Researchers on the Heart for Practical Nanomaterials (CFN), a U.S. Division of Vitality (DOE) Workplace of Science Consumer Facility at DOE’s Brookhaven Nationwide Laboratory, and Northrop Grumman, a multinational aerospace and protection expertise firm, have discovered a approach to preserve valley polarization at room temperature utilizing novel supplies and methods.
This discovery might result in gadgets that retailer and course of info in novel methods with out the necessity to maintain them at ultra-low temperatures. Their analysis was lately revealed in Nature Communications.
One of many paths being explored to realize these gadgets is a comparatively new area referred to as “valleytronics.” A fabric’s digital band construction—the vary of vitality ranges in every atom’s electron configurations—can dip up or down. These peaks and troughs are generally known as “valleys.” Some supplies have a number of valleys with the identical vitality. An electron in a system like this could occupy any one in all these valleys, presenting a singular approach to retailer and course of info based mostly on which valley the electron occupies.
One problem, nevertheless, has been the hassle and expense of sustaining the low temperatures wanted to maintain valley polarization secure. With out this stability, gadgets would start to lose info. So as to make a expertise like this possible for sensible, reasonably priced functions, specialists would want to discover a approach to round this constraint.
Exploring 2D landscapes for the proper valleys
Transition steel dichalcogenides (TMDs) are attention-grabbing, layered supplies that may be, at their thinnest, solely few atoms thick. Every layer within the materials consists of a two-dimensional (2D) sheet of transition steel atoms sandwiched between chalcogen atoms. Whereas the steel and the chalcogen are strongly certain by covalent bonds in a layer, adjoining layers are solely weakly certain by van der Waal’s interactions. The weak bonds that maintain these layers collectively allow TMDs to be exfoliated right down to a monolayer that is just one “molecule” thick. These are also known as 2D supplies.
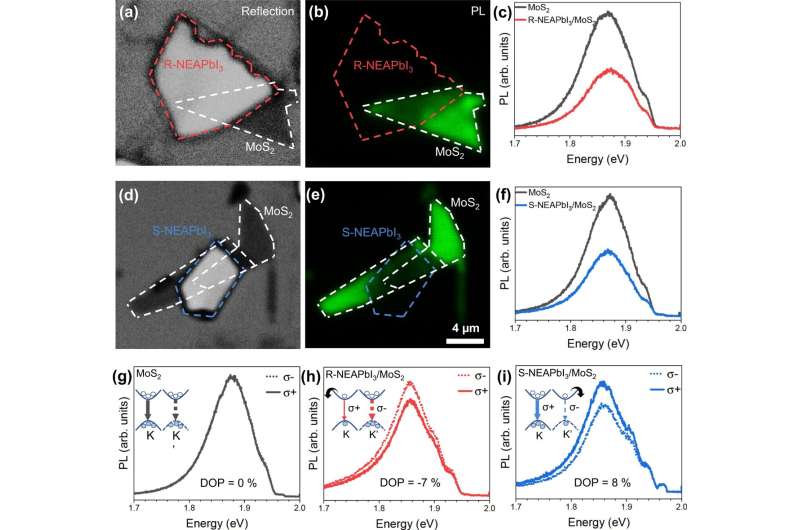
The group at CFN synthesized single crystals of chiral lead halide perovskites (R/S-NEAPbI3). Chirality describes a set of objects, like molecules, which are a mirror picture of one another however cannot be superimposed. It’s derived from the Greek phrase for “fingers,” an ideal instance of chirality. The 2 shapes are an identical, however if you happen to put one hand on high of the opposite, they won’t align. This asymmetry is essential for controlling valley polarization.
Flakes of this materials, roughly 500 nanometers thick or five-thousandths the thickness of a human hair, had been layered onto a monolayer of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) TMD to create what is named a heterostructure. By combining totally different 2D supplies with properties that have an effect on the cost switch on the interface between the 2 supplies, these heterostructures open up a world of chance.
After creating and characterizing this heterostructure, the group was wanting to see the way it behaved.
A level of freedom
“TMDs have two valleys with the identical vitality,” defined Shreetu Shrestha, a postdoctoral analysis affiliate at CFN and the creator of this paper. “An electron could be in a single valley or the opposite, which supplies it an extra diploma of freedom. Info can then be saved based mostly on which valley an electron occupies.”
