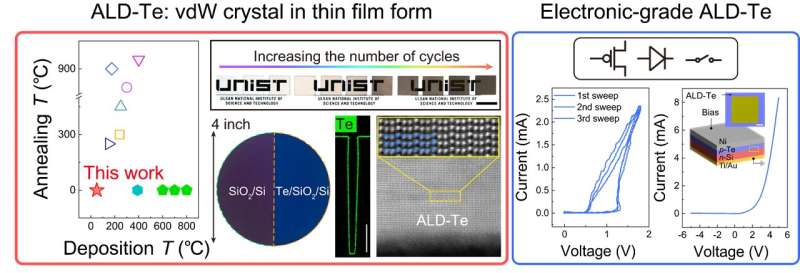
A analysis staff, led by Professor Joonki Suh within the Division of Supplies Science and Engineering and the Graduate College of Semiconductor Supplies and Gadgets Engineering at UNIST, has made a major breakthrough in skinny movie deposition expertise. By using an progressive atomic layer deposition (ALD) course of, Professor Website positioning efficiently achieved common association of tellurium (Te) atoms at low temperatures as little as 50 levels Celsius.
The ALD technique is a cutting-edge skinny movie course of that permits exact stacking of semiconductor supplies on the atomic layer stage on three-dimensional constructions—even at low course of temperatures. Nevertheless, conventional utility to next-generation semiconductors requires excessive processing temperatures above 250 levels Celsius and extra warmth remedy exceeding 450 levels Celsius.
On this analysis, the UNIST staff utilized ALD to monoelemental van der Waals tellurium—a fabric below in depth investigation for its potential functions in digital units and thermoelectric supplies.
Remarkably, they efficiently fabricated high-quality Te skinny movies with none post-deposition warmth remedy at an unprecedentedly low temperature of solely 50 levels Celsius. The ensuing movies exhibited distinctive uniformity with exactly managed thickness all the way down to nanometers scale—reaching excellent atom association with one out of each billion atoms.
To reinforce reactivity at decrease temperatures, the analysis staff employed two precursors with acid-base properties. Moreover, they launched co-reactants to enhance floor reactions and stability whereas adopting a repeating dosing method by injecting precursors in shorter intervals. These methods enabled the manufacturing of dense and steady Te skinny movies in comparison with typical strategies that always resulted in porous or discontinuous grain depositions.
The developed manufacturing course of allowed for wafer-scale development on complete 4-inch (100mm) wafers, offering exact atomic layer-level thickness management and uniform deposition. Moreover, the Te skinny movies demonstrated compatibility with vertical three-dimensional constructions—an important requirement for top gadget integration. This breakthrough holds important potential for varied digital units akin to transistors, rectifiers, and choice parts.
“This analysis fulfills all of the important standards of low-temperature, large-area, and high-quality synthesis in semiconductor deposition processes,” said Professor Suh.
The outcomes of this analysis have been printed in ACS Nano.
Extra info:
Changhwan Kim et al, Atomic Layer Deposition Path to Scalable, Digital-Grade van der Waals Te Skinny Movies, ACS Nano (2023). DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.3c03559
Quotation:
Research demonstrates atomic layer deposition path to scalable, electronic-grade van der Waals tellurium skinny movies (2023, September 18)
retrieved 19 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-atomic-layer-deposition-route-scalable.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

