The cells of all dwelling organisms are powered by the identical chemical gas: adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Now, researchers have discovered a strategy to generate ATP straight from electrical energy, which might turbocharge biotechnology processes that develop all the pieces from meals to gas to prescription drugs.
Interfacing fashionable electronics-based expertise with biology is notoriously tough. One main stumbling block is that the way in which they’re powered may be very completely different. Whereas most of our devices run on electrons, nature depends on the vitality launched when the chemical bonds of ATP are damaged. Discovering methods to transform between these two very completely different currencies of vitality could possibly be helpful for a bunch of biotechnologies.
Genetically engineered microbes are already getting used to supply varied high-value chemical substances and therapeutically helpful proteins, and there are hopes they may quickly assist generate greener jet gas, break down plastic waste, and even develop new meals in large bioreactors. However on the minute, these processes are powered by an inefficient means of rising biomass, changing it to sugar, and feeding it to the microbes.
Now, researchers on the Max Planck Institute for Terrestrial Microbiology in Germany have devised a way more direct strategy to energy organic processes. They’ve created a synthetic metabolic pathway that may straight convert electrical energy into ATP utilizing a cocktail of enzymes. And crucially, the method works in vitro and doesn’t depend on the native equipment of cells.
“Feeding electrical energy straight into chemical and biochemical reactions is an actual breakthrough,” Tobias Erb, who led the analysis, stated in a press launch. “It will allow synthesis of energy-rich helpful assets resembling starch, biofuels, or proteins from easy mobile constructing blocks—sooner or later even from carbon dioxide. It could even be doable to make use of organic molecules to retailer electrical vitality.”
In nature, ATP and its sister molecule adenosine di-phosphate (ADP) might be considered nearly like batteries. ATP is sort of a charged battery, storing vitality in its chemical bonds. If a cell must spend that vitality, it breaks off one of the molecule’s three phosphate teams and the vitality certain up in that chemical bond can then energy some mobile course of.
This course of converts the ATP molecule into ADP, which might be considered an empty battery. To recharge it, the cell wants to make use of vitality from meals or photosynthesis so as to add a phosphate group again onto the ADP molecule, turning it again into ATP.
However this recharging course of depends on a fancy sequence of reactions involving varied protein complexes embedded within the cell membrane. Re-engineering this method to work exterior of a cell is difficult as a result of it requires the assorted proteins to be rigorously oriented in a synthetic membrane, which makes it each finicky and fragile.
The brand new method, outlined in a paper in Joule, is far less complicated. Dubbed the “AAA cycle,” it includes simply 4 enzymes interacting in an answer. The important thing ingredient that made all of it doable was the invention of an enzyme known as aldehyde ferredoxin oxidoreductase (AOR) in a recently-discovered bacterium known as Aromaticum aromatoleum, which is ready to break down petroleum.
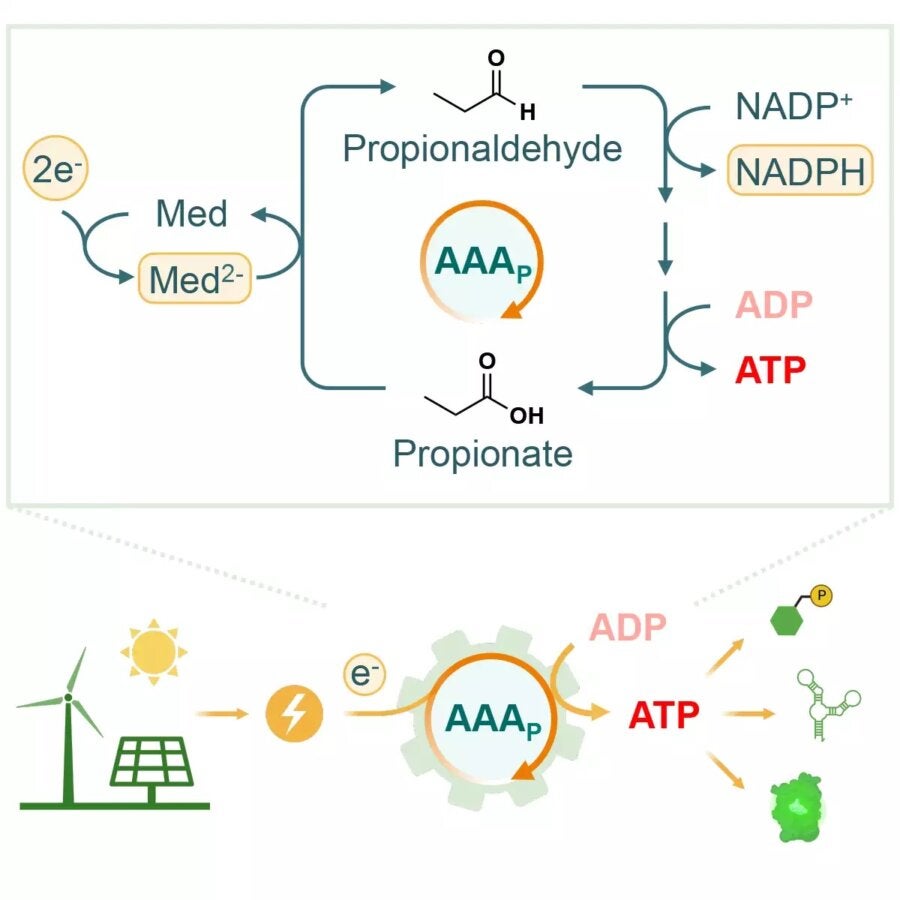
This enzyme is ready to take the electrons from an electrode and bind up their vitality in an aldehyde bond that’s added to a precursor chemical known as propionate. That is then cascaded by three extra enzymes that act on the chemical and in the end use the vitality saved in it to transform ADP to ATP. On the finish, a propionate molecule pops out that may then be fed again into the cycle.
“The straightforward AAA cycle is a intelligent and stylish method…that’s a lot less complicated than how biology naturally makes ATP,” Drew Endy, an artificial biologist at Stanford College, advised Science. He added that it could possibly be a key enabler to make “electrobiosynthesis” doable, the thought of utilizing electrical energy to straight energy the synthesis of helpful chemical substances by cells.
The researchers say the method nonetheless wants work, because the enzymes are unstable and solely in a position to convert a small quantity of vitality. But when the thought might be refined and scaled up, it might make it doable to run every kind of highly effective biotechnology processes on renewable vitality, not solely making them greener however considerably developing the quantity of vitality they will faucet into.