| Sep 11, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) A staff of researchers, affiliated with UNIST has made a groundbreaking development in enhancing the effectivity of hydrogen gasoline cells, that are gaining important consideration as eco-friendly next-generation power sources.
|
|
The analysis is printed in Angewandte Chemie (“Superprotonic Conductivity of MOFs Confining Zwitterionic Sulfamic Acid as Proton Supply and Conducting Medium”).
|
|
Led by Professor Myoung Soo Lah within the Division of Chemistry at UNIST, the staff efficiently developed strong electrolyte supplies using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs). This modern method considerably enhances the conductivity of hydrogen ions throughout the strong electrolyte employed in hydrogen gasoline cells.
|
|
Moreover, the analysis staff launched visitor molecules with low acidity—marking a pioneering achievement amongst intermediaries used for this objective. By implementing a novel methodology that will increase the variety of visitor molecules inside MOF pores, they achieved improved hydrogen ion conductivity.
|
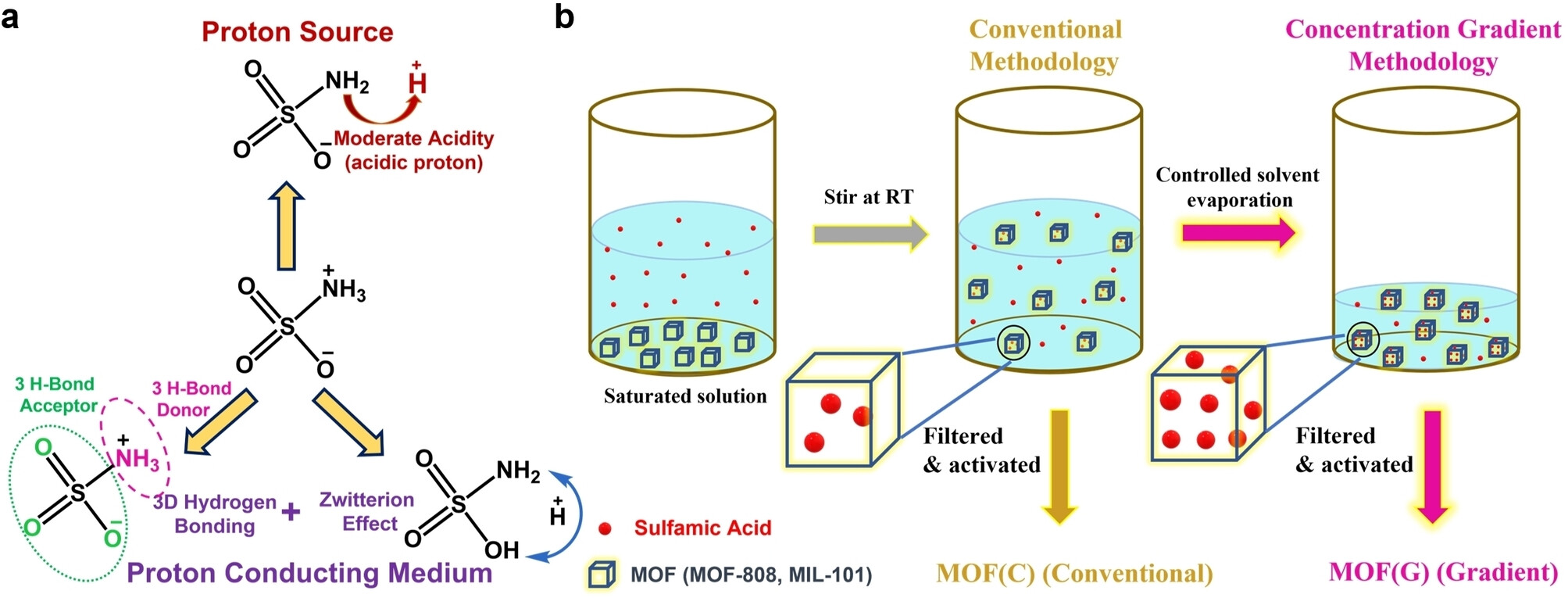 |
| Schematic Illustration of HSA Properties and Synthesis Methodology. (Picture: UNIST)
|
|
Hydrogen gasoline cells are extremely environment friendly and environmentally pleasant energy technology gadgets that straight convert chemical power derived from reactions between hydrogen and oxygen into electrical power. Presently, Proton-Trade Membrane Gas Cells predominantly make use of Nafion as an electrolyte materials as a result of its thermal, mechanical, and chemical stability alongside excessive hydrogen ion conductivity. Nonetheless, these methods face limitations relating to their working temperature vary and lack readability on their mechanisms for efficiency enhancement.
|
|
The analysis staff turned their consideration to MOFs as potential alternate options. MOFs are supplies composed of steel clusters interconnected by natural ligands to type a porous construction. With wonderful chemical and thermal stability properties, MOFs have not too long ago garnered appreciable curiosity to be used in gasoline cell functions. Furthermore, when generated, MOFs possess pores of various sizes that may be utilized for creating supplies with excessive hydrogen ion conductivity by introducing visitor molecules by these channels.
|
|
On this research carried out by the analysis staff at UNIST led by Professor Myoung Soo Lah’s group members , zwitterionic sulfamic acid—a low-acidity amphoteric ionic substance possessing each optimistic and unfavourable fees—was launched as visitor molecules into two sorts of MOFs, particularly MOF-808 and MIL-101.
|
|
Sulfamic acid, a visitor molecule with distinctive hydrogen bonding capabilities in numerous varieties, successfully operates as a medium for transferring hydrogen ions. By rising the quantity of sulfamic acid throughout the pores of MOFs, the staff efficiently developed supplies demonstrating excessive hydrogen ion conductivity (reaching ranges of 10-1 Scm-1 or increased). Furthermore, these supplies exhibited exceptional sturdiness as they maintained hydrogen ion conductivity over an prolonged interval.
|
|
The analysis findings maintain immense promise for advancing the effectivity and efficiency of hydrogen gasoline cells by the utilization of metal-organic frameworks. This breakthrough contributes to accelerating progress towards sustainable power options in keeping with international efforts in the direction of decarbonization.
|