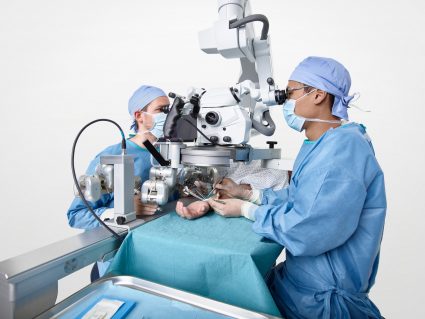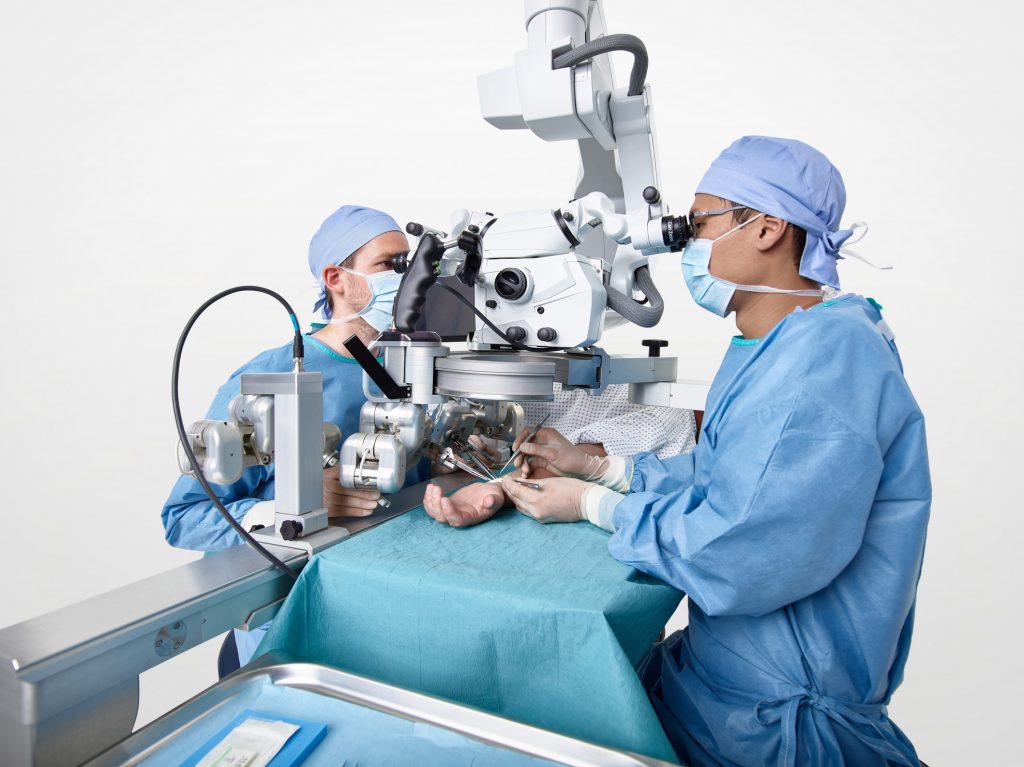
Superior robotics may help surgeons perform procedures the place there may be little margin for error. © Microsure BV, 2022
In a surgical procedure in India, a robotic scans a affected person’s knee to determine how greatest to hold out a joint substitute. In the meantime, in an working room within the Netherlands, one other robotic is performing extremely difficult microsurgery below the management of a health care provider utilizing joysticks.
Such situations look set to develop into extra widespread. At current, some handbook operations are so troublesome they are often carried out by solely a small variety of surgeons worldwide, whereas others are invasive and rely upon a surgeon’s particular talent.
Superior robotics are offering instruments which have the potential to allow extra surgeons to hold out such operations and accomplish that with a better price of success.
‘We’re coming into the subsequent revolution in drugs,’ mentioned Sophie Cahen, chief government officer and co-founder of Ganymed Robotics in Paris.
New knees
Cahen leads the EU-funded Ganymed challenge, which is growing a compact robotic to make joint-replacement operations extra exact, much less invasive and – by extension – safer.