To get a greater image of the fabric’s habits, the group leveraged instruments at CFN’s Superior Optical Spectroscopy and Microscopy facility. Scientists used a linearly polarized laser to excite the heterostructure they fabricated after which measured the sunshine that was emitted from the molybdenum disulfide TMD utilizing a confocal microscope. They carried out the identical course of with a TMD that did not have the chiral lead halide perovskite layer added.
Throughout these superior experiments, the researchers seen one thing attention-grabbing about the way in which mild was emitted. The heterostructure had a decrease emission than the naked TMD. The researchers attributed this habits to the cost transferred from the TMD to the perovskite within the heterostructure. Utilizing ultrafast spectroscopy, the researchers discovered that the cost transfers in a short time—just a few trillionths of a second.
The group additionally discovered that the depth of the left and proper circularly polarized elements of the sunshine emitted is dependent upon the handedness of the chiral perovskite used. The chiral nature of the perovskite acted like a filter for electrons with totally different spin. Relying on the handedness of the chiral perovskite, electrons that spin both up or down had been preferentially transferred from one valley over electrons with the alternative spin within the different valley. This phenomenon would allow researchers to selectively populate valleys and use their occupation in the identical manner present transistors on computer systems retailer the 1s and 0s of binary bits.
“An essential level to focus on on this experiment is that these outcomes had been realized at room temperature, which is the place the entire area ought to transfer,” mentioned Mircea Cotlet, a supplies scientist at Brookhaven Lab and the principal investigator of the venture. “Maintaining {hardware} on the low temperatures that had been getting used is a lot extra complicated and dear. It is encouraging to see these varieties of fabric properties at room temperature.”
Whereas valleytronics analysis remains to be at an early stage, researchers have already been interested by attainable functions. This expertise might enhance current gadgets in shocking methods, increasing the capabilities of classical computer systems, nevertheless it is also a part within the {hardware} of the long run.
“This may assist make classical computing extra environment friendly,” mentioned Shrestha, “however this expertise is also harnessed for quantum info science, which incorporates quantum computing, and even quantum sensing. These atomically skinny supplies have distinctive quantum properties, which we should always be capable of reap the benefits of.”

Fostering collaboration and innovation
CFN customers and collaborators come from a variety of fields in academia, analysis, and business. This experiment concerned contribution of a long-time collaborator from American world aerospace and protection expertise firm Northrop Grumman. In 2021, DOE’s Workplace of Vitality Effectivity and Renewable Vitality (EERE) awarded CFN with funding to collaborate with Northrop Grumman by means of the Technologist in Residence (TIR) program. The TIR program pairs senior technical workers from nationwide labs and business to conduct analysis and improvement. Applications like this strengthen nationwide lab–business relationships whereas advancing innovation in U.S. manufacturing and selling financial progress and vitality safety.
“Our collaborations with Northrop Grumman and Don DiMarzio return to 2015,” mentioned Cotlet. “We’ve a mutual curiosity in 2D supplies, notably how they may assist create the following era of computer systems. It is encouraging to have the experience of so many various folks right here underneath one roof. We’re a consumer facility with entry to a wide range of high-end devices and methods which give us the flexibility to place all this info collectively.”
This work additionally allowed Shrestha and Cotlet to increase on the continued analysis that they’ve each been doing on TMDs and cost switch.
“I had labored with perovskites throughout my Ph.D. analysis and my first postdoctoral place,” mentioned Shrestha, “so we had been capable of mix my experience in that space with Mircea’s experience in TMDs and the optical devices we’ve got in CFN’s Superior Optical Spectroscopy and Microscopy facility to find one thing promising. I used to be additionally excited to work with Suji Park and Xiao Tong of CFN and Mingxing Li, a scientist who was beforehand with CFN and is now at Innovare.
“This sort of understanding would not be attainable with out a collective effort and entry to all of those high-end amenities underneath a single rooftop. I am excited to see the place this work leads and look ahead to contributing extra perception to CFN’s 2D supplies program.”
Extra info:
Shreetu Shrestha et al, Room temperature valley polarization through spin selective cost switch, Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-40967-7
Supplied by
Brookhaven Nationwide Laboratory
Quotation:
Researchers discover revolutionary approach to retailer and course of info by sustaining valley polarization at room temperature (2023, September 8)
retrieved 9 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-valley-polarization-room-temperature.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

