| Aug 21, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Latest analysis in cell biology highlights groundbreaking outcomes. A global group of researchers have just lately established a instrument they developed to review the mechanics of the cell. The instrument can be utilized to review the internal forces of the cell, for instance, the stretching of the nuclear membrane. The microscopic power sensor, solely about 0.00002 mm lengthy, is constructed of unique components comparable to spider internet protein elements, fluorescent proteins from jellyfish, and antibodies from alpaca.
|
|
As well as, the multidisciplinary group of researchers has developed additional the sensitivity of super-resolution microscopy approach.
|
|
In lots of instances, cells are very lively of their motion and function energy turbines. The power of cells to supply bodily forces is without doubt one of the fundamental capabilities of the physique. When working, for instance, the forces generated within the cells trigger the muscle mass to contract and the breath to work. It has been attainable to measure even the forces skilled by particular person proteins by power sensors developed previously, however beforehand intracellular forces and mechanical strains couldn’t have been measured.
|
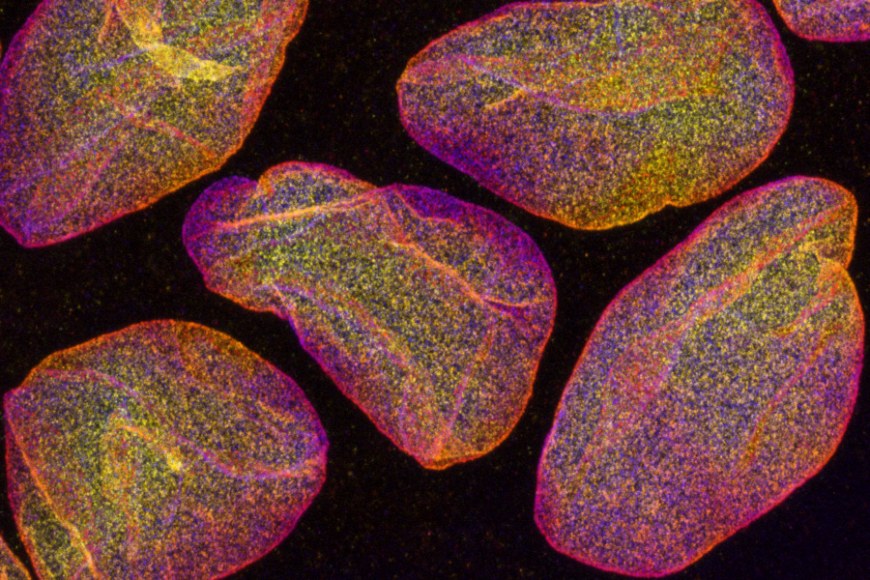 |
| Fluorescently labelled cell nuclei, imaged with confocal microscope. Picture measurement roughly 0.03 mm x 0.02 mm. (Picture: Teemu Ihalainen)
|
|
Along with the scientists from The Ohio State College OSU, cell biology researchers at Tampere College have developed a power sensor that may be hooked up to the aspect of a mechanically responding protein, permitting it to sense forces and pressure on the protein inside the cell.
|
|
The event of the micro-sized sensor started on a convention journey in December 2019.
|
|
“We had an thought for a brand new form of sensor whereas we have been at a dinner. The facility-sensing half is sort of a rubber band that adjustments color when stretched. This half is hooked up to the antibodies at each ends of the rubber band, which bind to the mobile goal protein beneath examine. The power or elongation of the studied protein can then be detected beneath a microscope by following the elongation of the rubber band, i.e. the color it produces,” Teemu Ihalainen, Senior Analysis Fellow from BioMediTech at Tampere College, says.
|
|
In response to Ihalainen, the power sensor, which is simply about twenty nanometres in measurement, may be simply generalised to a variety of cell biology analysis and numerous goal proteins. With the assistance of the protein biosensor, forces may be measured, for instance, within the nuclear membrane, between totally different proteins, or usually within the cytoskeleton of the cell. It permits the mechanics of the cell to be reworked into seen type for the primary time. There has already been nice curiosity on this know-how in numerous laboratories in Japan, India, Norway and the USA.
|
Inner forces of the cell present info on the mechanics of most cancers
|
|
Cells are topic to forces on a regular basis, each in regular bodily capabilities and illnesses.