The preliminary focus is on a sort of surgical procedure known as complete knee arthroplasty (TKA), although Ganymed is seeking to broaden to different joints together with the shoulder, ankle and hip.
Ageing populations and way of life modifications are accelerating demand for such surgical procedure, in line with Cahen. Curiosity in Ganymed’s robotic has been expressed in lots of quarters, together with distributors in rising economies comparable to India.
‘Demand is super-high as a result of arthroplasty is pushed by the age and weight of sufferers, which is rising all around the world,’ Cahen mentioned.
Arm with eyes
Ganymed’s robotic will intention to carry out two important capabilities: contactless localisation of bones and collaboration with surgeons to assist joint-replacement procedures.
It includes an arm mounted with ‘eyes’, which use superior computer-vision-driven intelligence to look at the precise place and orientation of a affected person’s anatomical construction. This avoids the necessity to insert invasive rods and optical trackers into the physique.
“We’re coming into the subsequent revolution in drugs.”
– Sophie Cahen, Ganymed
Surgeons can then carry out operations utilizing instruments comparable to sagittal saws – used for orthopaedic procedures – in collaboration with the robotic arm.
The ‘eyes’ help precision by offering so-called haptic suggestions, which prevents the motion of devices past predefined digital boundaries. The robotic additionally collects knowledge that it will probably course of in actual time and use to hone procedures additional.
Ganymed has already carried out a medical research on 100 sufferers of the bone-localisation know-how and Cahen mentioned it achieved the specified precision.
‘We had been extraordinarily happy with the outcomes – they exceeded our expectations,’ she mentioned.
Now the agency is performing research on the TKA process, with hopes that the robotic might be absolutely obtainable commercially by the tip of 2025 and develop into a mainstream device used globally.
‘We wish to make it inexpensive and accessible, in order to democratise entry to high quality care and surgical procedure,’ mentioned Cahen.
Microscopic issues
Robots are being explored not just for orthopaedics but additionally for extremely complicated surgical procedure on the microscopic degree.
The EU-funded MEETMUSA challenge has been additional growing what it describes because the world’s first surgical robotic for microsurgery licensed below the EU’s ‘CE’ regulatory regime.
Known as MUSA, the small, light-weight robotic is hooked up to a platform outfitted with arms in a position to maintain and manipulate microsurgical devices with a excessive diploma of precision. The platform is suspended above the affected person throughout an operation and is managed by the surgeon by means of specifically tailored joysticks.
In a 2020 research, surgeons reported utilizing MUSA to deal with breast-cancer-related lymphedema – a power situation that generally happens as a aspect impact of most cancers therapy and is characterised by a swelling of physique tissues because of a build-up of fluids.
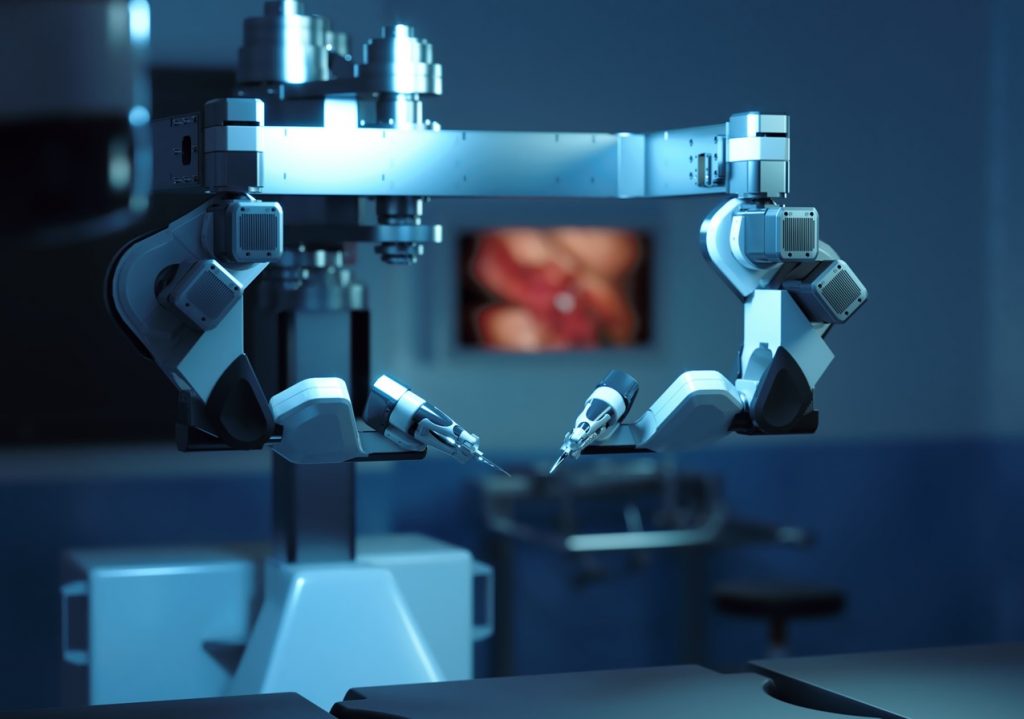
MUSA’s robotic arms. Microsure BV, 2022
To hold out the surgical procedure, the robotic efficiently sutured – or linked – tiny lymph vessels measuring 0.3 to 0.8 millimetre in diameter to close by veins within the affected space.
