| Aug 04, 2023 |
|
(Nanowerk Information) Researchers from Michigan State College and the College of British Columbia have invented a system that may rapidly and inexpensively detect airborne viruses utilizing the identical know-how that permits high-speed trains.
|
|
The staff confirmed {that a} approach often known as magnetic levitation can be utilized to simply acquire and focus viruses from air to assist stop future outbreaks of respiratory illness. The researchers printed their work within the journal ACS Nano (“Magnetic Levitation System Isolates and Purifies Airborne Viruses”).
|
|
“It’s essential to have real-time administration and real-time predictions in place for viruses,” mentioned Morteza Mahmoudi, an affiliate professor within the Division of Radiology and the Precision Well being Program at MSU. “What we’ve developed is a system that might assist us and different stakeholders get extra details about the several types of viruses within the air we breathe.”
|
|
“This might assist determine that an setting is contaminated earlier than a pandemic occurs,” mentioned Sepideh Pakpour, an assistant professor of engineering who led the analysis staff on the UBC Okanagan Campus.
|
|
Along with serving as an early-warning system, the staff’s new approach additionally might assist well being officers and epidemiologists higher monitor and hint publicity to viruses in public settings.
|
|
Pakpour and Mahmoudi first began this challenge making use of magnetic levitation, or maglev, to respiratory viruses in 2018 with assist from the Walsh Basis and the New Frontiers in Analysis Fund. Virtually half of decrease respiratory tract infections are attributable to viruses that folks breathe in whereas indoors, the researchers wrote of their report.
|
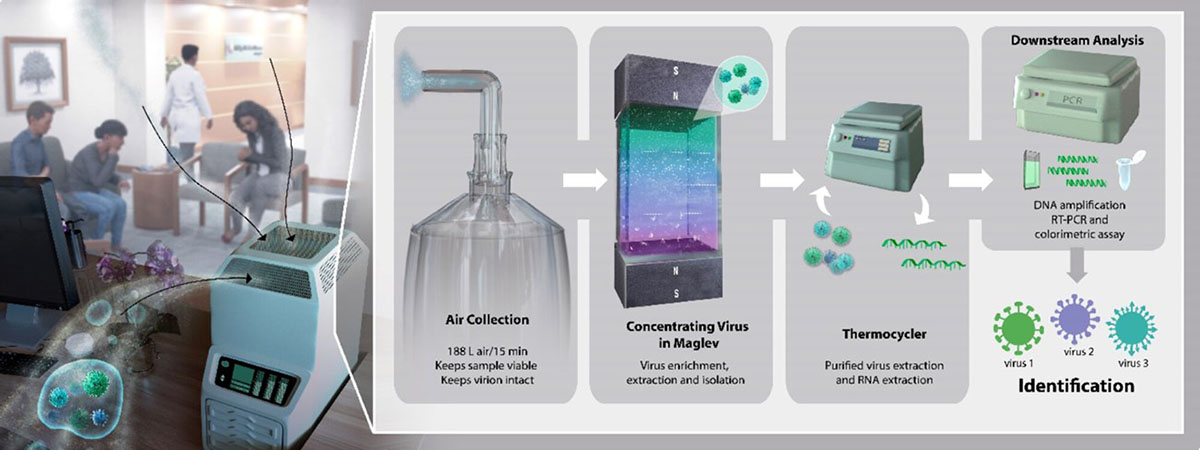 |
| The brand new system developed by researchers at Michigan State College and the College of British Columbia would first acquire air samples in a setting like a health care provider’s workplace or airport. That air pattern would then be injected right into a fluid, which permits the viruses to be separated from different particles within the pattern utilizing magnetic levitation. As soon as the viruses are remoted and purified, they are often handed to straightforward downstream analytics, equivalent to PCR — polymerase chain response — to determine the pathogens. Credit score: Reprinted with permission from “Magnetic Levitation System Isolates and Purifies Airborne Viruses.” (Picture: Pakpour, S. et al. ACS Nano. © American Chemical Society) (click on on picture to enlarge)
|
|
However when the coronavirus pandemic began and as they realized that it was attributable to an airborne virus, they knew they needed to redouble their efforts. The staff used a deactivated model of the coronavirus answerable for COVID-19 of their proof-of-concept report, together with H1N1 influenza and a virus that infects micro organism often known as bacteriophage MS2.
|
|
The system first collects air samples, then injects the pattern right into a fluid the place maglev separates viruses from different particles. The remoted and purified viral contents are then handed alongside to different commonplace analytical methods for identification in a matter of minutes. The strategy is so simple that it could possibly be utilized by nonexperts in quite a lot of settings, equivalent to clinics and airports, the researchers mentioned.
|
|
The staff is taking the primary steps towards commercializing its know-how whereas working to enhance it on the identical time.
|
|
Though downstream methods can determine which viruses are in a pattern, one of many staff’s future objectives is refining the maglev step to differentiate between completely different viruses by itself. The researchers are also working to intensify their approach’s sensitivity and detect viruses in air at decrease concentrations.
|
|
Nonetheless, the staff is worked up by what it was capable of accomplish in its preliminary work and by what it could allow different researchers to do.
|
|
“Utilizing maglev for illness detection and purifying viruses is model new, and it might open up purposes in many alternative fields,” Mahmoudi mentioned. “This opens up a essentially new route in analytical biochemistry.”
|
A profitable take a look at flight for virus levitation
|
|
Magnetic levitation, as its title suggests, makes use of magnets to counteract the downward pull of gravity. Maglev trains float above their tracks and, unencumbered by that contact friction, can obtain speeds upwards of 200 miles per hour. Whereas maglev trains have been round for many years, using magnetic levitation in biology is newer.
|
|
For instance, it was solely throughout the final decade that Stanford researchers confirmed that dwelling cells could possibly be magnetically levitated in liquid mixtures or options. They then used the approach to point out that varied cell varieties — yeast, micro organism, wholesome human cells and most cancers cells — could possibly be separated by their density.
|
|
Extra just lately, Pakpour and Mahmoudi have collaborated to point out that maglev might be utilized to proteins in blood plasma to search for indicators of opioid use and a number of sclerosis. That satisfied them maglev additionally ought to work with viruses.
|
|
“For those who take a look at the construction of viruses, they’re principally proteins, and we knew we might levitate proteins,” Pakpour mentioned. “So I knew this could work, however I used to be nonetheless shocked when it did.”
|
|
“It was very difficult, particularly at first,” Mahmoudi mentioned. “Standard maglev is just not able to gathering submicron viruses, however we made a number of modifications and had been capable of fine-tune the system.”
|
|
One of many challenges, for instance, was that the liquids utilized in standard maglev might injury or destroy viruses. The staff needed to discover new options that had fascinating magnetic properties and had been suitable with their targets.
|
|
“Like with many publications, what you see are solely the great outcomes,” Mahmoudi mentioned. “What you don’t see is the massive quantity of effort that goes into getting them.”
|
|
“College students spent months and months making all of it work,” Pakpour mentioned.
|
|
The challenges had been exacerbated by the pandemic, however the emergence of COVID-19 confirmed the staff how essential its work was — and the way resilient its members had been.
|
|
“There have been so many obstacles, even simply getting samples to one another,” Pakpour mentioned. “However we pushed ahead. And, if we gained that battle, I feel we will win every other.”
|

