Introduction
Within the data-driven period, the importance of high-quality knowledge can’t be overstated. The accuracy and reliability of information play a pivotal position in shaping essential enterprise selections, impacting a company’s status and long-term success. Nonetheless, dangerous or poor-quality knowledge can result in disastrous outcomes. To safeguard towards such pitfalls, organizations should be vigilant in figuring out and eliminating these knowledge points. On this article, we current a complete information to acknowledge and handle ten widespread instances of dangerous knowledge, empowering companies to make knowledgeable selections and keep the integrity of their data-driven endeavors.
What’s Dangerous Information?
Dangerous knowledge refers to knowledge with high quality not match for the reason for assortment and processing. The uncooked knowledge obtained instantly after extraction from completely different social media websites or another technique is dangerous high quality and uncooked knowledge. It requires processing and cleansing to extend its high quality.

Why is Information High quality Essential?
Information serves quite a few functions within the firm. Performing as the bottom of a number of selections and features, the compromise in high quality impacts the general course of. It’s accountable for accuracy. Consistency, reliability and completeness of information is a vital side requiring separate and detailed motion to work on.
Prime 10 Dangerous Information Points and Their Options
Listed here are high 10 poor knowledge points that you need to learn about and their potential options:
- Inconsistent Information
- Lacking Values
- Duplicate Entries
- Outliers
- Unstructured Information
- Information Inaccuracy
- Information Incompleteness
- Information Bias
- Insufficient Information Safety
- Information Governance and High quality Administration
Inconsistent Information
The info is outlined as inconsistent within the presence of conflicting or contradictory values. The causes are various sorts of outcomes obtained after assortment from completely different sources of information assortment strategies. It could additionally occur because of the misalignment of information from numerous time intervals owing to a number of causes like measurement errors, sampling methodologies and others.

Challenges
- Incorrect conclusions: Results in drawing incorrect or deceptive evaluation that impacts the outcomes
- Decreased belief: It decreases the
- Wasted sources: Assortment of information is a activity adopted by its processing. Engaged on inconsistent and mistaken knowledge wastes efforts, sources and time.
- Biased decision-making: The inconsistency ends in biased knowledge resulting in the era and acceptance of 1 perspective.
Options
- Be clear about knowledge limitations whereas presenting the info and its interpretation
- Confirm the info sources earlier than the analysis
- Examine knowledge high quality
- Select the suitable evaluation technique
Additionally Learn: Combating Information Inconsistencies with SQL
Lacking Values
There are numerous strategies to determine missing or NULL values within the dataset, resembling visible inspection, reviewing the abstract statistics, utilizing knowledge visualization and profiling instruments, descriptive queries and imputation methods.

Challenges
- Bias and sampling points: Results in
- Misinterpretation: The misinterpretation is seen in variable relationships resulting in unseen dependencies.
- Decreased pattern measurement: It poses limitations whereas utilizing size-specific software program or operate
- Lack of info: Leads to a lower in dataset richness and completeness.
Options
- Imputation: Through the use of imputation strategies to create full knowledge matrices with estimates generated from imply, median, regression, statistics and machine studying fashions. One can use single or a number of imputations.
- Understanding lacking and poor knowledge mechanism: Analyze the sample of lacking knowledge, which can lie in several sorts, resembling: Lacking Fully at Random (MCAR),
- Weighting: Use weighting methods to determine the influence of lacking values on the evaluation
- Assortment: Including extra knowledge could fill within the lacking values or decrease the influence
- Report: Give attention to the difficulty to start with to keep away from bias
Duplicate Entries
Duplicate entries or redundant data are recognized because the presence of a number of copies of information throughout the dataset. It happens resulting from merging knowledge, system glitches, knowledge entry and dealing with errors.
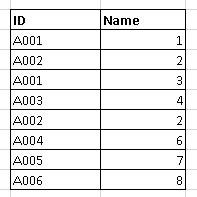
Impact
- Inaccurate evaluation: In addition to basic influence, the impact is seen on statistical measures with a consequence on knowledge insights
- Improper estimation: These result in over or underestimation of attributes
- Information integrity: Loss in accuracy and reliability resulting from mistaken knowledge
Challenges
- Storage: Elevated and irrelevant requirement results in elevated prices and waste of sources
- Processing: Decreases resulting from a rise in load on the system impacting the processing and evaluation
- Upkeep: Requires further effort for upkeep and group of information
Options
- Distinctive identifier: Enter or set a singular identifier to stop or simply acknowledge duplicate entries
- Constraints: Introduce knowledge constraints to make sure knowledge integrity
- Audit: Carry out common knowledge audits
- Fuzzy matching: Make the most of fuzzy matching algorithms for the identification of duplicates with slight variations
- Hashing: Helps within the identification of duplicate data by way of labeling
Outliers
Outliers are excessive values or observations seen mendacity far-off from the principle dataset. Their depth will be giant or small and could also be not often seen in knowledge. The rationale for his or her prevalence is knowledge entry errors and measurement errors accompanied by real excessive occasions in knowledge.