‘Lymphatic vessels are under 1 mm in diameter, so it requires a variety of talent to do that,’ mentioned Tom Konert, who leads MEETMUSA and is a medical area specialist at robot-assisted medical know-how firm Microsure in Eindhoven, the Netherlands. ‘However with robots, you possibly can extra simply do it. Thus far, with regard to the medical outcomes, we see very nice outcomes.’
Regular fingers
When such delicate operations are performed manually, they’re affected by slight shaking within the fingers, even with extremely expert surgeons, in line with Konert. With the robotic, this drawback may be averted.
MUSA may also considerably scale down the surgeon’s basic hand actions somewhat than merely repeating them one-to-one, permitting for even better accuracy than with standard surgical procedure.
‘When a sign is created with the joystick, now we have an algorithm that can filter out the tremor,’ mentioned Konert. ‘It downscales the motion as properly. This may be by a factor-10 or 20 distinction and provides the surgeon a variety of precision.’
Along with treating lymphedema, the present model of MUSA – the second, after a earlier prototype – has been used for different procedures together with nerve restore and soft-tissue reconstruction of the decrease leg.
Subsequent technology
Microsure is now growing a 3rd model of the robotic, MUSA-3, which Konert expects to develop into the primary one obtainable on a widespread business foundation.
“When a sign is created with the joystick, now we have an algorithm that can filter out the tremor.”
– Tom Konert, MEETMUSA
This new model could have numerous upgrades, comparable to higher sensors to reinforce precision and improved manoeuvrability of the robotic’s arms. It would even be mounted on a cart with wheels somewhat than a set desk to allow straightforward transport inside and between working theatres.
Moreover, the robots might be used with exoscopes – a novel high-definition digital digital camera system. This can permit the surgeon to view a three-dimensional display by means of goggles so as to carry out ‘heads-up microsurgery’ somewhat than the less-comfortable technique of wanting by means of a microscope.
Konert is assured that MUSA-3 might be broadly used throughout Europe and the US earlier than a 2029 goal date.
‘We’re at the moment finalising product improvement and making ready for medical trials of MUSA-3,’ he mentioned. ‘These research will begin in 2024, with approvals and begin of commercialisation scheduled for 2025 to 2026.’
MEETMUSA can also be wanting into the potential of synthetic intelligence (AI) to additional improve robots. Nonetheless, Konert believes that the intention of AI options could also be to information surgeons in direction of their objectives and assist them in excelling somewhat than reaching utterly autonomous surgical procedure.
‘I feel the surgeon will at all times be there within the suggestions loop, however these instruments will certainly assist the surgeon carry out on the highest degree sooner or later,’ he mentioned.
Analysis on this article was funded through the EU’s European Innovation Council (EIC).
This text was initially revealed in Horizon, the EU Analysis and Innovation journal.
Horizon Journal
brings you the newest information and options about thought-provoking science and revolutionary analysis tasks funded by the EU.

Horizon Journal
brings you the newest information and options about thought-provoking science and revolutionary analysis tasks funded by the EU.