
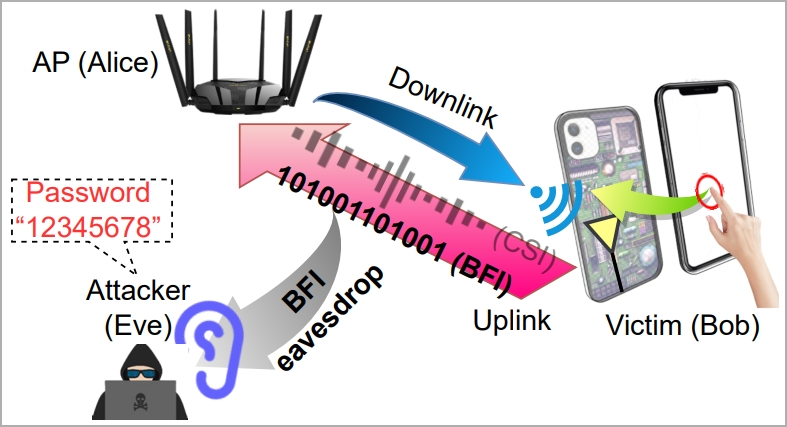
A brand new assault dubbed ‘WiKI-Eve’ can intercept the cleartext transmissions of smartphones linked to trendy WiFi routers and deduce particular person numeric keystrokes at an accuracy price of as much as 90%, permitting numerical passwords to be stolen.
WiKI-Eve exploits BFI (beamforming suggestions data), a function launched in 2013 with WiFi 5 (802.11ac), which permits gadgets to ship suggestions about their place to routers so the latter can direct their sign extra precisely.
The issue with BFI is that the data trade comprises knowledge in cleartext type, that means that this knowledge may be intercepted and readily used with out requiring {hardware} hacking or cracking an encryption key.
This safety hole was found by a crew of college researchers in China and Singapore, who examined the retrieval of potential secrets and techniques from these transmissions.
The crew discovered that it is moderately simple to determine numeric keystrokes 90% of the time, decipher 6-digit numerical passwords with an accuracy of 85%, and work out complicated app passwords at an accuracy of roughly 66%.
Whereas this assault solely works on numerical passwords, a research by NordPass confirmed that 16 out of 20 of the highest passwords solely used digits.
The WiKI-Eve assault
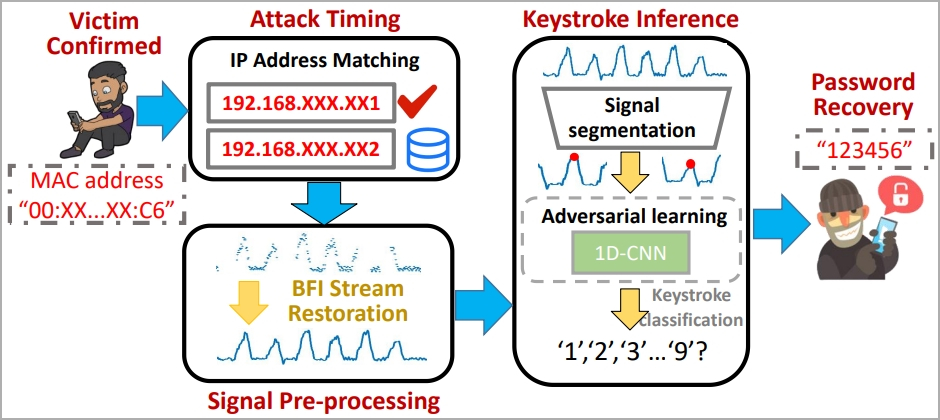
The WiKI-Eve assault is designed to intercept WiFi alerts throughout password entry, so it is a real-time assault that have to be carried out whereas the goal actively makes use of their smartphone and makes an attempt to entry a particular utility.
.jpg)
The attacker should determine the goal utilizing an id indicator on the community, like a MAC deal with, so some preparatory work is required.
“In actuality, Eve can purchase this data beforehand by conducting visible and visitors monitoring concurrently: correlating community visitors originating from varied MAC addresses with customers’ behaviors ought to permit Eve to hyperlink Bob’s bodily machine to his digital visitors, thereby figuring out Bob’s MAC deal with,” explains the researchers.