Significance
- Descriptive statistics: The influence is seen within the imply and commonplace deviation that impacts the info abstract.
- Skewed distribution: It results in improper assumptions of statistical exams and fashions.
- Inaccurate prediction: The outliers adversely influence the machine studying fashions resulting in inaccurate predictions
Mechanisms
- Enhanced variability: Outliers improve knowledge variability, leading to bigger commonplace deviations.
- Impact on central tendency: They modify the central worth and therefore change imply, median and different central data-based interpretations
- Bias in regression fashions: Outliers change the proportion and therefore result in biased coefficient estimates and mannequin efficiency
- Incorrect speculation testing: They violate the assumptions of exams, result in incorrect p-values and draw faulty conclusions.
Options
- Threshold-based detection: State a selected threshold worth in line with area information pr statistical technique
- Winsorization: Truncate or cap excessive values to cut back the influence of outliers
- Transformation: Apply logarithmic or sq. root transformations
- Modeling methods: Use strong regression or tree-based fashions
- Outlier elimination: Take away the values with cautious consideration in the event that they pose an excessive problem
Unstructured Information
The info missing a predefined construction or group poses challenges to evaluation and is known as unstructured knowledge. It outcomes from modifications in doc codecs, net scraping, lack of mounted knowledge mannequin, digital and analog sources and knowledge assortment methods.

Challenges
- Lack of construction: The issue causes evaluation utilizing conventional strategies
- Dimensionality: Such knowledge is very dimensional or accommodates a number of options and attributes
- Information heterogeneity: It will possibly use numerous codecs and languages, could have numerous encoding requirements and makes integration extra complicated
- Data extraction: Unstructured knowledge requires dealing with by way of Pure Language Processing (NLP), audio processing methods or pc imaginative and prescient.
- Affect on knowledge high quality: Leads to lack of accuracy and verifiable sources, causes issues with integration and generates irrelevant and mistaken knowledge.
Resolution
- Metadata administration: Use metadata for extra info for environment friendly evaluation and integration
- Ontologies and taxonomies: Create these for a greater understanding
- Laptop imaginative and prescient: Course of photographs and movies by way of pc imaginative and prescient for function extraction and object recognition
- Audio and knowledge processing: Implement audio processing methods for transcription, noise and irrelevant content material elimination
- Pure Language Processing (NLP): Use superior methods for processing and knowledge extraction from textual knowledge
Information Inaccuracy

Human errors, knowledge entry errors and outdated info comprise the info accuracy, which will be within the following varieties:
- Typographical errors: Presence of transposed digits, incorrect formatting, misspellings
- Incomplete knowledge: Lacking knowledge
- Information duplication: Redundant entries inflate or improve the numbers and skew statistical outcomes
- Outdated info: Results in lack of relevancy resulting in incorrect selections and conclusions
- Inconsistent knowledge: Recognized by the presence of various items in measurement and variable names and hindering the info evaluation and interpretation
- Information misinterpretation: Information current in several contexts or imparting completely different views or which means
Resolution
- Information cleansing and validation (most vital)
- Automated knowledge high quality instruments
- Validations guidelines and enterprise logic
- Standardization
- Error reporting and logging added
Essential of information cleansing and validation
- Value saving: Prevents inaccurate outcomes, thus saving expenditure on sources
- Decreased errors: Prevents the event of error-based stories
- Reliability: The info validation and cleansing course of generate dependable knowledge and therefore outcomes
- Efficient decision-making: The dependable knowledge aids in efficient resolution making
Information Incompleteness
The absence of attributes essential for evaluation, decision-making and understanding is known as lacking key attributes. These generate resulting from knowledge entry errors, incomplete knowledge assortment, knowledge processing points or intentional knowledge omission. The absence of full knowledge performs a key position in disrupting complete evaluation, evidenced by a number of points confronted in its presence.