|
|
As a most cancers cell grows and strikes, for instance, the cells are subjected to mechanical forces. Because the most cancers spreads e.g., when it enters blood or lymphatic vessels, the most cancers cell has to squeeze by way of slim gaps in its microenvironment. Thus, most cancers cells are subjected to highly effective compressive and stretching forces that may break down a number of the cells. Harm to the nucleus can alter its genome construction, which in some conditions may even be helpful for the event of most cancers.
|
|
“With the assistance of sensors, the mechanics of most cancers and associated processes may be monitored from a very new perspective,” Ihalainen mentions.
|
|
The examine was revealed in Nature Communications (“Nuclear lamina pressure states revealed by intermolecular power biosensor”).
|
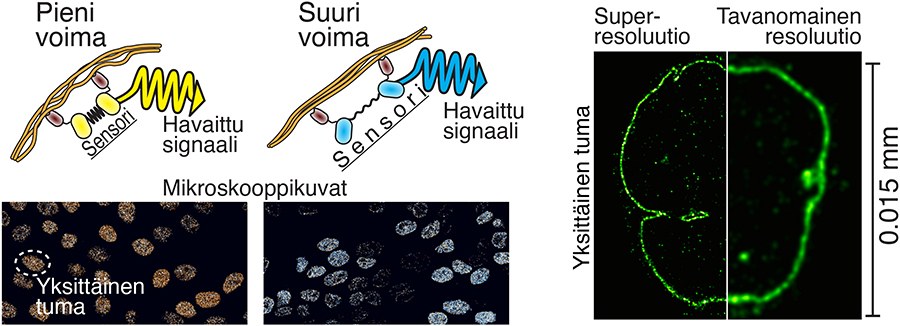 |
| The picture reveals the precept of motion of the intracellular power sensor on the left. The fluorescent proteins (yellow and cyan) are derived from jellyfish, whereas the rubber band half (black) has utilised spider internet protein. The goal protein-binding antibodies (darkish brown) are derived from alpacas. Within the picture to the fitting is a comparability of super-resolution microscopy and traditional microscopy imaging of the cell nucleus. (Picture: Teemu Ihalainen)
|
Even the smallest particulars may be seen with super-resolution microscopy
|
|
One other current examine refined growth microscopy by combining cell biology and sign processing experience. Along with cell biology researchers, imaging specialists from the College of Engineering and Pure Sciences at Tampere College and virologists from the College of Jyväskylä participated within the examine.
|
|
The decision of sunshine microscopy is proscribed because the particulars of small constructions within the pattern are blurred as a result of lens-light interactions. Nonetheless, totally different methods of super-resolution microscopy enable for the separation of very small particulars. One among these methods is so-called growth microscopy, the precept of which is to bodily enlarge a topic, e.g. a cell, and thus take a look at the tiny issues inside it. In observe, the pattern is forged in a smooth gel, which may be expanded fourfold or extra, and it additionally enlarges all the small print of the pattern.
|
|
“Nonetheless, the issue has been that the smaller the small print of the cell are examined, the less molecules are seen. Which means much less sign i.e., info, have been acquired from the pattern, and normally there may be a whole lot of noise, a bit like snow on a TV display screen,” Ihalainen says.
|
|
The analysis group discovered that the answer to the issue could possibly be repeated fluorescent labelling of the cells. They produced the concept of labelling the goal proteins many instances to make them seem brighter and supply extra info.
|
|
“In practise, what we did was to pump extra fluorescent molecules to the goal proteins as if we have been including reflectors. The easy and simple technique tremendously improved the decision and distinction of the picture. Noise was additionally computationally faraway from the photographs, which additional elevated the picture sharpness,” he mentions.
|
|
In contrast to many super-resolution microscopy methods, growth microscopy doesn’t require costly devices and is simple to implement. The approach developed by the researchers is especially helpful for learning actually small particulars. Wanting on the construction of the 120-nanometre Herpes virus, for instance, is now attainable even with a lightweight microscope. With conventional gentle microscopy, viruses are seen solely as single dots.
|
|
The examine was revealed in Molecular Biology of the Cell (“Iterative immunostaining mixed with growth microscopy and picture processing reveals nanoscopic community group of nuclear lamina”).
|
|
“Each these research are fundamental analysis. We seek for understanding how cells principally work. Subsequently, the analysis funding acquired from the Analysis Council of Finland and the chance to work at Tampere Institute for Superior Examine (IAS) have been massively necessary components in these tasks,” Ihalainen notes.
|


