
A brand new fileless malware named PyLoose has been concentrating on cloud workloads to hijack their computational assets for Monero cryptocurrency mining.
PyLoose is a comparatively easy Python script with a precompiled, base64-encoded XMRig miner, a extensively abused open-source software that makes use of CPU energy to unravel advanced algorithms required for cryptomining.
In line with researchers at Wiz, PyLoose’s direct execution from reminiscence makes it extremely stealthy and difficult to detect by safety instruments.
Fileless malware leaves no bodily footprint on the system’s drives, so it is much less susceptible to signature-based detection and usually makes use of official system instruments (residing off the land) to inject malicious code into official processes.
Wiz’s safety researchers first detected PyLoose assaults within the wild on June twenty second, 2023, and have since confirmed no less than 200 instances of compromise by the novel malware.
“So far as we all know, that is the primary publicly documented Python-based fileless assault concentrating on cloud workloads within the wild, and our proof exhibits near 200 situations the place this assault was used for cryptomining,” explains the brand new Wiz report.
PyLoose assault chain
Wiz noticed assaults that started by gaining preliminary entry to units by publicly accessible Jupyter Pocket book providers, which didn’t limit system instructions.
The attacker makes use of an HTTPS GET request to fetch the fileless payload (PyLoose) from a Pastebin-like web site, “paste.c-net.org,” and cargo it straight into Python’s runtime reminiscence.
The PyLoose script is decoded and decompressed, loading a precompiled XMRig miner immediately into the occasion’s reminiscence utilizing the “memfd” Linux utility, a recognized fileless malware approach in Linux.
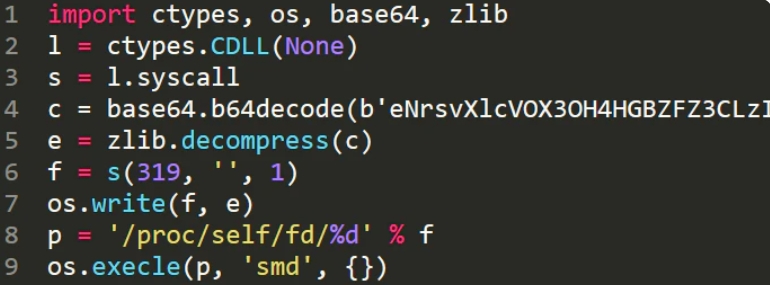
“The reminiscence file descriptor, memfd, is a Linux function that permits the creation of nameless memory-backed file objects that can be utilized for varied functions, reminiscent of inter-process communication or short-term storage,” explains Wiz within the report.
“As soon as the payload is positioned inside a reminiscence part created by way of memfd, attackers can invoke one of many exec syscalls on that reminiscence content material, treating it as if it have been an everyday file on disk, and thereby launch a brand new course of.”
This allows attackers to carry out payload execution straight from reminiscence, evading most conventional safety options.
The XMRig miner loaded into the compromised cloud occasion’s reminiscence is a reasonably latest model (v6.19.3) that makes use of the ‘MoneroOcean’ mining pool to mine for Monero.
Unknown risk actors
Wiz couldn’t attribute the PyLoose assaults to any specific risk actor, because the attacker left no helpful proof behind.
The researchers remark that the adversary behind PyLoose seems extremely refined and stands out from the standard risk actors participating in cloud workload assaults.
Cloud occasion directors are really useful to keep away from the general public publicity of providers vulnerable to code execution, use sturdy passwords and multi-factor authentication to guard entry to these providers, and place system command execution restrictions.