Challenges
- Problem in sample detection: They result in issues in detecting significant patterns and relationships inside knowledge
- Lack of info: The outcomes lack precious info and insights resulting from faulty knowledge
- Bias: The event of bias and issues with sampling is widespread because of the non-random distribution of lacking knowledge
- Statistical bias: Incomplete knowledge results in biased statistical evaluation and inaccurate parameter estimation
- Affect on mannequin efficiency: Key influence is seen within the efficiency of machine studying fashions and predictions
- Communication: Incomplete knowledge ends in miscommunication of outcomes to stakeholders
Options
- Gather further knowledge: Gather extra knowledge to simply fill within the gaps in poor knowledge
- Set indicators: Recognise the lacking info by way of indicators and deal with it effectively with out compromising the method and outcome
- Sensitivity evaluation: Search for the influence of lacking knowledge on evaluation outcomes
- Improve knowledge assortment: Discover out the errors or shortcomings within the knowledge assortment course of to optimize them
- Information auditing: Carry out common audits to search for errors within the course of of information assortment and picked up knowledge
Information Bias
Information bias is the presence of systematic errors or prejudice in a dataset resulting in inaccuracy or era of outcomes inclined towards one group. It could happen at any stage, resembling knowledge assortment, processing or evaluation.

Challenges
- Lack of accuracy: Information bias results in skewed evaluation and conclusions
- Moral issues: Generates moral issues when selections are in favor of an individual, neighborhood or services or products, serving to them
- Deceptive prediction: biased knowledge results in unreliable predictive fashions and inaccurate forecasts
- Unrepresentative samples: It impacts the method of generalizing the findings resulting in a broader inhabitants
Resolution
- Bias metrics: Use bias metrics for monitoring and monitoring bias within the knowledge
- Inclusivity: Do add knowledge from numerous teams to keep away from systematic exclusion
- Algorithmic equity: Implement ML algorithms able to bias discount
- Sensitivity evaluation: Carry out it to evaluate the influence of information bias on evaluation outcomes
- Information auditing and profiling: Audit and conduct knowledge profiling often
- Documentation: Clearly and exactly doc the info for transparency and to simply handle the biases
Insufficient Information Safety
The info safety points compromise knowledge integrity and the group’s status. The implications are seen by way of unauthorized entry, knowledge manipulation, ransomware assaults and insider threats.

Challenges
- Information vulnerability: Identification of susceptible factors
- Superior threats: Refined cyber assaults require superior and environment friendly administration methods
- Information privateness regulation: Guaranteeing knowledge safety whereas complying with evolving knowledge safety legal guidelines is complicated
- Worker consciousness: Requires educating every employees member
Options
- Encrypt: Requires encryption of delicate knowledge at relaxation and in transit for defense from unauthorized entry
- Entry controls: Implement strictly managed entry for the workers primarily based on their roles and requirement
- Firewalls and Intrusion Detection System (IDS): Deploy safety measures with built-in firewalls and set up of IDS
- Multi-factor authentication: Put within the multi-factor authentication for extra safety
- Information backup: It mitigates the influence of cyber assaults
- Vendor safety: Assess and implement knowledge safety requirements for third-party distributors
Information Governance and High quality Administration

Information governance issues coverage, process and guideline institution to make sure knowledge integrity, safety and compliance. Information high quality administration offers with processes and methods to enhance, assess and keep the accuracy, consistency and completeness of poor knowledge for reliability enhancement.
Challenges
- Information silos: Fragment knowledge is troublesome to combine and keep consistency
- Information privateness issues: Information sharing, privateness and dealing with delicate info poses a problem
- Organizational alignment: Purchase-in and alignment is complicated in giant organizations
- Information possession: Totally different to determine and set up possession
- Information governance maturity: It requires time for conversion from ad-hoc knowledge practices to mature governance.
Options
- Information enchancment: It consists of profiling, cleaning, standardization, knowledge validation and auditing
- Automation in high quality: Automate the method of validation and cleaning
- Steady monitoring: Frequently monitor knowledge high quality and concurrently handle the problems
- Suggestions mechanism: Create a mechanism resembling varieties or ‘elevate a question’ possibility for reporting knowledge high quality points and solutions
Conclusion
Recognizing and addressing poor knowledge is important for any data-driven group. By understanding the widespread instances of poor knowledge high quality, companies can take proactive measures to make sure the accuracy and reliability of their knowledge. Analytics Vidhya’s Blackbelt program provides a complete studying expertise, equipping knowledge professionals with the abilities and information to sort out knowledge challenges successfully. Enroll in this system in the present day and empower your self to turn into a proficient knowledge analyst able to navigating the complexities of information to drive knowledgeable selections and obtain outstanding success within the data-driven world.
Continuously Requested Questions
A. The 4 widespread knowledge high quality points seen in mistaken knowledge are the presence of inaccurate, incomplete, duplicate and outdated knowledge.
A. The components accountable for poor knowledge high quality are incomplete knowledge assortment, lack of information validation, knowledge integration points and knowledge entry errors.
A. Dangerous knowledge is seen to comprise duplicate entries, lacking values, outliers, contradictory info and different such presence.
A. The 5 traits of information high quality are accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness and relevance.
