nanowire assemblies, particularly the design with upright nanowires and a mean microgroove width of 2-3 μm, allow superior de-icing and defrosting performances.
Qixun Li, Research First Co-Creator and PhD Scholar, Dalian College of Expertise
This breakthrough design may end up in 2-3 instances shorter whole defrosting durations in comparison with the opposite three nanostructured surfaces with superhydrophobicity, photothermal impact, or a combination thereof. Remarkably, this design attains the very best defrosting effectivity (~100%) than the earlier works.
In precept, infusing the simple fabrication, excessive controllability, and variety in morphology, the design of nanowire assemblies is promising in broad de-icing and defrosting purposes that take away the necessity for conventional power enter. Nonetheless, the sturdiness, scalability, and chemical stability of the nanowire assemblies are restricted in sensible purposes involving advanced working circumstances. It’s essential to develop extra normal micro/nano materials processing strategies to enhance manufacturing effectivity, materials scale, and floor sturdiness. Regardless of this, the design idea of this work serves as a compass for future analysis endeavors, particularly in chilly areas dealing with energy scarcity.
Xuehu Ma, Research Corresponding Creator and Chemical Engineering Professor, Dalian College of Expertise
Journal Reference:
Yang, S., et al. (2023) Photothermal superhydrophobic copper nanowire assemblies: fabrication and deicing/defrosting purposes. Worldwide Journal of Excessive Manufacturing. dx.doi.org/10.1088/2631-7990/acef78.
Supply: http://ijemnet.com/