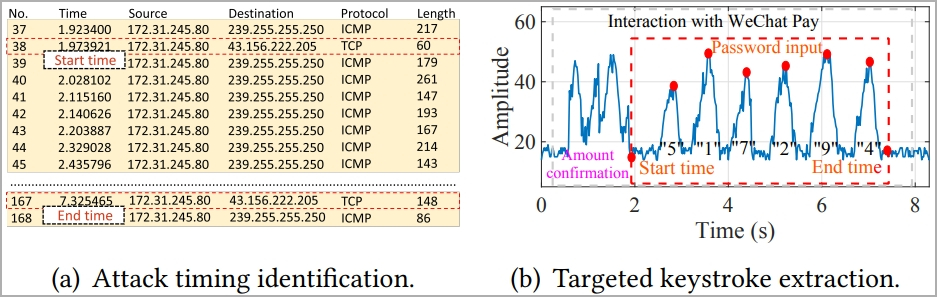
In the principle section of the assault, the sufferer’s BFI time collection throughout password entry is captured by the attacker utilizing a visitors monitoring instrument like Wireshark.
Every time the consumer presses a key, it impacts the WiFi antennas behind the display, inflicting a definite WiFi sign to be generated.
“Although they solely account for a part of the downlink CSIs in regards to the AP facet, the truth that on-screen typing straight impacts the Wi-Fi antennas (therefore channels) proper behind the display (see Determine 1) permits BFIs to include ample details about keystrokes,” reads the paper.
Nonetheless, the paper emphasizes that the recorded BFI collection would possibly blur boundaries between keystrokes, in order that they developed an algorithm for parsing and restoring usable knowledge.
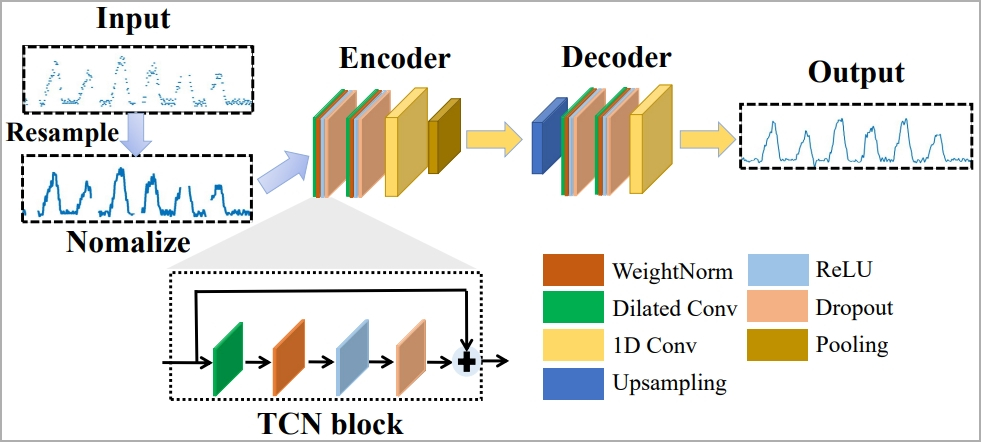
To sort out the problem of filtering out components that intrude with the outcomes, like typing fashion, typing velocity, adjoining keystrokes, and many others. the researchers use machine studying known as “1-D Convolutional Neural Community.”
The system is educated to constantly acknowledge keystrokes no matter typing kinds by the idea of “area adaptation,” which includes a function extractor, a keystroke classifier, and a website discriminator.
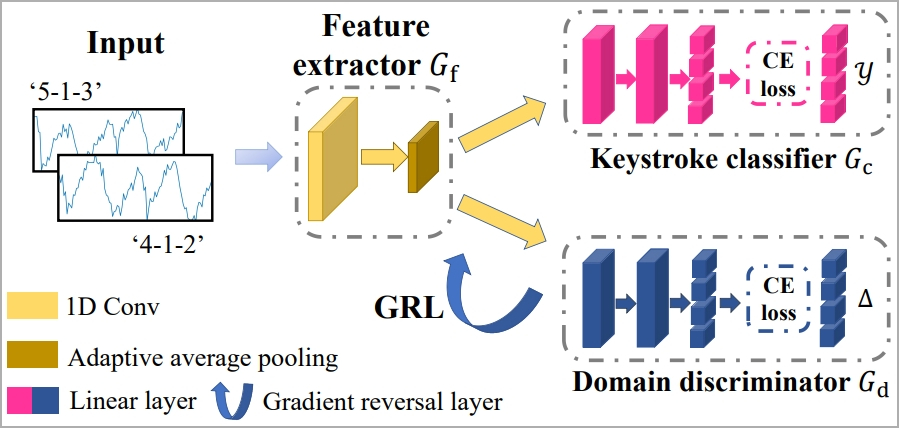
Lastly, a “Gradient Reversal Layer” (GRL) is utilized to suppress domain-specific options, serving to the mannequin be taught constant keystroke representations throughout domains.
