Relaxor–ferroelectric supplies are high-performance ultrasound era components exhibiting massive dielectric responses owing to their advanced constructions. Not too long ago, researchers from Japan made use of a novel polarization-angle-resolved Raman microscope developed by them to research the electrical polarization distribution in lead magnesium niobate-lead titanate crystals, a piezoelectric materials utilized in ultrasound tools and fish finder probes. The knowledge obtained on electrical polarization holds the potential for efficiency enhancement of next-generation ultrasound diagnostic gadgets.
Picture Credit score: Ritsumeikan College, Japan
The exploitation of polarization or cost separation in ferroelectric supplies has led to outstanding advances in varied fields, resembling the event of recent ultrasound diagnostic gadgets. Prominently, these ferroelectric supplies have led to piezoelectric gadgets able to remodeling electrical indicators into mechanical movement. Understanding how the electrical polarization is organized and fluctuates in a fabric is vital to constructing higher gadgets. Nonetheless, issues within the atomic association together with their inhomogeneous constructions can result in irregular cost distribution in particular areas, posing a elementary problem to the event of ferroelectric supplies.
To visualise the impact of issues on polarization habits, researchers led by Professor Yasuhiro Fujii from Ritsumeikan College, Japan, have developed an revolutionary polarization-angle-resolved Raman microscope. This patented approach builds upon the ideas of Raman microscopy and includes directing a centered laser beam onto a pattern and analyzing the scattered gentle to grasp the molecular construction of supplies. Not like conventional microscopes, the brand new approach incorporates a rotating half-wave plate into the microscope setup to think about the results of sunshine polarization with out the necessity to rotate the pattern underneath examine. This novel strategy produces spectra with completely different gentle polarization instructions at every level within the pattern underneath examine. Combining the spectral information makes it potential to establish not solely the vibration states of atoms but in addition the vibration instructions within the materials.
Now, in a examine revealed within the journal Communications Physics on 18 Might 2023 led by Prof. Shinya Tsukada from Shimane College and Prof. Fujii, researchers have used this method to watch the association of the electrical polarization and the time scale of its fluctuation in a piezoelectric lead magnesium niobate [Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3]-lead titanate [PbTiO3] or PMN-PT crystal, which is utilized in diagnostic ultrasound tools, revealing the rationale for the big dielectric fixed.
“The event of this polarization-angle-resolved Raman microscope together with the developments in analytical strategies can allow the incorporation of polarization info into the prevailing Raman imaging information and permit a deeper understanding of fabric properties,” explains Prof. Fujii, talking of the rationale behind the event of this method.
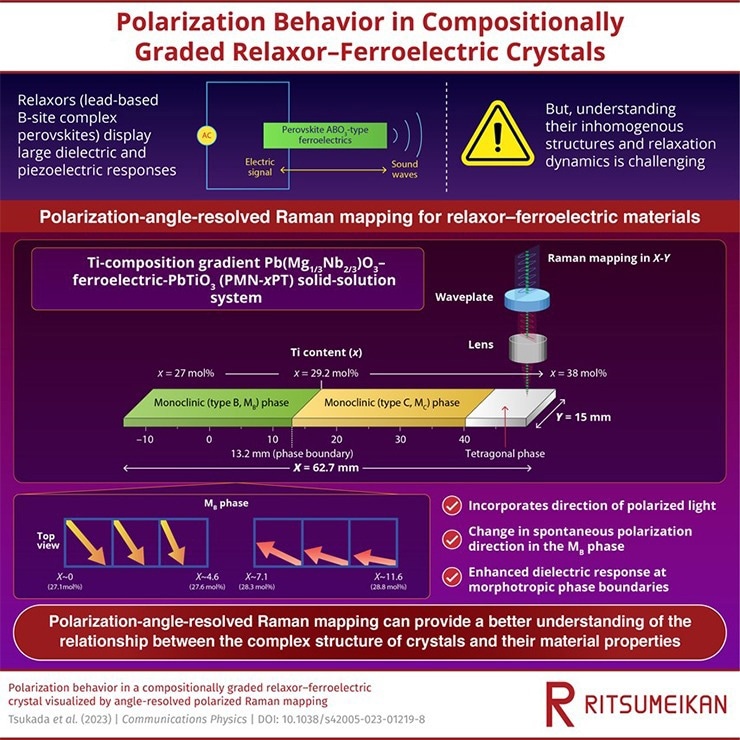
One notable attribute of PMN-PT crystals is their pronounced dielectric and piezoelectric response on the boundaries that separate completely different phases within the materials. The precise composition of the PMN-PT crystal, notably the focus of titanium (Ti), can have an effect on the formation and traits of part boundaries. To analyze the impact of Ti mixing ratios on the dielectric properties, the researchers imaged a 62.7 × 15.0 × 0.3 PMT-PT crystal pattern with the newly developed setup for Raman mapping within the microscope.
The Ti content material diversified from 27.0 mol% to 38.0 mol% alongside the size of the pattern, giving rise to a few distinct phases: a monoclinic (kind B) part the place the Ti content material ranged from 27 mol% and 29.2 mol%, a monoclinic (kind C) part the place it went as much as 34.5 mol%, and a tetragonal part with a excessive Ti content material of 34.8–38.0 mol%.
On analyzing the Raman spectra comparable to completely different gentle polarization values at every level within the pattern, the researchers noticed abrupt adjustments within the depth of the Raman peaks just for the monoclinic kind B part. Furthermore, additionally they famous a definite change within the course of spontaneous polarization on this part. The spectra revealed a slower leisure (reorientation of the electrical dipoles in response to a thermal perturbation) of the fabric’s polarization nearer to the part boundary between the monoclinic (kind B) and (kind C) phases. This, in flip, indicated that the realignment of the dipoles happens at a decreased charge, enabling the fabric to retailer a considerable amount of cost and show enhanced dielectric response at this part boundary.
“We discovered that the power of the relaxor–ferroelectric materials to retailer a big quantity of electrical cost is because of the sluggish response of nanometer-scale electrical polarization to the exterior voltage,” highlights Prof. Fujii.
In abstract, the remark of this attribute property of relaxor supplies highlights the potential of the polarization-angle-resolved microscope to offer polarization info, which may assist optimize a fabric’s dielectric efficiency. Specifically, the insights into the polarization habits of PMT-PT may improve the event of relaxor supplies with improved ultrasound detection and era properties for next-generation diagnostics.
Supply: https://en.ritsumei.ac.jp/
