Risk actors are utilizing an open-source rootkit referred to as Reptile to focus on Linux programs in South Korea.
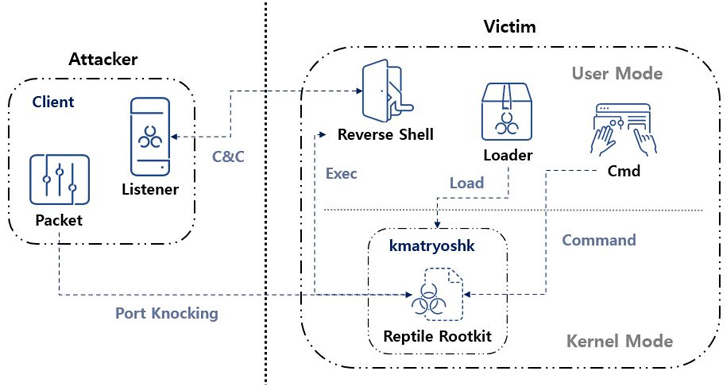
“In contrast to different rootkit malware that sometimes solely present concealment capabilities, Reptile goes a step additional by providing a reverse shell, permitting risk actors to simply take management of programs,” the AhnLab Safety Emergency Response Heart (ASEC) stated in a report printed this week.
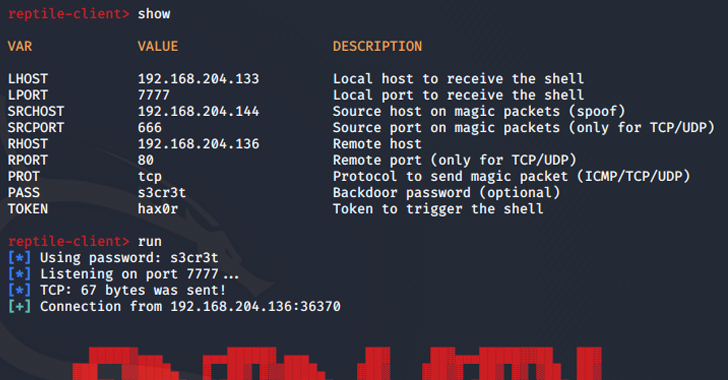
“Port knocking is a technique the place the malware opens a particular port on an contaminated system and goes on standby. When the risk actor sends a magic packet to the system, the acquired packet is used as a foundation to determine a reference to the C&C server.”
A rootkit is a malicious software program program that is designed to offer privileged, root-level entry to a machine whereas concealing its presence. A minimum of 4 totally different campaigns have leveraged Reptile since 2022.

The primary use of the rootkit was recorded by Development Micro in Could 2022 in reference to an intrusion set tracked as Earth Berberoka (aka GamblingPuppet), which has been discovered to make use of the malware to cover connections and processes associated to a cross-platform Python trojan referred to as Pupy RAT in assaults aimed toward playing websites in China.
Then in March 2023, Google-owned Mandiant detailed a set of assaults mounted by a suspected China-linked risk actor dubbed UNC3886 that employed zero-day flaws in Fortinet home equipment to deploy a lot of customized implants in addition to Reptile.
ExaTrack, that very same month, revealed a Chinese language hacking group’s use of a Linux malware referred to as Mélofée that is primarily based on Reptile. Lastly, in June 2023, a cryptojacking operation found by Microsoft used a shell script backdoor to obtain Reptile as a way to obscure its little one processes, recordsdata, or their content material.
A better examination of Reptile reveals using a loader, which makes use of a software referred to as kmatryoshka to decrypt and cargo the rootkit’s kernel module into reminiscence, after which it opens a particular port and awaits for the attacker to transmit a magic packet to the host over protocols comparable to TCP, UDP, or ICMP.

“The information acquired by the magic packet incorporates the C&C server tackle,” ASEC stated. “Primarily based on this, a reverse shell connects to the C&C server.”
It is value noting that using magic packets to activate the malicious exercise has been noticed beforehand in one other rootkit named Syslogk, which was documented by Avast final 12 months.
The South Korean cybersecurity agency stated it additionally detected an assault case within the nation that concerned using Reptile, whereas bearing some tactical similarities to Mélofée.
“Reptile is a Linux kernel mode rootkit malware that gives a concealment function for recordsdata, directories, processes, and community communications,” ASEC stated. “Nevertheless, Reptile itself additionally supplies a reverse shell, making programs with Reptile put in inclined to being hijacked by risk actors.”