Assault outcomes
The researchers experimented with WiKI-Eve utilizing a laptop computer and WireShark but in addition identified {that a} smartphone may also be used as an attacking machine, though it is likely to be extra restricted within the variety of supported WiFi protocols.
The captured knowledge was analyzed utilizing Matlab and Python, and the segmentation parameters have been set to values proven to supply the perfect outcomes.
Twenty members linked to the identical WiFi entry level used totally different telephone fashions. They typed varied passwords utilizing a mixture of lively background apps and ranging typing speeds whereas measurements have been taken from six totally different areas.
The experiments confirmed that WiKI-Eve’s keystroke classification accuracy stays secure at 88.9% when sparse restoration algorithm and area adaptation are used.
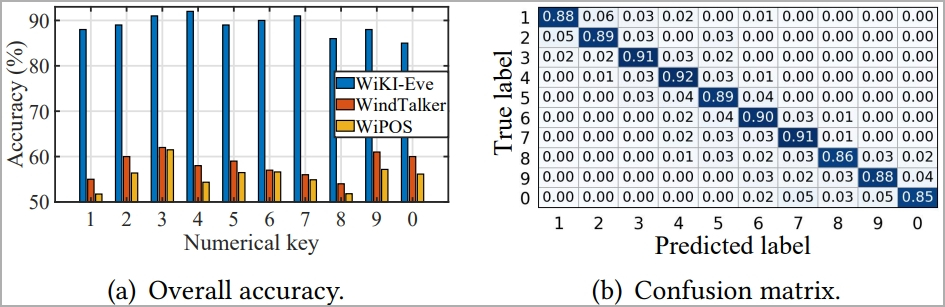
For six-digit numerical passwords, WiKI-Eve might infer them with an 85% success price in underneath 100 makes an attempt, remaining constantly above 75% in all examined environments.
Nonetheless, the space between the attacker and the entry level is essential to this efficiency. Rising that distance from 1m to 10m resulted in a 23% profitable guess price drop.
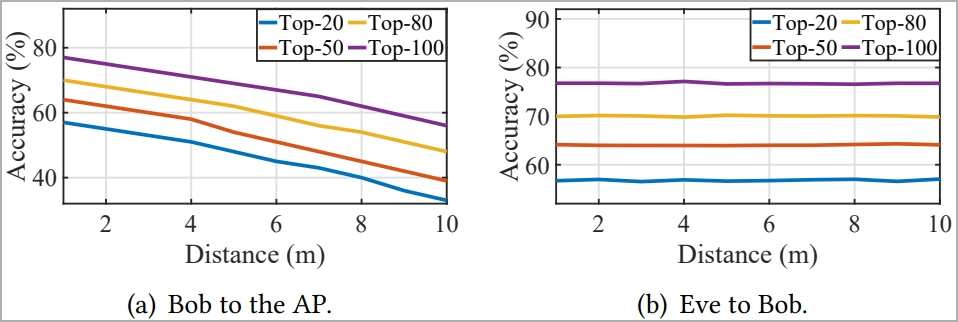
The researchers additionally experimented with retrieving consumer passwords for WeChat Pay, emulating a practical assault state of affairs, and located that WiKI-Eve deduced the passwords accurately at a price of 65.8%.
The mannequin constantly predicted the right password inside its prime 5 guesses in over 50% of the 50 assessments carried out. This implies an attacker has a 50% probability of gaining entry earlier than hitting the safety threshold of 5 incorrect password makes an attempt, after which the app locks.
In conclusion, the paper exhibits that adversaries can deduce secrets and techniques with out hacking entry factors and by merely utilizing community visitors monitoring instruments and machine studying frameworks.
This requires heightened safety in WiFi entry factors and smartphone apps, like doubtlessly keyboard randomization, encryption of knowledge visitors, sign obfuscation, CSI scrambling, WiFi channel scrambling, and extra.
