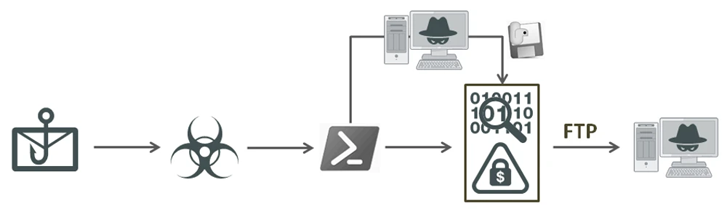
A brand new “all-in-one” stealer malware named EvilExtractor (additionally spelled Evil Extractor) is being marketed on the market for different menace actors to steal knowledge and information from Home windows programs.
“It consists of a number of modules that each one work through an FTP service,” Fortinet FortiGuard Labs researcher Cara Lin mentioned. “It additionally incorporates atmosphere checking and Anti-VM capabilities. Its main function appears to be to steal browser knowledge and data from compromised endpoints after which add it to the attacker’s FTP server.”
The community safety firm mentioned it has noticed a surge in assaults spreading the malware within the wild in March 2023, with a majority of the victims situated in Europe and the U.S. Whereas marketed as an academic software, EvilExtractor has been adopted by menace actors to be used as an info stealer.
Bought by an actor named Kodex on cybercrime boards like Cracked since October 22, 2022, it is frequently up to date and packs in varied modules to siphon system metadata, passwords and cookies from varied net browsers in addition to file keystrokes and even act as a ransomware by encrypting information on the goal system.
The malware can also be mentioned to have been used as a part of a phishing e-mail marketing campaign detected by the corporate on March 30, 2023. The emails lure recipients into launching an executable that masquerades as a PDF doc below the pretext of confirming their “account particulars.”
The “Account_Info.exe” binary is an obfuscated Python program designed to launch a .NET loader that makes use of a Base64-encoded PowerShell script to launch EvilExtractor. The malware, in addition to gathering information, may also activate the webcam and seize screenshots.
“EvilExtractor is getting used as a complete information stealer with a number of malicious options, together with ransomware,” Lin mentioned. “Its PowerShell script can elude detection in a .NET loader or PyArmor. Inside a really quick time, its developer has up to date a number of capabilities and elevated its stability.”
The findings come as Secureworks Counter Risk Unit (CTU) detailed a malvertising and search engine optimization poisoning marketing campaign used to ship the Bumblebee malware loader through trojanized installers of reputable software program.
Bumbleebee, documented first a 12 months in the past by Google’s Risk Evaluation Group and Proofpoint, is a modular loader that is primarily propagating by means of phishing strategies. It is suspected to be developed by actors related to the Conti ransomware operation as a substitute for BazarLoader.
Zero Belief + Deception: Be taught Easy methods to Outsmart Attackers!
Uncover how Deception can detect superior threats, cease lateral motion, and improve your Zero Belief technique. Be a part of our insightful webinar!
The usage of search engine optimization poisoning and malicious advertisements to redirect customers trying to find common instruments like ChatGPT, Cisco AnyConnect, Citrix Workspace, and Zoom to rogue web sites internet hosting tainted installers has witnessed a spike in latest months after Microsoft started blocking macros by default from Workplace information downloaded from the web.
In a single incident described by the cybersecurity agency, the menace actor used the Bumblebee malware to acquire an entry level and transfer laterally after three hours to deploy Cobalt Strike and bonafide distant entry software program like AnyDesk and Dameware. The assault was in the end disrupted earlier than it proceeded to the ultimate ransomware stage.
“To mitigate this and comparable threats, organizations ought to be certain that software program installers and updates are solely downloaded from identified and trusted web sites,” Secureworks mentioned. “Customers shouldn’t have privileges to put in software program and run scripts on their computer systems.”