
Even the temperate, mountainous nation of Switzerland isn’t proof against local weather change. Scorching warmth waves are melting alpine glaciers, killing bushes and fish and, within the cities, seemingly inflicting an uptick in human deaths.
Rosmarie Wydler-Wälti, who lives in Basel, is conscious about this. A girl in her 70s, she belongs to the demographic most weak to heat-related dying. To her, the federal government’s response to latest warmth waves—cautioning seniors to remain within the shade throughout sizzling days, as an example — appeared like a Band-Help. She wished to see folks tackling the issue’s root trigger: international locations like Switzerland not doing sufficient to curb emissions of planet-warming greenhouse gases.
With assist from Greenpeace Switzerland, Wydler-Wälti and different members of a bunch of senior girls local weather activists filed a lawsuit towards the Swiss authorities in 2016, demanding that the state curb emissions extra rapidly. They argued that the federal government, by not sticking to insurance policies per the worldwide aim of limiting warming to lower than 2 levels Celsius above pre-industrial temperatures, was threatening senior girls’s elementary human proper to life. Certainly, most of the girls concerned in the end reported having skilled coronary heart palpitations, vomiting, swollen legs and arms and breathlessness throughout latest warmth waves, and some reported having fainted.
A whole bunch of lawsuits like these have been filed world wide lately, as activists, annoyed by the gradual tempo at which nations are appearing to chop greenhouse fuel emissions, have turned to the courts for assist. The success charge has stunned many specialists. Of these circumstances filed outdoors the USA—the main target of 1 evaluation—dozens had outcomes that inspired extra aggressive local weather motion, in line with a 2022 report from the Grantham Analysis Institute on Local weather Change and the Atmosphere on the London Faculty of Economics and Political Science. In a single landmark case that concluded in 2019, for instance, Dutch courts ordered the federal government to set extra bold local weather targets.
However such circumstances don’t all the time succeed. To Wydler-Wälti’s disappointment, after a collection of courts dismissed the case, the Swiss Supreme Courtroom concluded in 2020 that the ladies’s rights hadn’t been violated severely sufficient to benefit a case. “We must be half useless for them to imagine that we’re notably affected,” Wydler-Wälti says angrily.
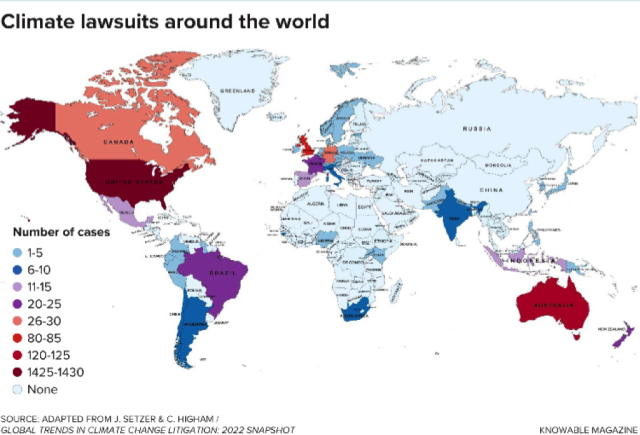
Analyzing why some circumstances succeed whereas others don’t is essential to understanding the way forward for this quickly rising subject of litigation. Specialists say that success hinges on many elements—not solely on the plaintiffs’ arguments but additionally on the design of a rustic’s authorized system, its political atmosphere, and the obvious willingness and/or means of judges to interpret the scientific proof round local weather change.
“One of many causes it’s so vital to look carefully at these circumstances and the impression they’re having is as a result of their impression is more likely to solely develop within the years to return, as folks more and more see litigation as an vital technique to tackle the issues of local weather change,” says Hari Osofsky, a human rights regulation skilled now at Northwestern College’s Pritzker Faculty of Legislation, who in 2020 co-authored an outline of local weather change litigation within the Annual Overview of Legislation and Social Science.
That mentioned, “litigation by itself is just not going to shut the emissions hole,” Osofsky provides. “Options to local weather change require lots of totally different sorts of motion.”

